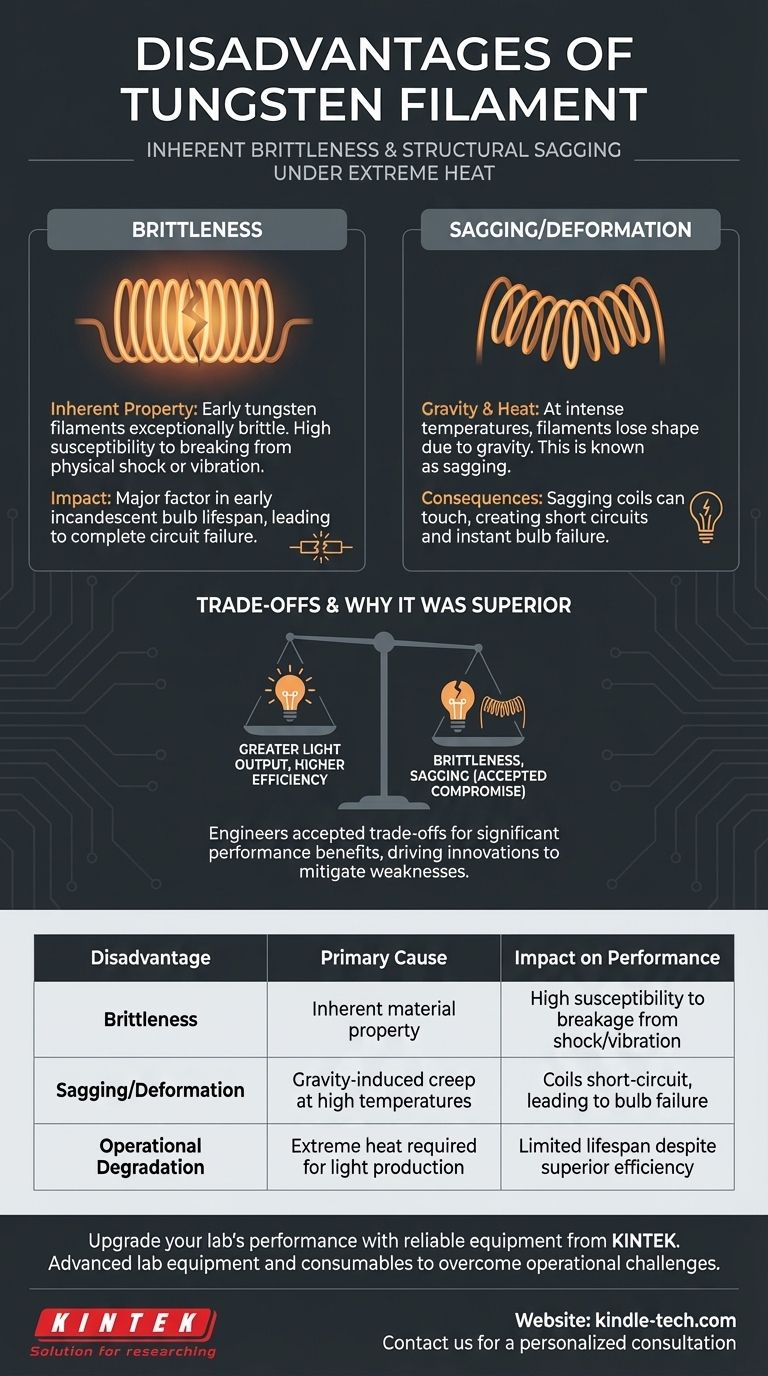
Despite its revolutionary impact on lighting, the primary disadvantages of the tungsten filament are its inherent brittleness and its tendency to physically deform under the extreme heat required for operation. These material limitations create significant engineering challenges and are the root cause of bulb failure.
The core challenge of the tungsten filament lies in a paradox: the very high temperatures required for efficient light production also accelerate its physical degradation, primarily through structural sagging and eventual material failure.

The Fundamental Material Challenge: Brittleness
An Inherent Property
Early tungsten filaments were exceptionally brittle. This characteristic made them fragile and highly susceptible to breaking from physical shock or vibration.
Impact on Durability
This brittleness was a major factor in the lifespan of early incandescent bulbs. While tungsten was strong, its lack of ductility meant that any small fracture could lead to complete failure of the filament circuit.
The Operational Failure Mode: Sagging
The Effect of Gravity
At the intense temperatures needed to produce light, coiled tungsten filaments would slowly lose their shape due to the constant pull of gravity. This phenomenon is known as sagging.
Consequences of Deformation
As the filament sagged, the coils could eventually touch, creating a short circuit that would cause the bulb to fail instantly. This deformation was a significant and predictable point of failure in bulb design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Why Tungsten Was Still Superior
Despite these clear disadvantages, tungsten was a massive improvement over the carbon filaments it replaced. It offered far greater light output and higher efficiency, measured in lumens per watt.
A Necessary Compromise
Engineers accepted the trade-offs of brittleness and sagging because tungsten's performance benefits were so significant. The problem then shifted from finding a new material to engineering solutions that could mitigate tungsten's known weaknesses.
How to Apply This Understanding
- If your primary focus is historical technology: Recognize that tungsten's flaws directly drove innovations in filament manufacturing and bulb design to improve durability.
- If your primary focus is material science: View the tungsten filament as a classic case study where a material's primary strength (heat resistance) is undermined by secondary operational stresses like gravity-induced creep.
Understanding these limitations reveals why the search for more durable and efficient lighting technologies was destined to continue.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Primary Cause | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Brittleness | Inherent material property | High susceptibility to breakage from shock/vibration |
| Sagging/Deformation | Gravity-induced creep at high temperatures | Coils short-circuit, leading to bulb failure |
| Operational Degradation | Extreme heat required for light production | Limited lifespan despite superior efficiency |
Upgrade your lab's performance with reliable equipment from KINTEK. Just as material limitations drove innovation beyond tungsten filaments, KINTEK provides advanced lab equipment and consumables to overcome your operational challenges. Whether you need durable heating elements, precise temperature control systems, or long-lasting laboratory tools, our solutions are engineered for efficiency and longevity.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and reliability. Reach out via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are tungsten-rhenium (W/Re) thermocouples selected for monitoring the combustion synthesis of ferroalloys? - Up to 2400°C
- Is tungsten shock resistant? Uncovering the Surprising Brittleness of a Hard Metal
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- How does electric resistance heat work? Harnessing Direct Energy Conversion for Precise Heating
- Do heating elements degrade over time? Understanding the Inevitable Decay for Better Performance
- What are the heating elements in a furnace? A Guide to High-Temp Materials & Selection
- How do thermocouples and thermal sensors ensure process stability? Master Zirconium Thermal Reduction Control
- What uses resistive heating? From Toasters to Furnaces, Harnessing Simple, Direct Heat



















