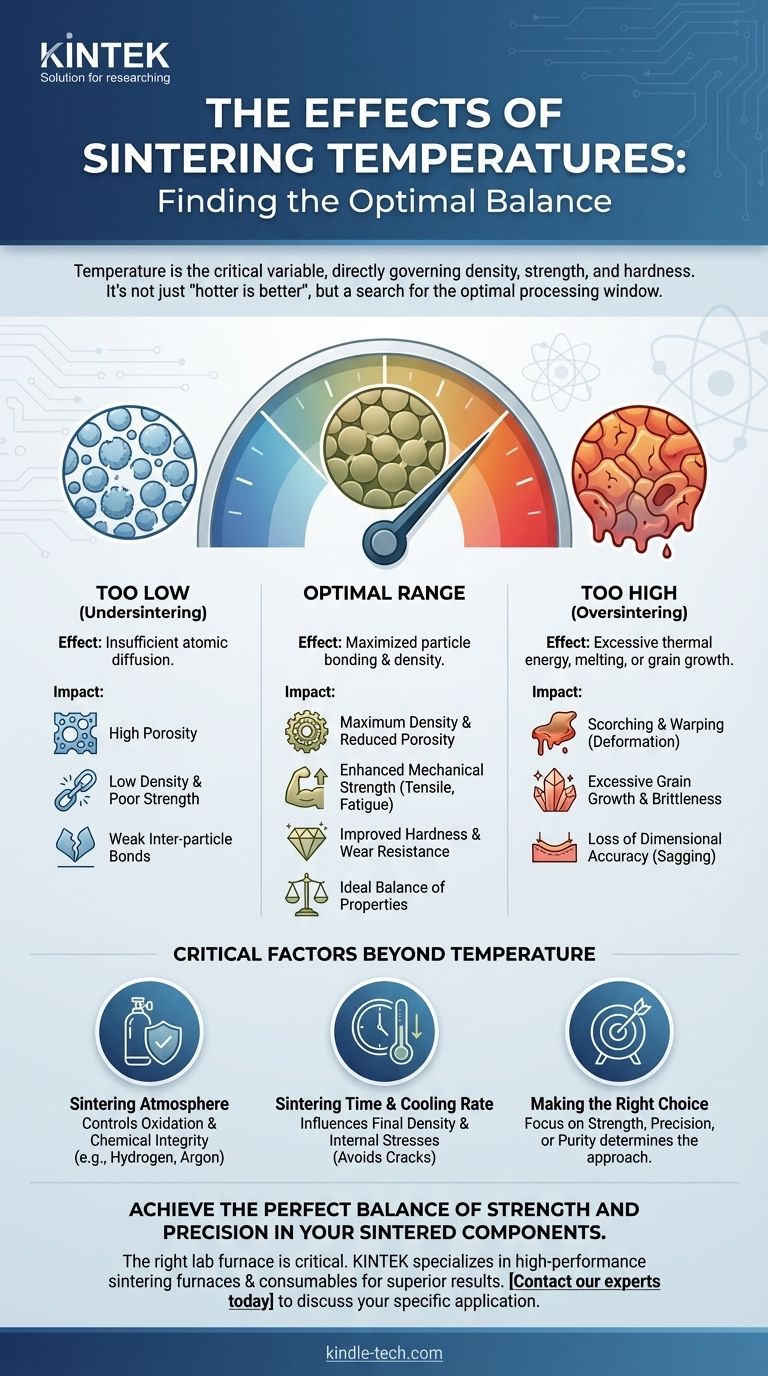
The single most critical variable in the sintering process is temperature. It directly governs the final density, strength, and hardness of a component by controlling how effectively individual particles bond together. While higher temperatures generally lead to improved mechanical properties, exceeding a material's optimal range can cause defects like scorching and warping, ultimately degrading the part's performance.
Sintering is fundamentally a balancing act. The goal is to find the precise temperature that maximizes particle bonding and density without introducing thermal distortion or other heat-induced defects. It is not a simple case of "hotter is better," but rather a search for the optimal processing window.

The Fundamental Goal: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Temperature is the engine that drives this transformation.
How Atomic Bonding Occurs
At the microscopic level, sintering involves particles of a powder fusing at their contact points. This process reduces the empty space, or porosity, between them.
Temperature as the Driving Force
Heat provides the necessary thermal energy for atoms to migrate, or diffuse, across the boundaries of the particles. As temperature increases, this atomic movement accelerates dramatically, leading to faster and more complete bonding.
How Temperature Governs Final Properties
Adjusting the sintering temperature is the primary method for controlling the final characteristics of the manufactured part.
Increasing Density and Reducing Porosity
The most direct effect of higher sintering temperature is an increase in the part's density. As atoms diffuse more rapidly, the voids between particles shrink and close, resulting in a more solid, less porous final structure.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength
A denser part with stronger inter-particle bonds is mechanically superior. Higher temperatures typically yield significant improvements in tensile strength, bending fatigue strength, and impact energy, as there are fewer pores to act as potential failure points.
Improving Hardness
Hardness is directly related to density. By eliminating porosity, the material becomes more resistant to surface indentation and abrasion, leading to a higher hardness value.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
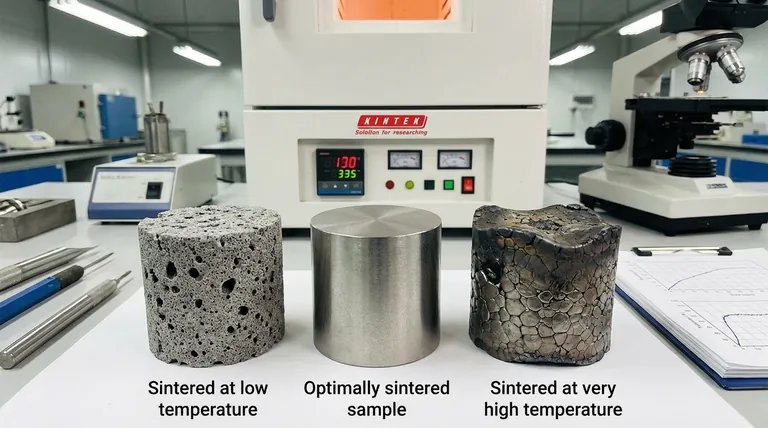
Choosing the right temperature is about navigating the fine line between optimal properties and process failure. Both undershooting and overshooting the ideal temperature have significant consequences.
The Risk of Oversintering (Too Hot)
Exceeding the optimal temperature can lead to several defects. The part may begin to melt, losing its shape, or experience excessive grain growth, which can paradoxically make the material more brittle. This can also lead to scorching, a defect that degrades the part's properties.
The Problem of Undersintering (Too Cold)
If the temperature is too low, atomic diffusion is insufficient. The particles will not bond effectively, leaving the final part with high porosity, low density, and poor mechanical strength.
Physical Deformation: Warping and Sagging
At elevated temperatures, the material softens before it is fully densified. During this stage, it is vulnerable to the forces of gravity and friction, which can cause the part to warp, sag, or otherwise lose its intended dimensional accuracy.
Critical Factors Beyond Temperature
While temperature is paramount, it does not act in isolation. A successful sintering process requires controlling other key variables that work in conjunction with heat.
The Sintering Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace has a profound impact. A reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen) or an inert atmosphere (like argon) is often used to prevent oxidation of the material at high temperatures, which is critical for maintaining its chemical integrity and properties.
Sintering Time and Cooling Rate
The duration the part is held at the peak temperature also influences the final density. A longer time can sometimes compensate for a slightly lower temperature. Furthermore, the rate of cooling is critical, as cooling too quickly can introduce internal stresses and cracks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sintering temperature depends entirely on the primary objective for your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: Aim for a temperature in the upper range recommended for your material, but implement careful monitoring to prevent physical deformation or scorching.
- If your primary focus is preserving precise dimensions: Use a more moderate temperature, potentially combined with a longer hold time, to minimize the risks of warping and sagging.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing oxidation: Your temperature choice must be paired with the correct protective atmosphere (e.g., vacuum, argon, nitrogen) to protect the part.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is an exercise in precise thermal control to achieve the ideal balance between density and integrity.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Effect | Impact on Final Part |
|---|---|
| Too Low (Undersintering) | High porosity, low density, poor mechanical strength |
| Optimal Range | Maximum density, high strength, improved hardness, strong particle bonds |
| Too High (Oversintering) | Scorching, warping, sagging, excessive grain growth, potential brittleness |
Achieve the perfect balance of strength and precision in your sintered components. The right lab furnace is critical for precise thermal control. KINTEK specializes in high-performance sintering furnaces and consumables for laboratories, helping you optimize temperature, atmosphere, and cooling rates for superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal sintering solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How to maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety
- Why do we use a muffle furnace? For Pure, Precise, and Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- What is the purpose of a muffle furnace? Achieve High-Purity Heating for Your Lab
- What is the primary use of furnace in the chemical industry? Master Thermal Treatment for Material Transformation



















