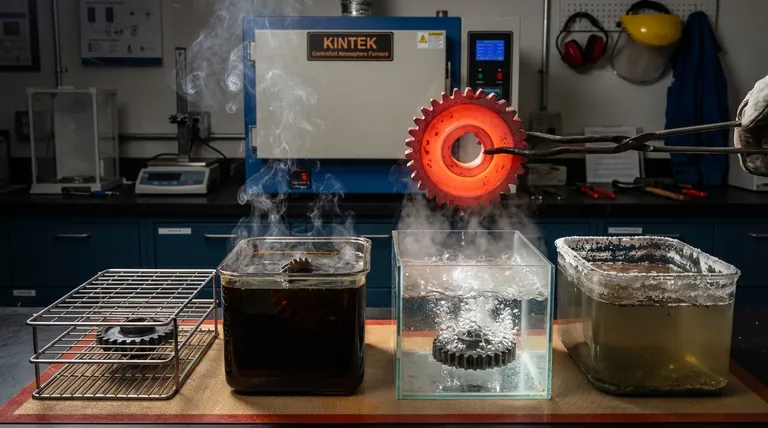
When hardening metals through heat treatment, the choice of cooling medium, or quenchant, is one of the most critical decisions. The primary types of quenchants are air, oil, water, and brine, each offering a different cooling rate. The selection is dictated by the specific alloy being treated and the final mechanical properties required, such as hardness and toughness.
The core principle of quenching is not to cool the metal as fast as possible, but to cool it at a specific, controlled rate. The ideal quenchant matches this rate to the alloy's characteristics, achieving the desired hardness without introducing defects like warping or cracking.
The Purpose of Quenching
Quenching is a metallurgical process used to rapidly cool a workpiece to "lock in" a specific material structure. For steels, this typically means cooling from a high temperature (the austenitizing temperature) fast enough to form a very hard, brittle crystalline structure called martensite.
The Three Stages of Cooling
Understanding how a liquid quenchant works involves recognizing three distinct phases of heat transfer as the hot metal is submerged.
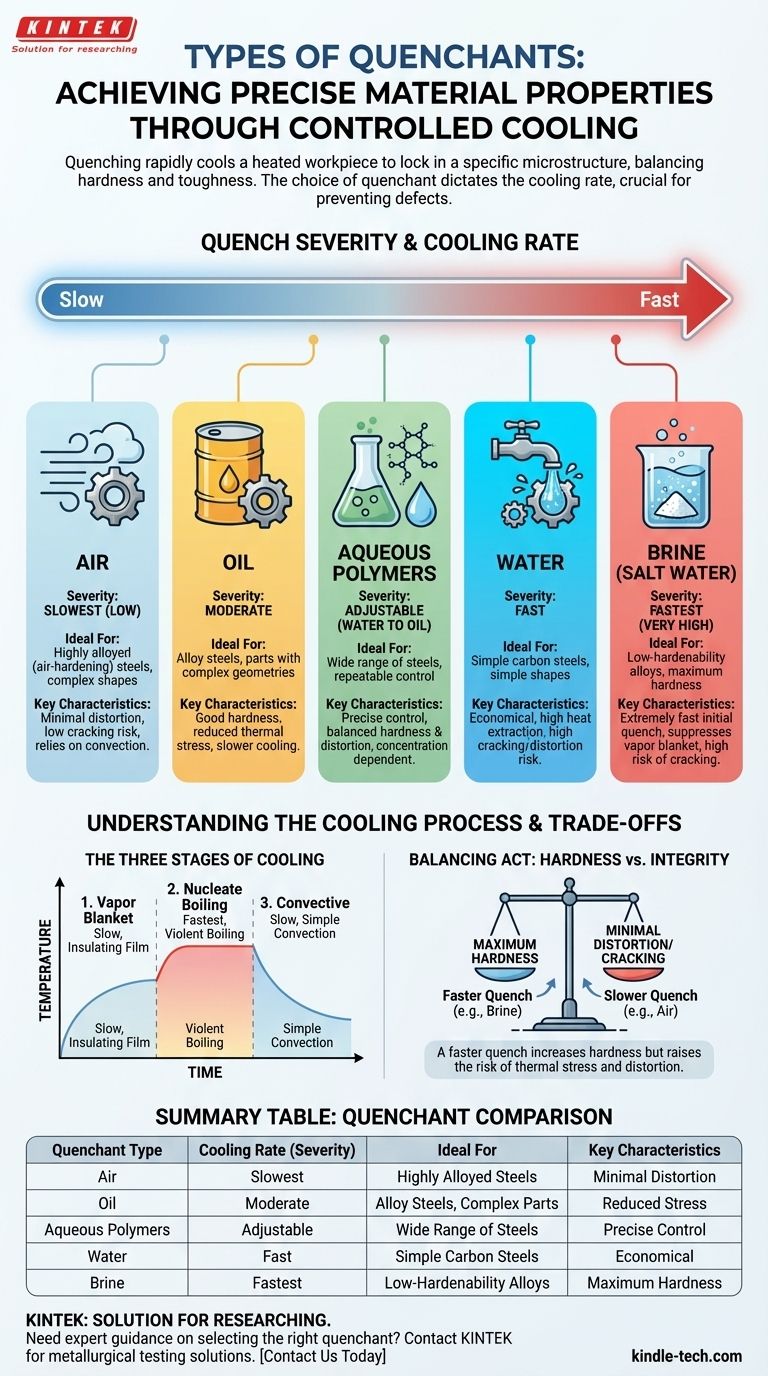
- Vapor Blanket Stage: A thin film of vapor immediately forms around the hot part, insulating it and slowing down heat transfer. A prolonged vapor blanket can lead to soft spots.
- Nucleate Boiling Stage: As the part's surface cools, the vapor blanket collapses, and the liquid makes direct contact. This causes violent boiling, which rapidly extracts a massive amount of heat. This is the fastest stage of cooling.
- Convective Stage: Once the part cools below the boiling point of the liquid, boiling stops. Heat is then removed at a much slower rate through simple convection.
Defining Quench Severity
Quench severity is a measure of how quickly a quenchant can extract heat from a material. This is the primary factor used to compare different quenching media. A higher severity means a faster cooling rate.
A Breakdown of Common Quenchants
Quenchants are best understood by arranging them on a spectrum from the slowest (lowest severity) to the fastest (highest severity).
Air
Air is the mildest quenchant. It relies solely on convection to remove heat, resulting in a very slow and uniform cooling rate.
This method is reserved for highly alloyed steels, often called "air-hardening" steels, which are designed to achieve full hardness even with slow cooling. It produces minimal distortion and a very low risk of cracking.
Oil
Oil is one of the most common industrial quenchants, offering a cooling rate faster than air but significantly slower and less severe than water.
Its slower cooling through the martensitic transformation range reduces internal stresses, making it ideal for many alloy steels and parts with complex geometries where cracking or distortion is a major concern.
Water
Water is an effective and economical quenchant that provides a very fast cooling rate. Its high heat extraction capacity comes from the intense nucleate boiling stage.
However, its rapid cooling can induce high internal stresses, making it suitable primarily for simple carbon steels and parts with simple shapes. Using it on more complex or highly alloyed parts risks severe distortion or quench cracking.
Brine (Salt Water)
Brine is one of the most severe quenchants available. Adding salt (typically sodium chloride) to water suppresses the initial vapor blanket stage.
This allows the violent nucleate boiling stage to begin almost immediately, resulting in an extremely fast initial quench. It is used for low-hardenability alloys where maximum hardness is required and the risk of cracking is acceptable.
Aqueous Polymers
Aqueous polymer quenchants are engineered solutions that bridge the gap between water and oil. By adjusting the concentration of polymer (like glycol) in water, the cooling rate can be precisely controlled.
This flexibility allows for a customized quench that can be faster than oil but less severe than water, offering an excellent balance of hardness and distortion control for a wide range of steels.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a quenchant is always a balancing act between achieving the desired properties and maintaining the integrity of the part.
Hardness vs. Cracking Risk
A faster quench generally produces a harder final part. However, this speed also creates immense thermal stress, dramatically increasing the risk of quench cracks, especially in sharp corners or thin sections.
Distortion and Warping
Every quench introduces some level of distortion. The more severe and less uniform the quench, the more likely the part is to warp or change dimensions. Air and oil are much gentler in this regard than water or brine.
Safety and Environmental Factors
Oil quenchants can produce smoke and present a fire hazard if not properly controlled. Water and brine are safer but can be highly corrosive. Polymer quenchants often offer a good compromise but require careful maintenance of their concentration.
Matching the Quenchant to Your Goal
The correct choice depends entirely on the material you are working with and your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness on a simple carbon steel: Brine or water will provide the severe quench needed.
- If your primary focus is hardening a common alloy steel with a good balance of properties: Oil is the traditional and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion on a highly-alloyed tool steel: Air is the only suitable option.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable control for sensitive alloys: Aqueous polymers offer the most tunable and flexible solution.
Ultimately, the right quenchant is the one that cools the steel just fast enough to achieve the target microstructure and nothing more.
Summary Table:
| Quenchant Type | Cooling Rate (Severity) | Ideal For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air | Slowest (Low) | Highly alloyed (air-hardening) steels | Minimal distortion, low cracking risk |
| Oil | Moderate | Alloy steels, complex parts | Good hardness with reduced stress |
| Water | Fast | Simple carbon steels, simple shapes | Economical but high cracking risk |
| Brine | Fastest (Very High) | Low-hardenability alloys | Maximum hardness, high cracking risk |
| Aqueous Polymers | Adjustable (Water to Oil) | Wide range of steels | Precise control, balanced hardness/distortion |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right quenchant for your lab's heat treatment processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for metallurgical testing and material hardening. Our team can help you choose the optimal quenching media to achieve precise hardness, minimize distortion, and enhance your results. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can support your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



