The primary disadvantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) for graphene synthesis are rooted in the complexities of process control, particularly the behavior of the metal catalyst. While CVD is the leading method for large-area production, its sensitivity to parameters like temperature and cooling rates creates significant challenges in achieving perfectly uniform, defect-free, single-layer graphene.
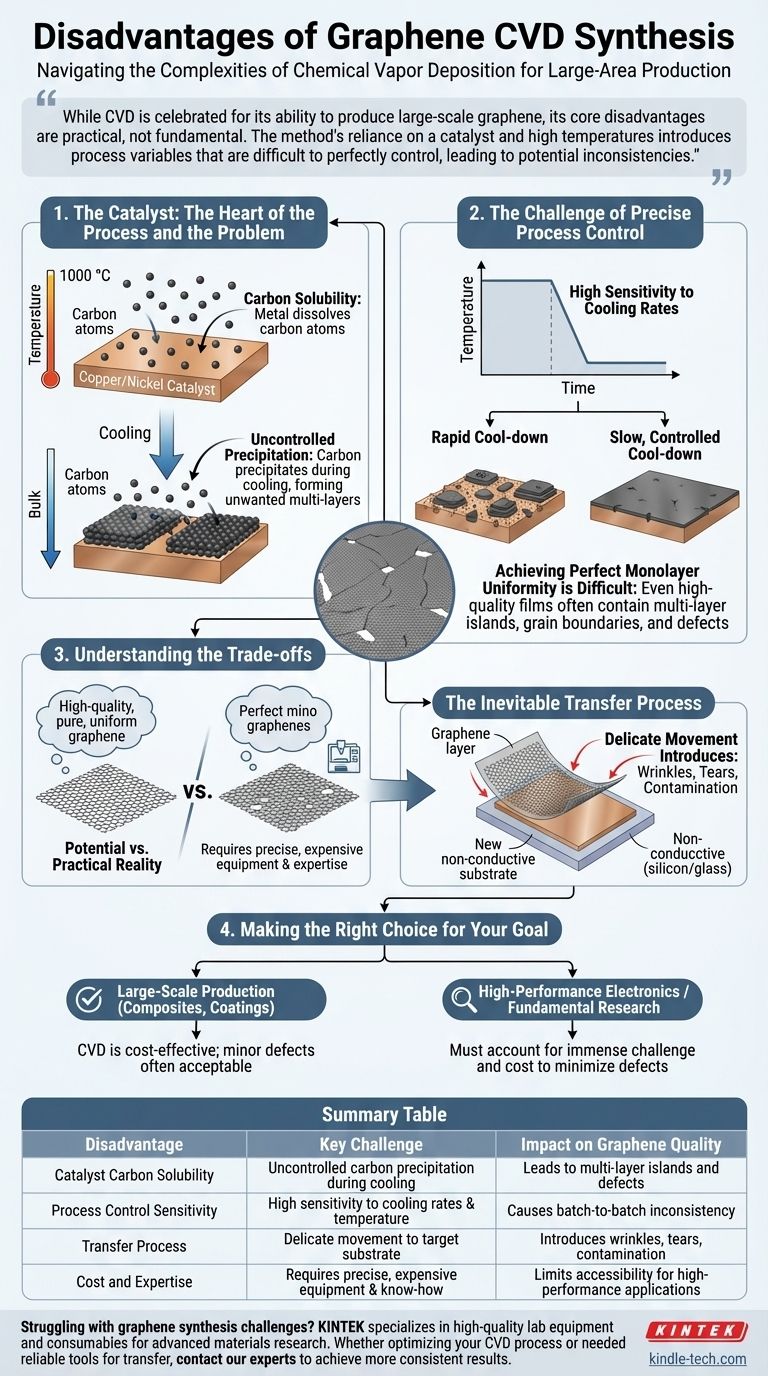
While CVD is celebrated for its ability to produce large-scale graphene, its core disadvantages are practical, not fundamental. The method's reliance on a catalyst and high temperatures introduces process variables that are difficult to perfectly control, leading to potential inconsistencies in the final material's quality.
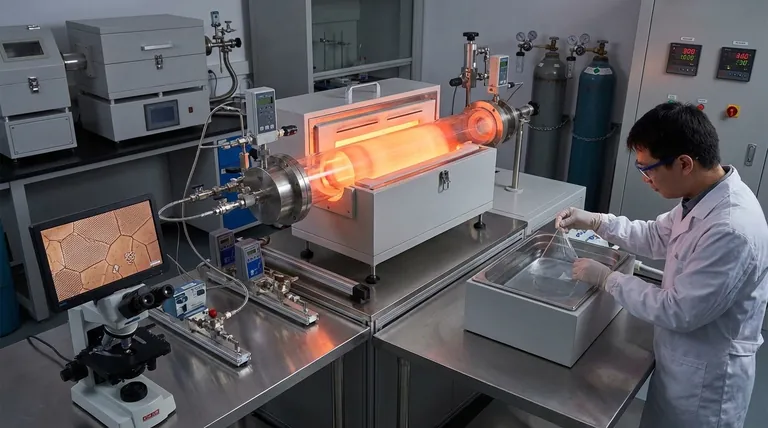

The Catalyst: The Heart of the Process and the Problem
The transition metal catalyst, typically copper or nickel, is essential for graphene growth but is also the source of several key challenges. Its interaction with carbon at high temperatures dictates the quality of the final film.
The Problem of Carbon Solubility
Many metal catalysts have a finite carbon solubility, meaning they can dissolve carbon atoms into their bulk structure at the high temperatures required for CVD (around 1000 °C).
This process sequesters carbon that is intended for surface-level graphene formation, creating a reservoir of atoms within the metal itself.
Uncontrolled Precipitation During Cooling
As the system cools after growth, the catalyst's ability to hold dissolved carbon decreases sharply. This forces the trapped carbon atoms to precipitate back onto the surface.
This precipitation is often uncontrolled and can lead to the formation of unwanted additional graphene layers or amorphous carbon deposits, compromising the uniformity of the desired single layer.
The Challenge of Precise Process Control
Beyond the catalyst's chemistry, the physical parameters of the CVD process are extremely sensitive. Minor deviations can have a significant impact on the final product.
High Sensitivity to Cooling Rates
The rate at which the catalyst is cooled is a critical variable. Different cooling rates directly affect how the dissolved carbon precipitates.
A rapid cool-down might trap defects or result in a different layer thickness compared to a slow, controlled cool-down. This makes achieving batch-to-batch consistency a significant engineering challenge.
Achieving Perfect Monolayer Uniformity
The combination of carbon solubility, uncontrolled precipitation, and sensitivity to cooling means that producing a truly homogenous, large-area monolayer is difficult.
Even in high-quality films, it is common to find small multi-layer islands, grain boundaries, or defects that can degrade the exceptional electronic properties of perfect graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No production method is perfect. The disadvantages of CVD must be weighed against its significant strengths, which are unmatched by other synthesis techniques.
Potential vs. Practical Reality
The references are clear that CVD can and does produce high-quality, pure, and uniform graphene. The disadvantage is the gap between this potential and the practical reality of production.
Achieving this high quality requires extremely precise, expensive, and well-calibrated equipment, along with significant process expertise.
The Inevitable Transfer Process
A major practical disadvantage not directly related to growth is that the graphene is formed on a metal substrate and must be transferred to a new, non-conductive substrate (like silicon or glass) for most applications.
This transfer process is delicate and can introduce wrinkles, tears, and contamination, which can degrade the material's properties more than the initial growth defects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The significance of these disadvantages depends entirely on your intended application for the graphene.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production for applications like composites or coatings: CVD is the most cost-effective and scalable method, as minor defects or uniformity issues are often acceptable.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or fundamental research: You must account for the immense challenge and cost of perfecting the CVD process and subsequent transfer to minimize defects that would compromise performance.
Understanding these inherent challenges is the first step toward mastering the process and leveraging its powerful capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Challenge | Impact on Graphene Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst Carbon Solubility | Uncontrolled carbon precipitation during cooling | Leads to multi-layer islands and defects |
| Process Control Sensitivity | High sensitivity to cooling rates and temperature | Causes batch-to-batch inconsistency |
| Transfer Process | Delicate movement from metal to target substrate | Introduces wrinkles, tears, and contamination |
| Cost and Expertise | Requires precise, expensive equipment and know-how | Limits accessibility for high-performance applications |
Struggling with graphene synthesis challenges? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for advanced materials research. Whether you're optimizing your CVD process or need reliable tools for graphene transfer, our expertise can help you achieve more consistent and high-quality results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in graphene production and beyond.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs



















