Ultimately, the disadvantages of PVD are not found in the quality of the final coating but in the demanding and precise nature of the application process itself. Its primary drawbacks relate to operational complexity, infrastructure requirements, and inherent geometric limitations that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
The core trade-off with PVD is accepting a more complex and controlled manufacturing process in exchange for a superior, high-performance thin-film coating. The main challenges are its line-of-sight application, high vacuum and temperature needs, and the requisite infrastructure.

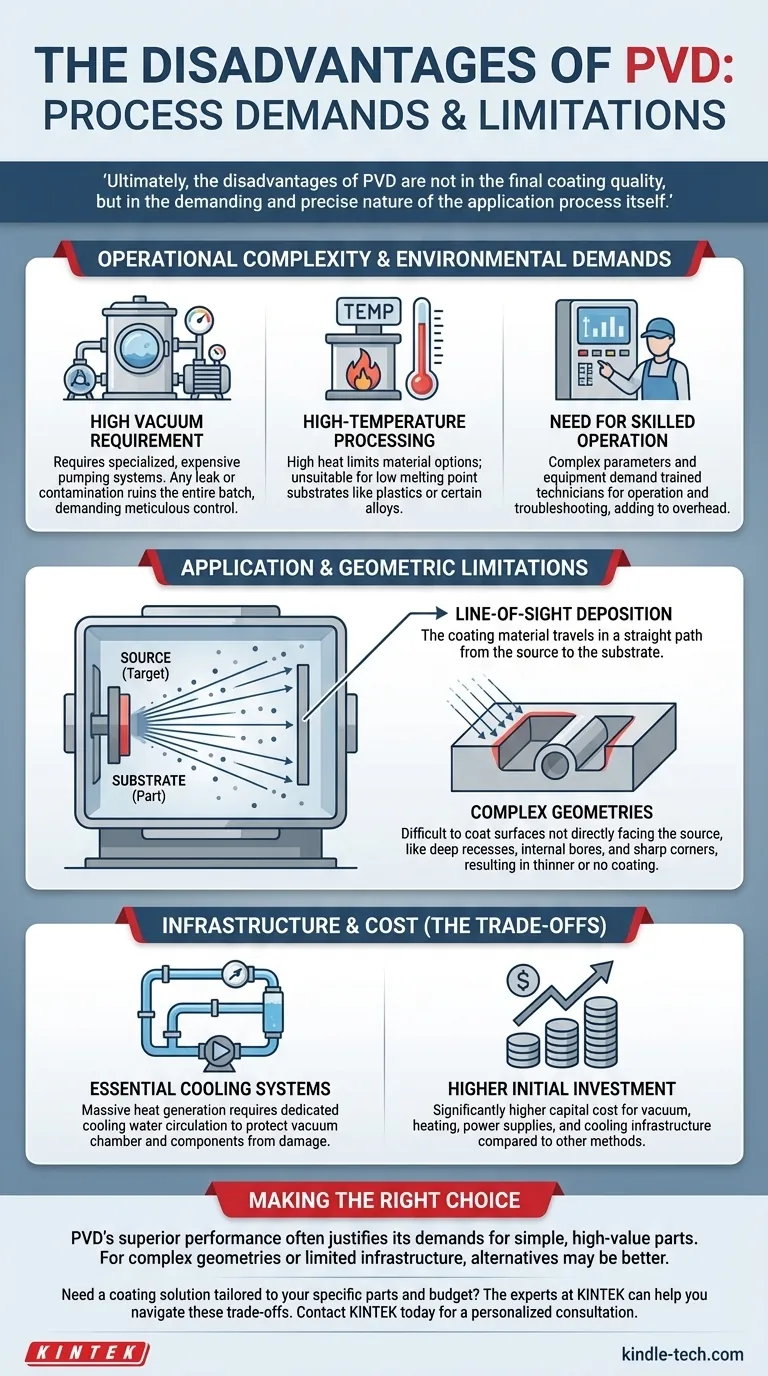
Operational Complexity and Environmental Demands
The PVD process requires a highly controlled environment, which introduces several operational challenges that can increase cost and complexity compared to other coating methods.
High Vacuum Requirement
PVD takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. Achieving and maintaining this vacuum requires specialized, expensive pumping systems and adds significant time to each coating cycle for pump-down.
This environment is unforgiving; any leak or contamination can compromise the vacuum and ruin the entire batch, demanding meticulous process control.
High-Temperature Processing
Many PVD processes operate at elevated temperatures to ensure proper film adhesion and structure. This high-heat environment limits the types of materials that can be successfully coated.
Substrates with low melting points, such as many plastics or certain alloys, may deform or be damaged, making them incompatible with these PVD techniques.
Need for Skilled Operation
The combination of high vacuum, high temperatures, and precise deposition parameters means PVD equipment cannot be operated by untrained staff.
It requires skilled technicians who can manage the equipment, monitor the process with high attention to detail, and troubleshoot issues as they arise, adding to operational overhead.
Application and Geometric Limitations
The physics of how PVD works creates fundamental limitations on the types of shapes that can be effectively coated.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
The core limitation of most PVD processes is that they are "line-of-sight." The coating material travels in a straight path from the source (the "target") to the substrate.
Challenges with Complex Geometries
Because of this line-of-sight nature, coating surfaces that are not directly facing the source is extremely difficult.
Deep recesses, internal bores, sharp corners, and undercuts will receive a much thinner coating or no coating at all. While complex part-rotation systems can mitigate this, they add significant complexity and may not achieve perfect uniformity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Infrastructure and Cost
The demands of the PVD process translate directly into significant infrastructure and investment requirements that must be considered.
Essential Cooling Systems
The energy involved in the PVD process generates a massive amount of heat. This requires dedicated, closed-loop cooling water circulation systems to protect the vacuum chamber and other critical machine components from damage.
This is not an optional add-on; it's a fundamental piece of infrastructure that must be installed and maintained, adding to the system's overall footprint and cost.
Higher Initial Investment
Compared to methods like wet painting or electroplating, the capital investment for a PVD system is significantly higher. The cost of vacuum pumps, heating elements, power supplies, control systems, and cooling infrastructure makes it a major expenditure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is coating high-value parts with simple geometries: The operational demands of PVD are often a justifiable trade-off for the superior hardness, durability, and finish.
- If your parts have complex internal surfaces or deep, narrow features: You must carefully evaluate if PVD can provide adequate coverage, or if an alternative like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or electroplating is required.
- If you have limited capital or facility infrastructure: The high equipment and support system costs associated with PVD may make simpler, less demanding coating methods a more practical choice.
Understanding these process-related disadvantages is the key to leveraging PVD's exceptional coating strengths for the right applications.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Operational Complexity | High vacuum requirements, high-temperature processing, need for skilled technicians |
| Geometric Limitations | Line-of-sight deposition, poor coverage for complex shapes, recesses, and internal surfaces |
| Infrastructure & Cost | High initial investment, essential cooling water systems, significant facility requirements |
Need a Coating Solution Tailored to Your Specific Parts and Budget?
While PVD offers superior coating performance, its process demands and geometric limitations mean it's not the right fit for every application. The experts at KINTEK can help you navigate these trade-offs.
We specialize in providing laboratory equipment and consumables, including coating solutions. Our team can help you determine if PVD is the right choice for your high-value parts or if an alternative method would be more effective and cost-efficient for your needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation. Let us help you select the ideal coating technology to achieve the durability, finish, and performance your laboratory work requires.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















