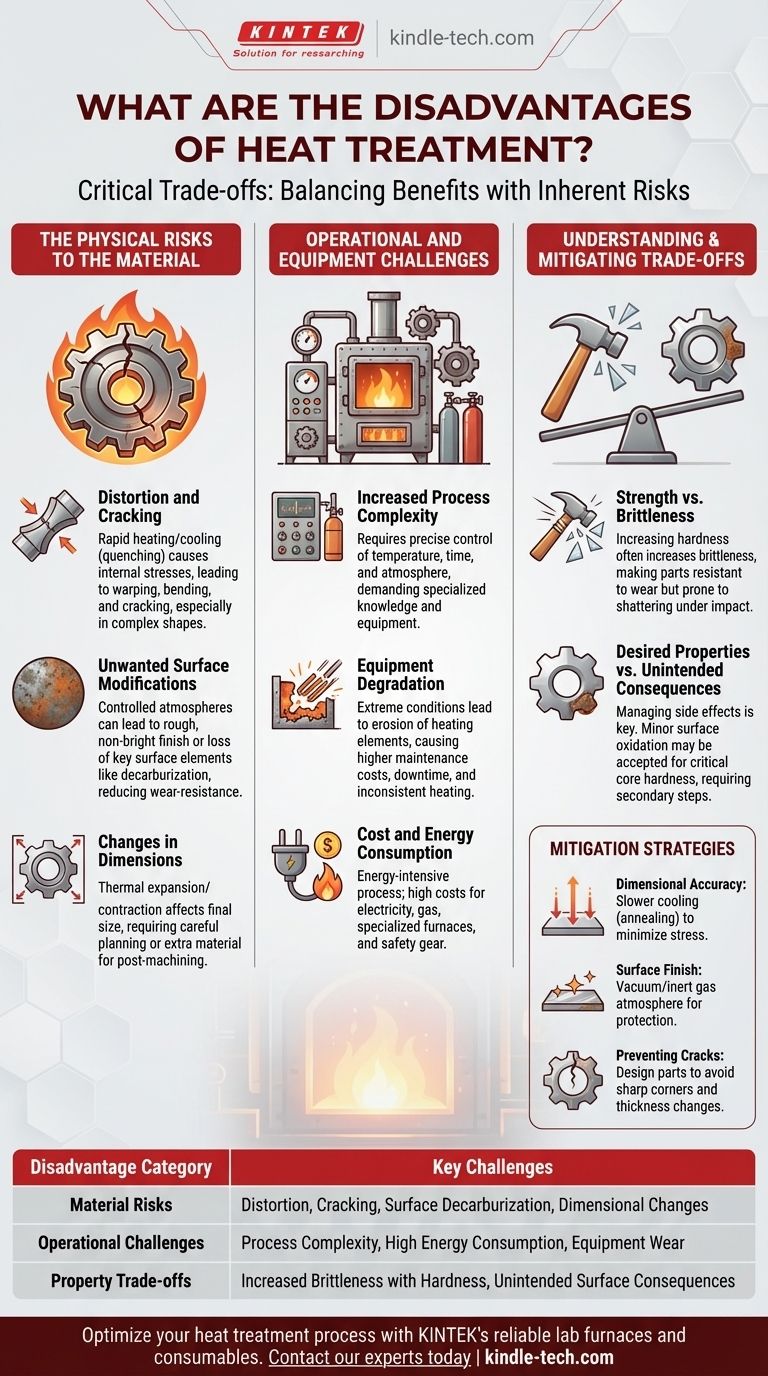
While incredibly beneficial, heat treatment is not a flawless process and introduces a series of critical trade-offs. The primary disadvantages are the risk of physical damage to the workpiece, such as distortion, cracking, and undesirable surface changes, alongside increased operational complexity, cost, and equipment wear.
Heat treatment's disadvantages are not failures of the process but inherent consequences of inducing massive structural change in a material. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for managing the process successfully to achieve a desired outcome without introducing unacceptable flaws.

The Physical Risks to the Material
Applying extreme temperatures fundamentally alters a material. While the goal is to improve properties, this change can also manifest in undesirable ways if not perfectly controlled.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
Rapid or uneven heating and cooling are the primary culprits behind internal stresses.
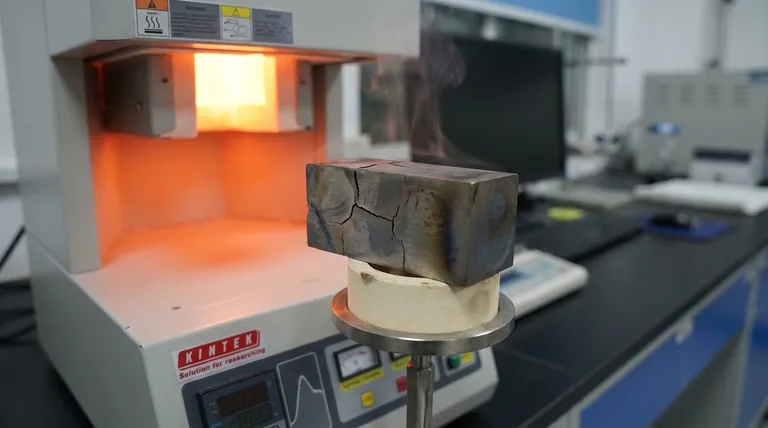
Processes like quenching, which involves rapid cooling in a liquid medium, are highly effective for hardening but put immense stress on the part. This can cause the material to warp, bend, or even crack, especially in complex geometries with both thick and thin sections.
Unwanted Surface Modifications
The interaction between high heat and the surrounding atmosphere can degrade the material's surface.
In a controlled atmosphere treatment, for example, the workpiece can emerge with a rough and non-bright surface. More critically, it can lead to the loss of key surface metal elements, such as the decarburization of steel, which leaves the surface softer and less wear-resistant than intended.
Changes in Dimensions
All materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. While predictable, this can lead to final dimensions that are outside of required tolerances.
This requires careful planning and, in some cases, leaving extra material on the part for a final machining pass after heat treatment, adding another step to the manufacturing process.
Operational and Equipment Challenges
Beyond the workpiece itself, heat treatment introduces significant logistical and financial considerations. These factors contribute to the overall cost and complexity of manufacturing.
Increased Process Complexity
Effective heat treatment is a precise science. It demands exact control over temperature, time, and atmospheric composition.
Managing the gasses used in a controlled atmosphere, for instance, presents challenges in both usage and recovery. This complexity requires specialized knowledge and equipment to execute correctly.
Equipment Degradation
The extreme conditions inside a furnace take a toll on the equipment itself.
The references note the erosion of electric heating elements as a significant issue. This leads to higher maintenance costs, potential downtime, and inconsistent heating if not addressed.
Cost and Energy Consumption
Heating large metal components to very high temperatures is an energy-intensive process. The cost of electricity or gas, combined with the expense of specialized furnaces and safety equipment, makes heat treatment a significant investment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of heat treatment must be weighed against its powerful benefits. Nearly every desired property improvement comes with a corresponding risk that must be managed.
Strength vs. Brittleness
A common goal is to increase a material's hardness and strength. However, for many metals, particularly steel, increasing hardness also increases brittleness. A very hard part may be resistant to wear but could shatter under a sudden impact.
Desired Properties vs. Unintended Consequences
The decision to heat treat is a commitment to managing its side effects. You might accept minor surface oxidation to achieve a critical core hardness, knowing that a secondary cleaning or polishing step will be required. The goal is to control the process so the benefits—like stress relief or improved wear resistance—far outweigh the managed drawbacks.
How to Mitigate the Disadvantages
By anticipating the potential downsides, you can select the right process and build steps into your plan to counteract them.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: Opt for slower cooling methods like normalizing or annealing instead of quenching to minimize the internal stresses that cause warping.
- If your primary focus is surface finish: Use a vacuum furnace or a precisely controlled inert gas atmosphere to prevent surface oxidation and decarburization, or plan for post-treatment grinding or machining.
- If your primary focus is preventing cracks: Ensure part designs avoid sharp internal corners and drastic changes in thickness, which act as stress concentrators during rapid cooling.
By understanding and planning for these potential drawbacks, you can harness the full power of heat treatment while controlling for its inherent risks.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Material Risks | Distortion, cracking, surface decarburization, dimensional changes |
| Operational Challenges | Process complexity, high energy consumption, equipment wear and tear |
| Property Trade-offs | Increased brittleness with hardness, unintended surface consequences |
Optimize your heat treatment process and protect your materials. The challenges of distortion, surface degradation, and equipment costs are significant, but they can be managed with the right expertise and equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and consumables, providing the reliable, precise tools your laboratory needs to achieve successful heat treatment outcomes while minimizing risks.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















