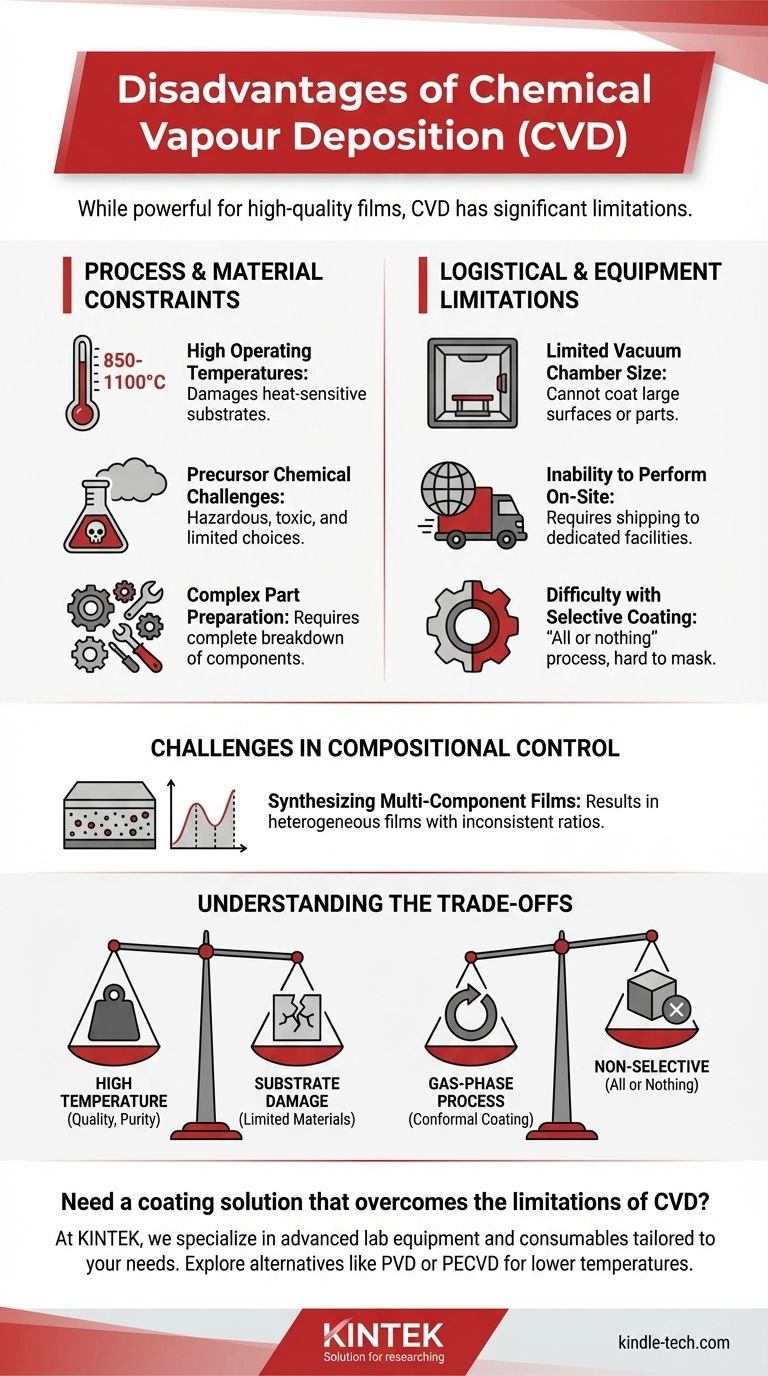
While a powerful technique for creating high-quality films, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not without significant limitations. Its primary disadvantages stem from the high temperatures required, the hazardous and limited nature of precursor chemicals, and logistical constraints related to equipment size and the inability to perform selective coatings easily. These factors can restrict the types of materials that can be coated and increase operational complexity.
The core disadvantages of CVD are a direct consequence of its fundamental process: using high thermal energy to drive chemical reactions from a gas phase. This creates a powerful but inflexible system with major constraints on temperature, material compatibility, and process control that must be carefully evaluated.
Process and Material Constraints
The most significant hurdles in CVD are often related to the demanding physical and chemical conditions of the process itself.
High Operating Temperatures
The chemical reactions central to CVD typically require very high temperatures, often in the range of 850-1100°C.
This extreme heat means many potential substrate materials, such as polymers, certain metal alloys, or fully assembled components, simply cannot withstand the process without being damaged or destroyed.
Precursor Chemical Challenges
The process relies on volatile precursor chemicals that can be transported as a gas. Finding precursors that are highly volatile but also non-toxic and non-pyrophoric (not self-igniting) is a major challenge.
This lack of ideal chemicals can limit the types of films that can be deposited or introduce significant safety and handling complexities into the manufacturing process.
Complex Part Preparation
To ensure a uniform coating, parts must often be completely broken down into individual components before being placed in the reaction chamber.
This requirement adds significant labor, time, and logistical complexity, especially for intricate assemblies.
Logistical and Equipment Limitations
Beyond the core process, practical limitations related to the equipment and its operation can make CVD impractical for certain applications.
Limited Vacuum Chamber Size
CVD is performed inside a vacuum chamber, and the size of this chamber dictates the maximum size of the part that can be coated. This makes it difficult or impossible to coat very large surfaces or components.
Inability to Perform On-Site
CVD is a specialized industrial process requiring dedicated, complex equipment. It generally cannot be performed on-site, meaning parts must be shipped to a dedicated coating center, adding to lead times and costs.
Difficulty with Selective Coating
The gaseous nature of the precursors means they will deposit a film on all exposed surfaces within the chamber. This makes CVD an "all or nothing" process, where selectively coating only a specific area of a part is extremely difficult and often requires complex masking.
Challenges in Compositional Control
For advanced applications requiring precise material blends, CVD presents unique difficulties.
Synthesizing Multi-Component Films
Creating films from multiple materials (e.g., complex alloys) is challenging. Each precursor chemical has a different vapor pressure, reaction rate, and growth characteristic.
This variation makes it difficult to control the final composition uniformly, often resulting in a heterogeneous film where the material ratios are inconsistent across the surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of CVD are not arbitrary; they are the direct trade-offs for its key advantages.
Quality vs. Temperature
The high process temperature is a primary disadvantage, but it is also what provides the necessary energy to form highly pure, dense, and well-crystallized films. The quality of the coating is directly linked to the high-energy environment.
Conformal Coating vs. Selectivity
The gas-phase nature of the process is responsible for its "all or nothing" disadvantage. However, this same characteristic allows CVD to produce excellent "wrap-around" properties, conformally coating complex shapes and internal surfaces that line-of-sight processes cannot reach.
Purity vs. Precursor Hazard
The goal of creating exceptionally high-purity films often requires the use of highly reactive precursor chemicals. This reactivity is what ensures a clean reaction, but it is also what can make the chemicals hazardous to handle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Evaluating these disadvantages against your project goals is critical for making an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum film quality and purity for a thermally stable substrate: CVD is often the superior choice, provided you can manage the operational constraints.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive materials like polymers or certain alloys: You must consider lower-temperature variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) or explore alternative methods like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
- If you require selective coating on specific areas of a large component: The "all or nothing" nature of CVD makes it a poor fit; other methods like sputtering or thermal spray may be more practical.
- If you are developing complex, multi-component alloy films: The challenges in controlling stoichiometry with CVD are significant, and you must be prepared for extensive process development.
Understanding these limitations is the first step toward leveraging CVD's power effectively or choosing a more suitable alternative for your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenge | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Process & Material | High operating temperatures (850-1100°C) | Limits substrate materials; can damage components. |
| Process & Material | Hazardous/limited precursor chemicals | Increases safety complexity and restricts film types. |
| Logistical & Equipment | Limited vacuum chamber size | Cannot coat very large surfaces or components. |
| Logistical & Equipment | Inability for selective coating | Coats all exposed surfaces; difficult to mask areas. |
| Compositional Control | Difficulty with multi-component films | Hard to achieve uniform material ratios (heterogeneous films). |
Need a coating solution that overcomes the limitations of CVD?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Whether you're exploring alternatives like PVD or require equipment for Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) to lower process temperatures, our experts can help you find the right solution for your materials and application.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















