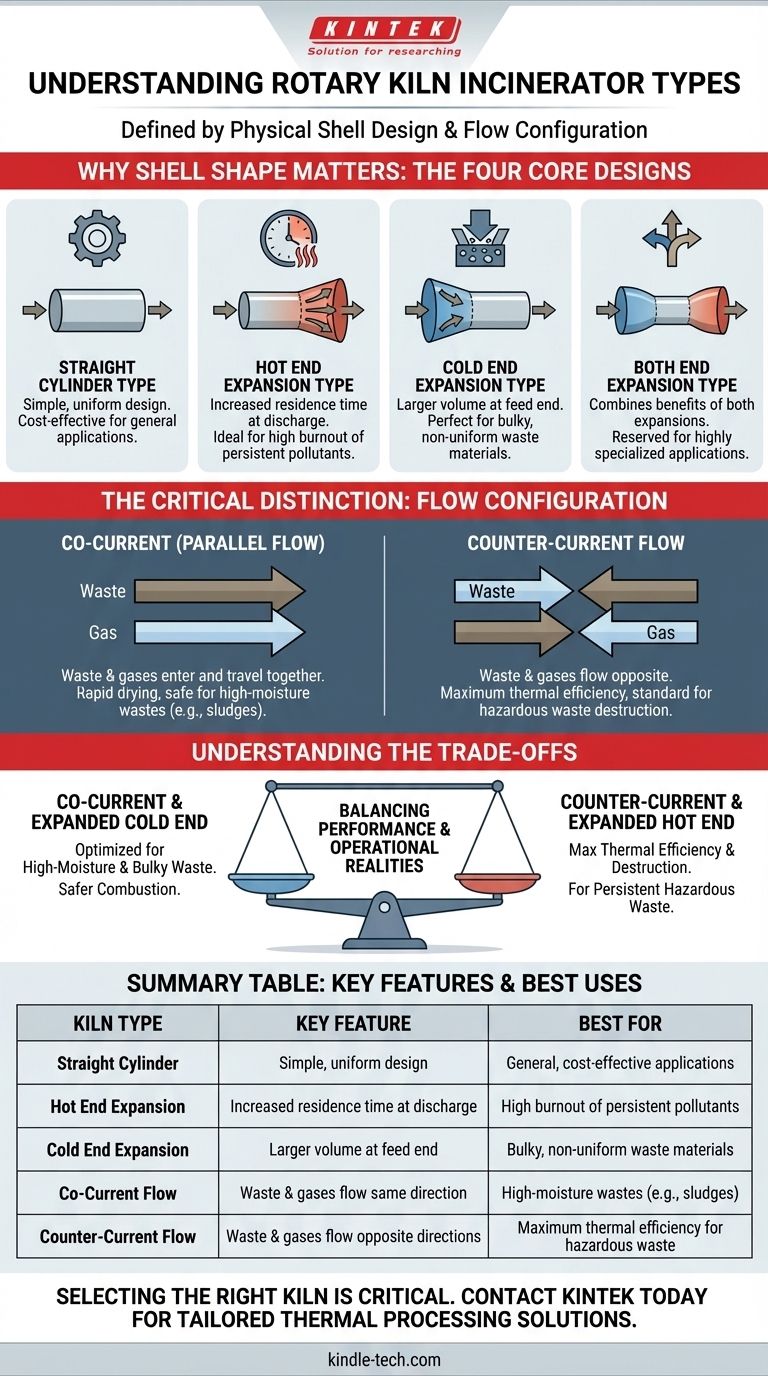
At its core, a rotary kiln incinerator's type is defined by its physical shell design. Based on this classification, there are four main types: the straight cylinder, the hot end expansion, the cold end expansion, and the both end expansion. These designs are engineered to control how waste material moves and how long it is exposed to high temperatures, directly impacting the incinerator's efficiency and suitability for different kinds of waste.
The physical shape of the kiln shell is a starting point, but the most critical distinction is how the waste and the hot combustion gases flow relative to each other. This flow configuration—either co-current or counter-current—is what truly dictates the incinerator's performance and application.
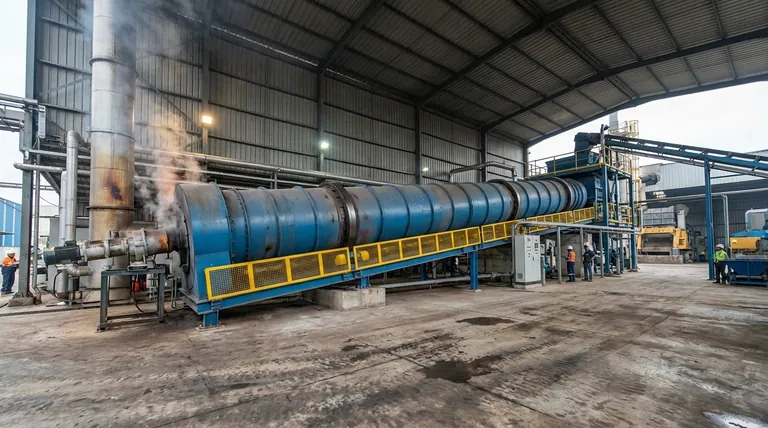

Why Shell Shape Matters: The Four Core Designs
The geometry of the kiln shell is the first level of specialization. Each design modifies the internal volume and material flow to optimize a specific part of the incineration process.
Straight Cylinder Type
This is the most common and straightforward design. It consists of a simple, uniform-diameter cylinder, making it easier and less expensive to manufacture.
Its primary advantage is its simplicity. However, it offers less control over material residence time in specific temperature zones compared to more complex designs.
Hot End Expansion Type
In this design, the diameter of the kiln increases at the discharge end (the "hot end"). This expansion slows down the movement of the ash and solids.
The key benefit is an increased residence time in the hottest part of the kiln. This ensures more complete combustion and destruction of persistent organic pollutants, making it ideal for certain hazardous wastes.
Cold End Expansion Type
Here, the kiln's diameter is larger at the feed end (the "cold end"). This design is particularly useful for processing bulky or non-uniform waste materials.
The larger volume at the entrance allows for better material distribution and prevents blockages. It also provides a larger area for the initial drying and volatilization of the waste before it enters the high-temperature zone.
Both End Expansion Type
As the name implies, this kiln is expanded at both the feed and discharge ends, creating a "cigar" shape. This is the most complex and costly design.
It attempts to combine the benefits of both hot and cold end expansion: accommodating bulky waste at the inlet while ensuring maximum burnout at the outlet. This design is reserved for highly specialized applications.
The Critical Distinction: Flow Configuration
Beyond shell shape, the operational principle that defines a kiln's function is the direction of gas flow relative to the waste flow. This is a far more significant factor in performance.
Co-Current (Parallel Flow)
In a co-current design, the waste material and the hot combustion gases enter at the same end and travel in the same direction through the kiln.
This configuration exposes the incoming wet or volatile waste to the highest temperatures immediately. It is exceptionally effective for high-moisture wastes (like sludges) as it provides rapid drying and minimizes the risk of uncontrolled combustion of volatiles at the cold end.
Counter-Current Flow
In a counter-current design, the waste is fed at one end, and the hot gases are introduced from the opposite end, flowing against the movement of the solids.
This is the most common configuration for hazardous waste incineration due to its high thermal efficiency. As the waste moves toward the hot end, it is preheated by the exiting gases, and the solids experience the highest temperature just before they are discharged. This ensures maximum destruction and removal efficiency (DRE).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a rotary kiln design involves balancing performance requirements with operational realities. No single type is universally superior.
Co-Current vs. Counter-Current
The primary trade-off is between front-end processing and overall thermal efficiency. Co-current flow excels at handling high-moisture or highly volatile waste safely but is less thermally efficient.
Counter-current flow is the champion of thermal efficiency and destruction, making it the standard for most hazardous wastes. However, it can be problematic for wastes that release large amounts of combustible gas upon initial heating.
Simple vs. Expanded Shells
The trade-off here is cost versus specialization. A straight cylinder is a reliable, cost-effective workhorse for a variety of waste streams.
An expanded shell adds manufacturing complexity and cost but solves specific problems. An expanded hot end is a solution for waste requiring extended burnout, while an expanded cold end is a solution for bulky, difficult-to-feed materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection must be guided by the specific characteristics of your waste stream and your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency for low-moisture hazardous waste: A counter-current kiln is the most effective and standard choice.
- If your primary focus is processing high-moisture sludge or volatile materials: A co-current design offers safer, more stable combustion by rapidly drying and igniting the material.
- If your primary focus is handling bulky, non-uniform industrial or municipal solid waste: A kiln with an expanded cold end will prevent feeding issues and improve initial processing.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible destruction of highly persistent materials: A counter-current kiln, potentially with an expanded hot end, provides the longest residence time at peak temperature.
Ultimately, understanding these design variables empowers you to select a rotary kiln system that is precisely engineered for your specific waste management challenge.
Summary Table:
| Kiln Type | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Straight Cylinder | Simple, uniform design | General, cost-effective applications |
| Hot End Expansion | Increased residence time at discharge | High burnout of persistent pollutants |
| Cold End Expansion | Larger volume at feed end | Bulky, non-uniform waste materials |
| Co-Current Flow | Waste & gases flow same direction | High-moisture wastes (e.g., sludges) |
| Counter-Current Flow | Waste & gases flow opposite directions | Maximum thermal efficiency for hazardous waste |
Selecting the right rotary kiln is critical to your operation's efficiency and compliance. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory and industrial equipment, including systems for advanced thermal processing. Our experts can help you analyze your waste stream and identify the optimal kiln design to meet your specific destruction and efficiency goals.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your application and receive a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing














