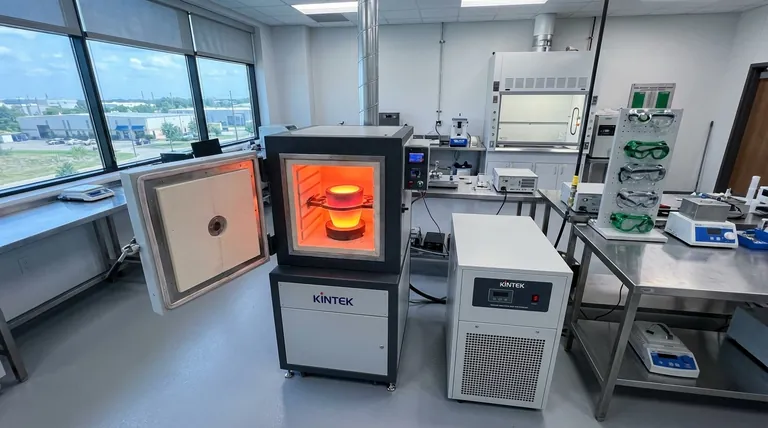
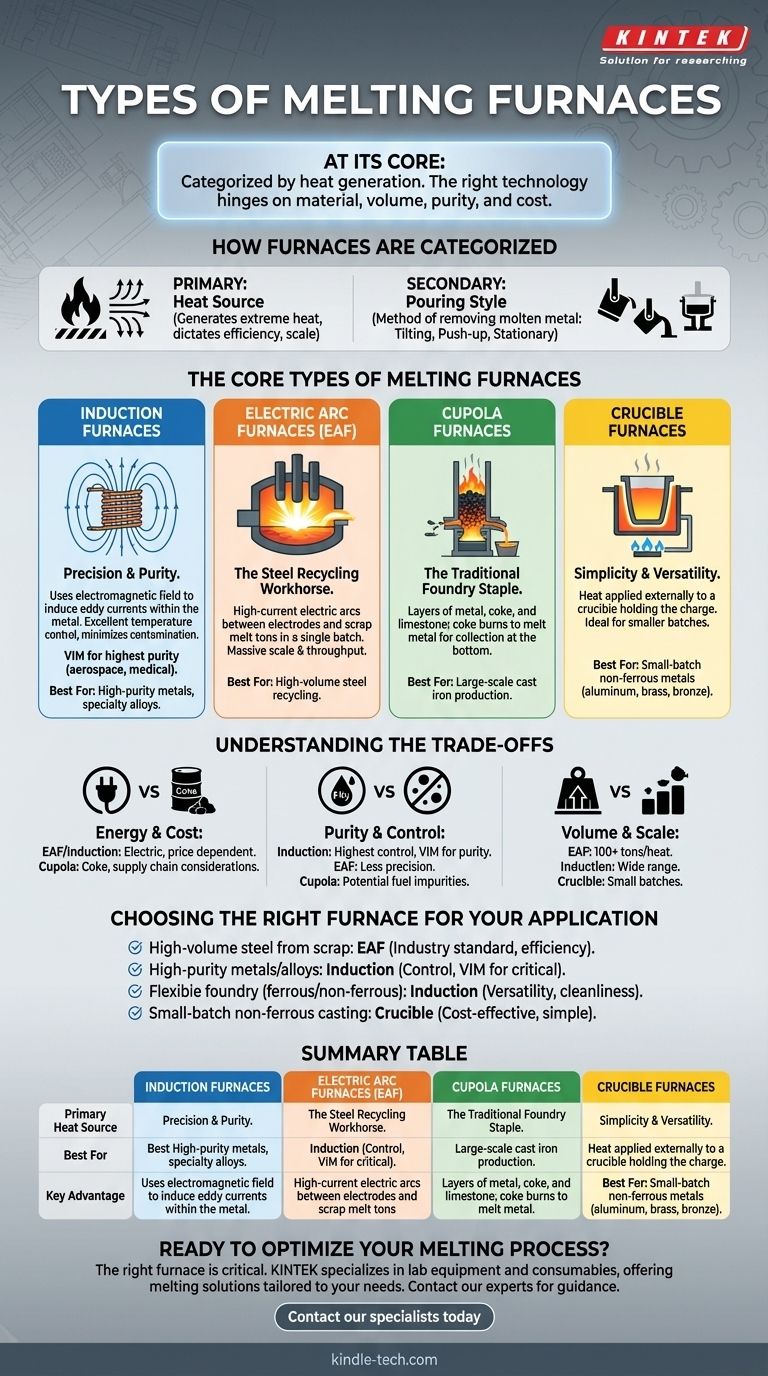
At its core, a melting furnace is categorized by how it generates heat. The four primary industrial types are the Induction Furnace, the Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), the Cupola Furnace, and the Crucible Furnace. Each uses a distinct method—from electromagnetic fields to high-current electric arcs—to melt materials for casting, recycling, or refinement.
Choosing a furnace is not about finding the "best" one, but about matching the right technology to the specific goal. The decision hinges on the material being melted, the required production volume, purity standards, and operational costs.

How Furnaces are Categorized
To understand the different types, it's essential to recognize the two main ways they are classified: by their heat source and by their physical design for pouring molten metal.
The Primary Method: Heat Source
The most fundamental distinction between furnace types is the principle they use to generate extreme heat. This choice dictates the furnace's efficiency, scale, and suitability for different metals.
A Secondary Method: Pouring Style
Beyond the heating method, furnaces are also described by how the molten metal is removed. A furnace might be a tilting furnace that pivots to pour, a push-up furnace where the crucible is lifted out, or a stationary furnace that is tapped from the bottom.
The Core Types of Melting Furnaces
Each major furnace type serves a distinct role in the industry, from massive steel mills to small-scale foundries.
Induction Furnaces: Precision and Purity
An induction furnace uses alternating electric currents to create a powerful electromagnetic field. This field induces eddy currents within the metal charge, generating intense, clean heat from the inside out.
This method provides excellent temperature control and minimizes contamination, as the heat source does not come into direct contact with the metal.
For applications requiring the highest purity, such as aerospace components or medical implants, a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is used. This variant operates in a vacuum to remove dissolved gases and prevent oxidation.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF): The Workhorse of Steel Recycling
The EAF is the dominant technology for recycling steel scrap. It operates by passing an immense electric current through large graphite electrodes.
The electrodes are lowered into a chamber of scrap metal, and a powerful arc forms between them and the metal. This arc generates temperatures high enough to melt tons of steel in a single batch. EAFs are known for their massive scale and high throughput.
Cupola Furnaces: The Traditional Foundry Staple
A cupola is a tall, cylindrical vertical shaft furnace. Layers of metal, coke (a high-carbon fuel), and limestone (a fluxing agent) are loaded from the top.
As the coke burns with the help of forced air, it melts the metal, which trickles down to a collection point at the bottom. Cupolas are traditionally used for producing large quantities of cast iron.
Crucible Furnaces: Simplicity and Versatility
The crucible furnace is the simplest type. It consists of a refractory container, the crucible, which holds the metal charge.
Heat is applied to the outside of the crucible, often by gas burners or electric resistance elements, which then transfers through the crucible wall to melt the metal inside. These furnaces are ideal for smaller batches and are commonly used for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each furnace technology comes with a distinct profile of costs, benefits, and limitations.
Energy Source and Cost
EAFs and Induction furnaces are entirely electric, making their operational cost dependent on local electricity prices. Cupolas rely on coke, a fossil fuel, which involves different supply chain and environmental considerations.
Material Purity and Control
Induction furnaces, especially VIM systems, offer the highest level of purity and metallurgical control. EAFs are highly effective for bulk recycling but offer less precision. Cupolas can introduce impurities from the fuel and are less suited for high-specification alloys.
Production Volume and Scale
EAFs are built for massive scale, melting over 100 tons per heat. Induction furnaces offer a wide range of capacities, from a few kilograms to many tons. Crucible furnaces are generally limited to smaller, batch-oriented operations.
Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace is a critical decision based on your specific operational needs.
- If your primary focus is high-volume steel production from scrap: The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the industry standard due to its unmatched scale and efficiency for this task.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metals or specialty alloys: An Induction Furnace provides the necessary control, with a Vacuum Induction (VIM) furnace being the ultimate choice for critical applications.
- If your primary focus is flexible foundry work for various metals: An Induction Furnace offers excellent versatility, cleanliness, and a wide range of capacities for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
- If your primary focus is small-batch, non-ferrous casting: A Crucible Furnace is the most straightforward and cost-effective solution for materials like aluminum and bronze.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one that aligns perfectly with your material, volume, and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Heat Source | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | Electromagnetic Field | High-purity metals, specialty alloys | Excellent temperature control, minimal contamination |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | High-current Electric Arc | High-volume steel recycling | Massive scale, high throughput |
| Cupola Furnace | Coke Combustion | Large-scale cast iron production | Traditional, cost-effective for iron |
| Crucible Furnace | External Gas/Electric Heat | Small-batch non-ferrous metals | Simple operation, versatility |
Ready to optimize your melting process? The right furnace is critical for achieving your production goals in quality, efficiency, and cost. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing lab equipment and consumables, including melting solutions tailored to your specific laboratory and foundry needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace technology for your materials and volume requirements.
Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can support your melting applications and enhance your operational performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a channel type induction furnace? A Guide to Efficient Metal Holding & Melting
- Why are high-temperature melting furnaces and platinum crucibles used in XRF for magnesium slag? Achieve Peak Precision
- What is the working principle of induction? Harnessing Direct, Contactless Heat
- How do you use an induction heater? A 3-Step Guide to Safe, Targeted Heating
- Does induction heating work with copper? Yes, with the right high-frequency equipment.
- What function does a graphite rod serve when using induction heating to test SiC cladding? | KINTEK Thermal Solutions
- What is the role of a high-frequency induction heating system in nuclear fuel testing? Enhance Safety with LOCA Simulation
- How fast is induction heating? Achieve Near-Instantaneous Heating for Metals



















