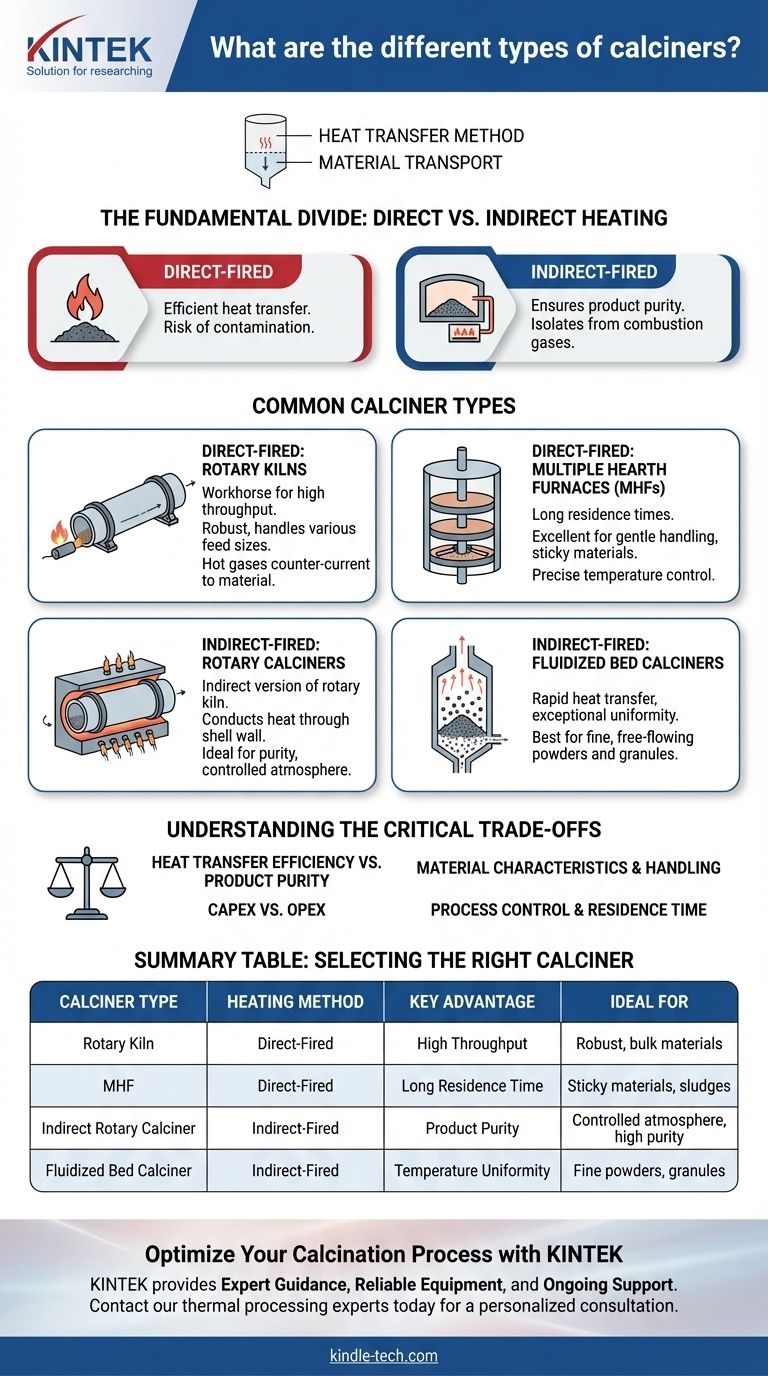
At its core, calcination is a thermal treatment process, and the equipment used—calciners—can be broadly categorized based on two fundamental principles: how heat is transferred to the material and how the material is transported through the system. The most common types are direct-fired rotary kilns, indirect-fired rotary calciners, multiple hearth furnaces, and fluidized bed calciners, each with distinct operational advantages.
The choice of a calciner is not about finding the single "best" technology, but about making a strategic trade-off. Your decision must be driven by the specific properties of your feed material, the required purity of your final product, and your operational cost priorities.
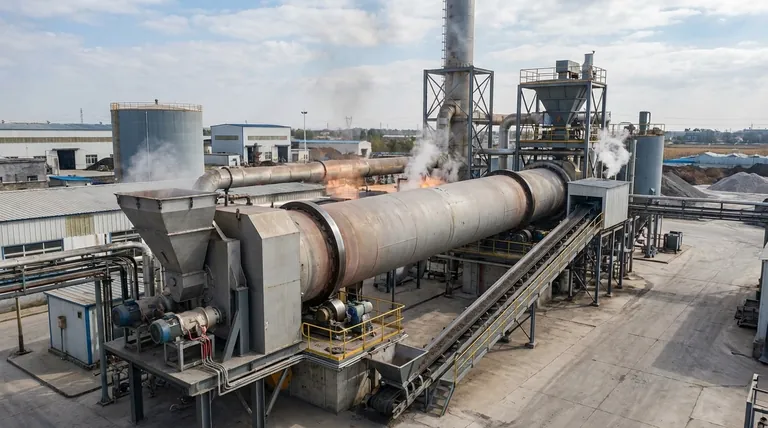

The Fundamental Divide: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Before examining specific equipment, it's crucial to understand the primary distinction in calciner design: the method of heat transfer. This single choice has major implications for product quality, energy efficiency, and environmental control.
Direct-Fired Calciners
In a direct-fired system, the material being processed comes into direct contact with the hot combustion gases (the flame and its products).
This method provides very efficient heat transfer. However, it introduces the risk of the material reacting with or being contaminated by the byproducts of combustion, such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, or trace elements from the fuel.
Indirect-Fired Calciners
In an indirect-fired system, the material is contained within a chamber, tube, or shell that is heated from the outside. The heat transfers through a solid wall, separating the material from the flame and combustion gases.
This design is essential when product purity is paramount or when the gases released from the material itself (off-gases) need to be collected in a pure, concentrated stream for further processing or environmental treatment.
A Closer Look at Common Calciner Types
With the direct vs. indirect framework in mind, we can now analyze the most prevalent calciner designs.
Direct-Fired: Rotary Kilns
The rotary kiln is a workhorse of the thermal processing industry. It consists of a large, rotating cylinder (the kiln) set at a slight angle.
Material is fed into the high end and slowly tumbles toward the low end as the kiln rotates. A burner at the low end fires a flame directly into the kiln, with hot gases flowing counter-current to the material. They are robust and can handle a wide variety of feed sizes at very high throughputs.
Direct-Fired: Multiple Hearth Furnaces (MHFs)
A multiple hearth furnace is a vertical cylinder containing a series of circular, stacked hearths. A central rotating shaft with "rabble arms" plows the material across each hearth.
Material is fed to the top hearth and drops from hearth to hearth until it exits at the bottom. Burners are placed in the side walls, allowing for precise temperature control in different zones. This design provides very long residence times and is excellent for materials that require gentle handling or are sticky.
Indirect-Fired: Rotary Calciners
Often called an indirect kiln, this is the indirect-fired version of the rotary kiln. The rotating cylinder containing the material is enclosed within a stationary furnace.
Burners heat the outside of the rotating shell, and that heat conducts through the shell wall to the material tumbling inside. This is the go-to solution when you need the material transport of a rotary kiln but cannot allow contact with combustion gases.
Indirect-Fired: Fluidized Bed Calciners
A fluidized bed calciner operates by forcing a stream of hot gas upward through a bed of solid particles. If the gas velocity is high enough, the particles become suspended and behave like a boiling fluid.
This "fluidization" results in extremely rapid heat transfer and exceptional temperature uniformity throughout the material bed. It is ideal for processing fine, free-flowing powders and granules where precise temperature control is critical.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting the right calciner involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single solution that is best for every application.
Heat Transfer Efficiency vs. Product Purity
Direct-fired systems like a rotary kiln generally offer higher thermal efficiency because heat is transferred directly to the product. The trade-off is the potential for product contamination.
Indirect-fired systems guarantee purity by isolating the product but introduce a thermal barrier (the shell wall), which can slightly reduce overall energy efficiency.
Material Characteristics and Handling
The physical nature of your material is a primary constraint. Lumpy, abrasive, or non-uniform materials are well-suited for a robust rotary kiln.
Fine powders that require precise temperature control are perfect for a fluidized bed. Sticky or sludge-like materials that need long processing times are often best handled in a multiple hearth furnace.
Capital Cost (CapEx) vs. Operating Cost (OpEx)
Simpler, more established designs like direct-fired rotary kilns may have a lower initial capital investment.
However, more sophisticated systems like fluidized beds can offer lower long-term operating costs due to superior energy efficiency and tighter process control, leading to less off-spec product.
Process Control and Residence Time
A rotary kiln has a broad distribution of residence times—some particles move through quickly, others more slowly. An MHF offers a very long and controllable residence time.
A fluidized bed provides extremely uniform processing conditions, but typically with a shorter residence time than a kiln or MHF.
Selecting the Right Calciner for Your Process
Your final decision should be a direct reflection of your primary process requirements.
- If your primary focus is high throughput for robust, bulk materials: A direct-fired rotary kiln is the most common and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute product purity or controlled atmosphere processing: An indirect-fired rotary calciner is the clear solution.
- If your primary focus is exceptional temperature uniformity for fine particles: A fluidized bed calciner will provide the best performance and process control.
- If your primary focus is a long residence time for gentle processing of sludges or sticky materials: A multiple hearth furnace is uniquely suited for the task.
By aligning the calciner's fundamental design with your material properties and process goals, you ensure an efficient, reliable, and cost-effective thermal processing solution.
Summary Table:
| Calciner Type | Heating Method | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Kiln | Direct-Fired | High Throughput | Robust, bulk materials |
| Multiple Hearth Furnace (MHF) | Direct-Fired | Long Residence Time | Sticky materials, sludges |
| Indirect Rotary Calciner | Indirect-Fired | Product Purity | Controlled atmosphere, high purity |
| Fluidized Bed Calciner | Indirect-Fired | Temperature Uniformity | Fine powders, granules |
Optimize Your Calcination Process with KINTEK
Selecting the right calciner is critical for achieving your desired product quality, throughput, and operational efficiency. The wrong choice can lead to contamination, energy waste, and inconsistent results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between direct and indirect heating, material handling, and cost considerations to identify the perfect thermal processing solution for your specific application—whether you require the high throughput of a rotary kiln or the precise control of a fluidized bed calciner.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Tailored recommendations based on your material properties and process goals.
- Reliable Equipment: High-performance calciners and associated lab equipment.
- Ongoing Support: Ensuring your thermal processing operates at peak efficiency.
Don't leave your calcination results to chance. Contact our thermal processing experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity



















