The most common gases used for brazing are not fuels, but protective atmospheres designed to shield the joint from oxygen. The primary gases used are Nitrogen (N₂), Hydrogen (H₂), Argon (Ar), and mixtures of these, often created from dissociated ammonia. Each gas serves the critical purpose of preventing oxidation during the high-temperature brazing cycle.
The core principle to understand is that the role of a brazing "gas" in furnace or induction brazing is almost always atmospheric control. Its job is to prevent the formation of metal oxides, which are the primary barrier to creating a strong, clean, and properly wetted brazed joint.

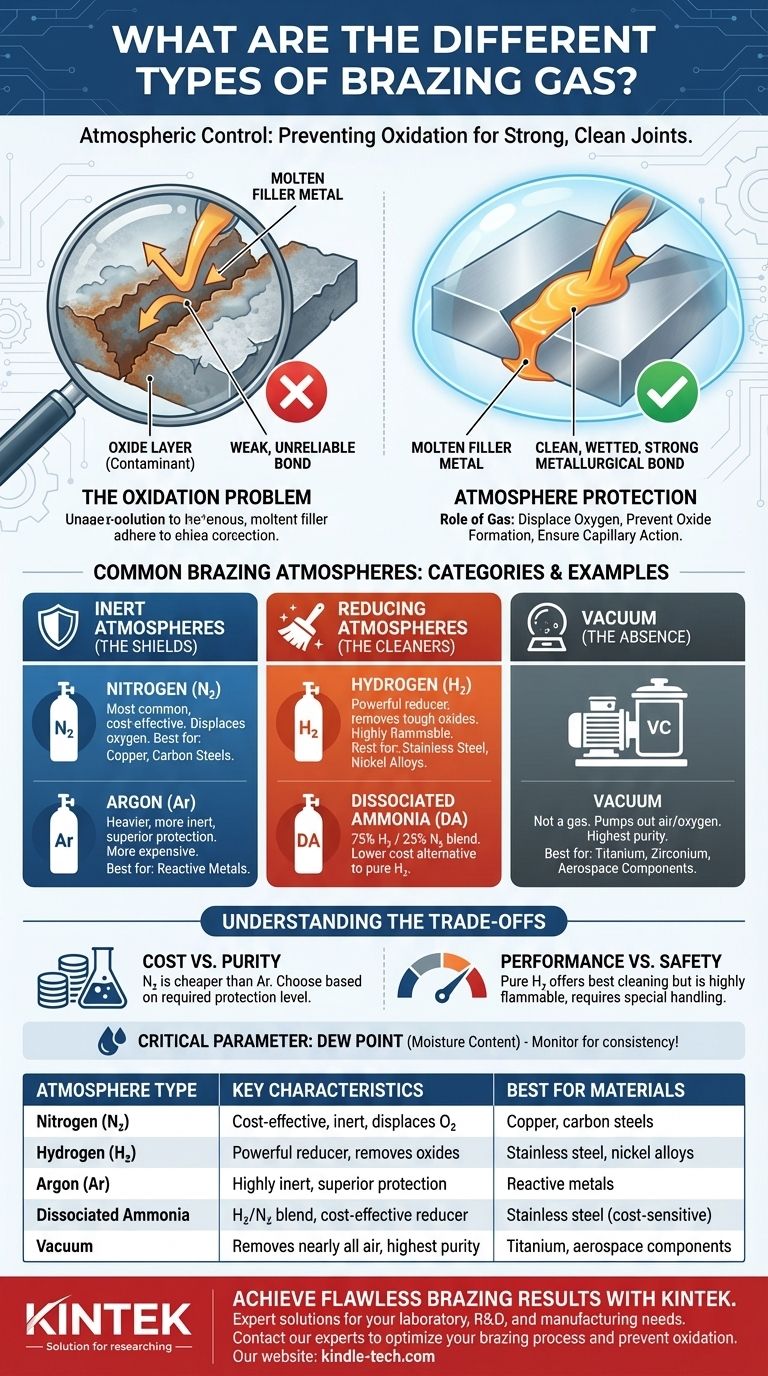
Why a Protective Atmosphere is Critical
At brazing temperatures, metals react very quickly with oxygen in the air. This reaction creates a thin, often invisible layer of oxide on the surface of the parts you are trying to join.
The Problem of Oxidation
Oxides act as a contaminant layer. They prevent the molten brazing filler metal from making direct, clean contact with the base metals.
Think of it like trying to apply a sticker to a dusty surface. The sticker adheres to the dust, not the surface itself, resulting in a weak and unreliable bond.
How an Atmosphere Protects the Joint
A controlled atmosphere displaces the oxygen-rich air from the brazing environment. By surrounding the parts with a specific gas, you either prevent oxygen from reaching the metal or actively remove any light oxides that have already formed.
This ensures the filler metal can flow cleanly across the metal surfaces through capillary action, creating a strong metallurgical bond.
Common Types of Brazing Atmospheres
Brazing atmospheres are generally categorized as either inert or chemically active (reducing). The choice depends on the base metals being joined and the desired outcome.
Inert Atmospheres: The Shields
Inert gases are non-reactive. Their only job is to physically displace the oxygen from the furnace or brazing area.
- Nitrogen (N₂): This is the most common and cost-effective atmosphere for preventing oxidation, especially for brazing copper and carbon steels.
- Argon (Ar): Argon is a heavier and more inert gas than nitrogen. It is more expensive but provides superior protection for highly reactive metals.
Reducing Atmospheres: The Cleaners
Reducing atmospheres don't just displace oxygen; they actively react with and remove existing light oxides from the metal surfaces.
- Hydrogen (H₂): Pure hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent and is excellent for brazing stainless steels, nickel alloys, and other materials that form tough oxides. It produces exceptionally bright and clean joints.
- Dissociated Ammonia (DA): This is a lower-cost alternative to pure hydrogen. Ammonia (NH₃) is heated to break it down into a mixture of 75% Hydrogen and 25% Nitrogen, creating a highly reducing atmosphere.
- Nitrogen-Hydrogen Blends: For more control, specific blends (e.g., 95% N₂ / 5% H₂) offer some reducing capability while being non-flammable and safer to handle than pure hydrogen.
Vacuum: The Ultimate Absence of Atmosphere
While not a gas, a vacuum is the most effective "atmosphere" for brazing. By pumping nearly all the air out of a sealed chamber, you remove the oxygen and other contaminants.
This method is essential for brazing extremely reactive metals like titanium and zirconium, as well as for complex, high-purity aerospace applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right atmosphere involves balancing cost, performance, and safety. There is no single "best" gas for all applications.
Cost vs. Purity
Nitrogen is significantly cheaper than Argon. For many common applications, nitrogen provides sufficient protection, making it the default choice where possible.
Performance vs. Safety
Pure hydrogen delivers the cleanest results on difficult-to-braze metals. However, it is highly flammable and requires specialized handling procedures and safety-equipped furnaces, increasing operational complexity and cost.
Gas Purity and Dew Point
The effectiveness of any atmosphere is highly dependent on its purity. Even small amounts of moisture (water vapor) or oxygen contamination can lead to oxidation. Dew point, a measure of moisture content, is a critical parameter to monitor for consistent brazing results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of brazing gas is dictated by the materials you are joining and the quality requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective brazing of copper or carbon steel: Nitrogen is typically the best choice for providing excellent protection at a low cost.
- If you are brazing stainless steel or alloys with tough oxides: A hydrogen blend or pure hydrogen atmosphere is necessary to actively reduce oxides and ensure a clean joint.
- If you are joining highly reactive metals like titanium or for critical aerospace components: A high-quality vacuum is the only reliable option to prevent component contamination.
- If you need the performance of hydrogen but have cost constraints: Dissociated ammonia offers a powerful reducing atmosphere at a lower price point than pure hydrogen.
Ultimately, selecting the correct atmosphere is fundamental to achieving a successful braze.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Atmosphere Type | Key Characteristics | Best For Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Cost-effective, inert, displaces oxygen | Copper, carbon steels |
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Powerful reducing agent, removes oxides | Stainless steel, nickel alloys |
| Argon (Ar) | Highly inert, superior protection | Reactive metals |
| Dissociated Ammonia | 75% H₂ / 25% N₂ blend, cost-effective reducer | Stainless steel (cost-sensitive) |
| Vacuum | Removes nearly all air, highest purity | Titanium, zirconium, aerospace components |
Achieve Flawless Brazing Results with KINTEK
Selecting the right brazing atmosphere is critical to preventing oxidation and ensuring the strength and integrity of your joints. The wrong choice can lead to weak bonds, contamination, and product failure.
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for all your brazing and thermal processing needs. We help our customers in R&D, manufacturing, and quality control navigate these complex decisions to optimize their processes.
Let us help you:
- Identify the ideal atmosphere for your specific base metals and filler materials.
- Source high-purity gases and reliable equipment to maintain consistent, high-quality results.
- Improve your brazing yield and efficiency while reducing costs and scrap rates.
Don't let oxidation compromise your products. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can bring reliability and precision to your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- What is hydrogen atmosphere heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Purity & Brightness
- Why is a hydrogen atmosphere furnace necessary for W-Cu composite? Unlock Superior Infiltration and Density
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing



















