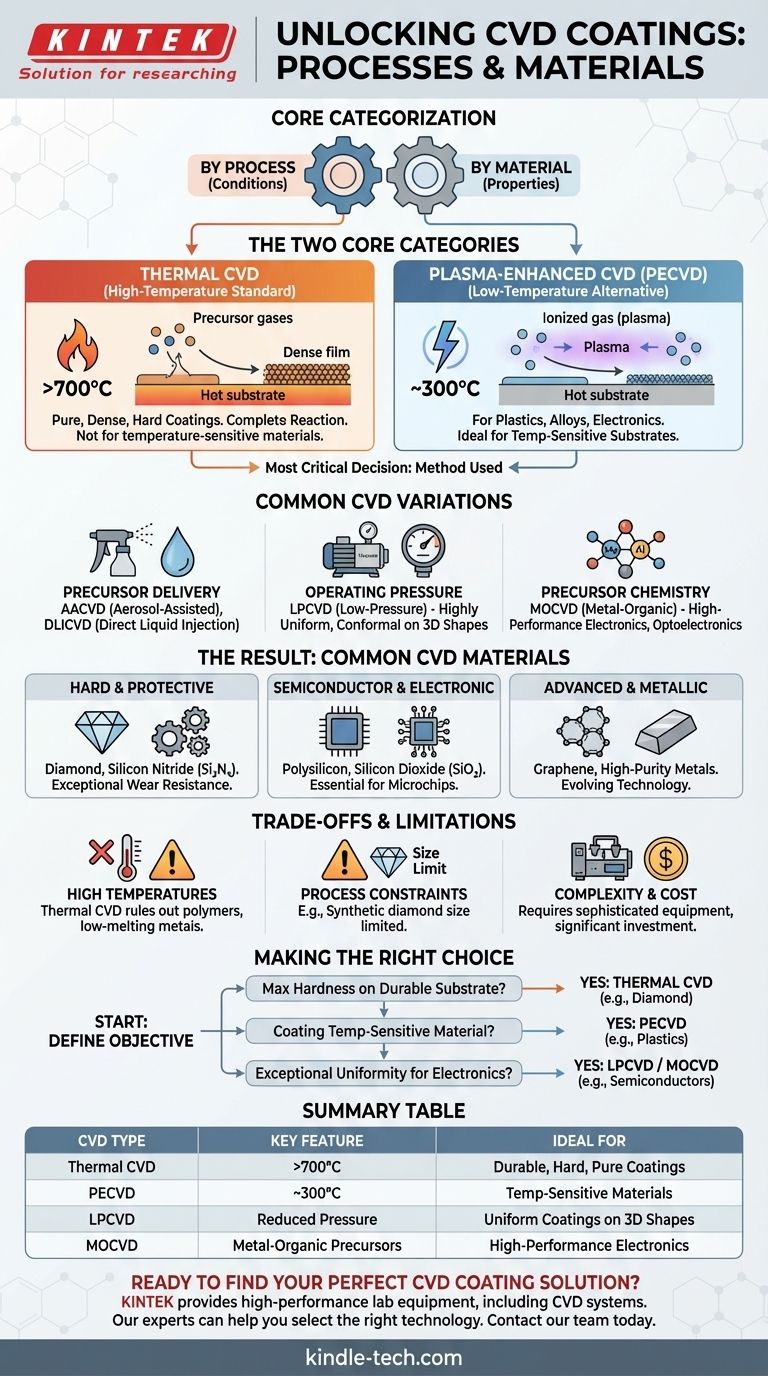
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is categorized in two primary ways: by the process used to create the coating and by the final material that is deposited. The process dictates the conditions required, such as temperature and pressure, while the material determines the final properties of the coating, like hardness or conductivity.
The most critical distinction in CVD is not the coating material itself, but the method used to apply it. The choice between high-temperature Thermal CVD and low-temperature Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the fundamental decision that dictates which materials can be coated and what properties can be achieved.
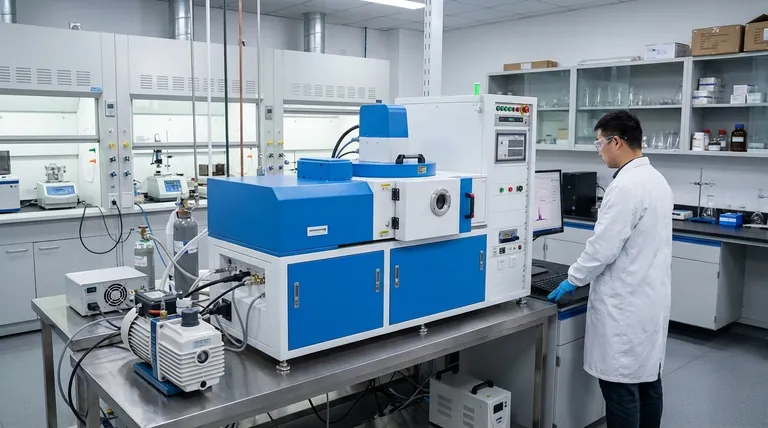

The Two Core Categories of CVD Processes
Understanding CVD begins with the two dominant approaches to initiating the chemical reaction that forms the coating. This choice is primarily driven by the temperature sensitivity of the substrate being coated.
Thermal CVD: The High-Temperature Standard
Thermal CVD is the traditional method. It uses high heat, often above 700°C, to provide the energy needed for the precursor gases to react and decompose, forming a solid film on the substrate.
This process is valued for producing coatings that are exceptionally pure, dense, and hard. The high temperature ensures a complete chemical reaction.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): The Low-Temperature Alternative
Plasma-Enhanced CVD, or PECVD, uses an electric field to generate a plasma (an ionized gas). This highly reactive plasma provides the energy to drive the chemical reaction instead of high heat.
Because it operates at much lower temperatures, typically around 300°C, PECVD is ideal for coating materials that cannot withstand the intense heat of thermal CVD, such as plastics or certain metal alloys.
Common Variations in CVD Methods
Beyond the core thermal versus plasma distinction, several specialized CVD methods exist, typically named for their unique approach to energy, pressure, or chemistry.
Based on Precursor Delivery
Aerosol-Assisted CVD (AACVD) uses an aerosol to carry the chemical precursor, simplifying its transport into the reaction chamber.
Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLICVD) involves injecting a liquid precursor directly into a heated chamber, where it vaporizes just before deposition.
Based on Operating Pressure
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) is conducted at a reduced pressure. This allows the gas molecules to travel further, resulting in highly uniform and conformal coatings that can evenly cover complex, three-dimensional shapes.
Based on Precursor Chemistry
Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD) is a specific subset of CVD that uses metal-organic compounds as the precursor gases. This technique is crucial for manufacturing high-performance electronic and optoelectronic components.
The Result: Common CVD Coating Materials
The process chosen is a means to an end: depositing a specific material with desired properties. CVD can produce an incredibly wide range of high-performance coatings.
Hard and Protective Coatings
Diamond and Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) are two of the most common hard coatings. They provide exceptional wear resistance and are frequently used on machine tools and other components subject to friction.
Semiconductor and Electronic Materials
CVD is fundamental to the electronics industry. Polysilicon and Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) films are deposited as essential layers in the fabrication of microchips and transistors.
Advanced and Metallic Coatings
The technology continues to evolve, enabling the creation of advanced materials like Graphene and Graphene nanoribbons. It is also used to deposit highly pure films of various metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, CVD technology is not without its challenges. Objectively understanding these limitations is key to its successful application.
The Challenge of High Temperatures
The primary limitation of Thermal CVD is its reliance on extreme heat. This completely rules out its use on many polymers, fully assembled electronic devices, and low-melting-point metals.
Inherent Process Limitations
Some processes have very specific constraints. For example, CVD methods for creating synthetic diamonds are currently limited in the maximum size of the diamond they can produce, often topping out around 3.2 carats.
Process Complexity and Cost
CVD is not a simple coating process like painting. It requires sophisticated vacuum chambers, precise gas handling systems, and complex energy sources, making the initial equipment investment significant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right CVD approach depends entirely on your specific objective, balancing the needs of the substrate material with the desired outcome of the coating.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and purity on a durable substrate: Thermal CVD is the superior choice for materials like diamond and silicon nitride, provided the underlying component can survive the heat.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the definitive solution, enabling advanced coatings on plastics, complex electronics, and certain alloys.
- If your primary focus is exceptional uniformity for complex electronics: Specialized methods like Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) and Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD) are the industry standards for building semiconductor devices.
Ultimately, selecting the right CVD coating is a matter of matching the process capabilities to your material's limits and your final performance goals.
Summary Table:
| CVD Type | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD | High-temperature (>700°C) process | Durable substrates needing hard, pure coatings (e.g., diamond, silicon nitride) |
| Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Low-temperature (~300°C) process | Temperature-sensitive materials (e.g., plastics, electronics) |
| Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) | Operates under reduced pressure | Highly uniform coatings on complex 3D shapes (e.g., semiconductors) |
| Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD) | Uses metal-organic precursors | High-performance electronic and optoelectronic components |
Ready to find the perfect CVD coating solution for your specific substrate and performance goals? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including CVD systems tailored for applications from hard coatings to semiconductor fabrication. Our experts can help you select the right technology to enhance your materials' durability, conductivity, or functionality. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















