In electrical applications, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are primarily valued for their exceptional conductivity and mechanical strength at the nanoscale. Their most significant commercial use today is as a conductive additive in the electrodes of lithium-ion batteries. Beyond this, they are being integrated into advanced electronics as transistors and transparent films, and used to create novel conductive polymers and composites for a range of industries.
While often discussed in futuristic terms, the most significant electrical application of carbon nanotubes today is not as a primary conductor but as a critical additive. By creating a highly efficient conductive network within other materials, CNTs unlock higher performance in everything from batteries to advanced polymers.
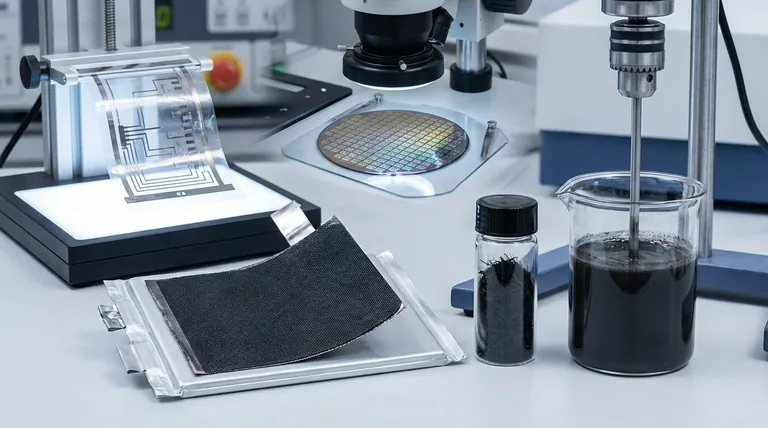

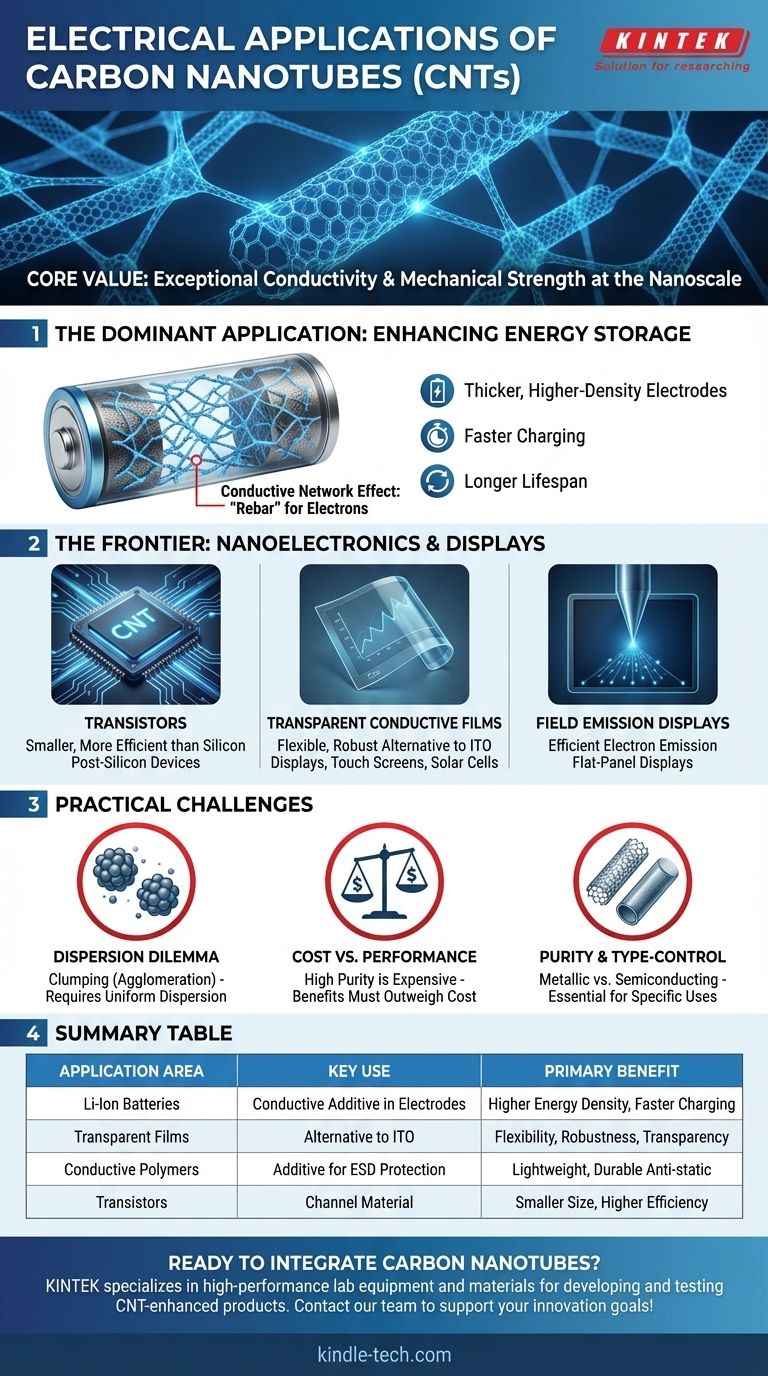
The Dominant Application: Enhancing Energy Storage
The most mature and widespread electrical application of CNTs is in energy storage, specifically within lithium-ion batteries. They are not the primary material but a powerful enabler.
How CNTs Revolutionize Lithium-Ion Batteries
Carbon nanotubes are introduced in small weight percentages into both the cathode and anode of a battery. They act as a conductive additive, fundamentally improving the electrode's ability to transport electrons.
This is a step-change improvement over traditional additives like carbon black, which require much higher loading levels for less effect and can impede ion flow.
The Conductive Network Effect
CNTs have an extremely high aspect ratio (they are very long and thin). This allows them to form a percolation network—a connected, three-dimensional web for electrons to travel through—at very low concentrations.
Think of it like adding steel rebar to concrete for strength; CNTs create a conductive "rebar" inside the electrode material, ensuring every part of it is electrically connected.
Enabling Thicker, Higher-Density Electrodes
A key bottleneck in battery design is that as an electrode gets thicker to hold more energy, its internal electrical resistance increases, hurting performance.
Because CNTs provide such superior conductivity, they allow manufacturers to design thicker electrodes without this performance penalty. This directly translates to batteries with higher energy density (more power in the same space).
Improving Performance and Lifespan
The robust, conductive network created by CNTs also provides mechanical stability to the electrode during charging and discharging cycles. This leads to better capacity retention, faster charging capabilities, and a wider operational temperature range.
The Frontier: Nanoelectronics and Displays
While batteries represent the largest market today, CNTs are a key material for next-generation electronics where silicon is approaching its physical limits.
Transistors for Next-Generation Chips
Individual semiconducting CNTs can be used to create transistors that are significantly smaller and more energy-efficient than their silicon counterparts.
Research focuses on integrating CNT-based devices with traditional microelectronics processing (CMOS), paving the way for ultra-large-scale integrated circuits that blend the benefits of both materials.
Transparent Conductive Films (TCFs)
A network of CNTs can be deposited as a thin film that is both electrically conductive and optically transparent.
This makes them a promising, flexible, and more robust alternative to brittle Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) in applications like flexible displays, touch screens, and solar cells.
Field Emission Displays
The sharp tips of carbon nanotubes emit electrons very efficiently when an electric field is applied. This property is harnessed in field emission applications, including novel types of flat-panel displays and cross-sectional SEM imaging.
Understanding the Practical Challenges
The remarkable properties of CNTs are not without implementation challenges. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for successful application.
The Dispersion Dilemma
By nature, individual nanotubes are strongly attracted to each other and tend to clump together (agglomerate). Poorly dispersed clumps act as defects rather than a conductive network.
Achieving uniform dispersion within a host material (like a battery slurry or a polymer) is the single most critical factor for unlocking their electrical benefits and is a major area of industrial know-how.
Cost vs. Performance
High-purity carbon nanotubes remain more expensive than traditional conductive additives. Their use is justified only when the performance gains—such as higher energy density or superior ESD protection—provide a competitive advantage that outweighs the added material cost.
Purity and Type-Control
CNTs can be metallic or semiconducting, single-walled or multi-walled. An application like a transparent film requires a different type of CNT than one used in a battery anode.
Manufacturing processes that can control these properties and produce them with high purity are essential for advanced electronics, but this adds complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right way to leverage CNTs depends entirely on your specific engineering objective.
- If your primary focus is improving battery performance: Use CNTs as a conductive additive to enhance electrode conductivity, enabling higher energy density and faster charging rates.
- If your primary focus is creating conductive plastics or composites: Introduce a low weight-percentage of CNTs to achieve reliable electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection or anti-static properties in polymers.
- If your primary focus is next-generation electronics or displays: Explore high-purity CNTs for creating robust transparent conductive films or as a channel material for post-silicon transistors.
Ultimately, leveraging carbon nanotubes effectively is about using their unique nanoscale properties to solve macro-level engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use of CNTs | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Conductive additive in electrodes | Higher energy density, faster charging, longer lifespan |
| Transparent Conductive Films | Alternative to ITO for displays & solar cells | Flexibility, robustness, transparency |
| Conductive Polymers/Composites | Additive for ESD protection | Lightweight, durable anti-static properties |
| Transistors & Nanoelectronics | Channel material for post-silicon devices | Smaller size, higher efficiency |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your next-generation electrical applications? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and materials, including advanced solutions for developing and testing CNT-enhanced products. Whether you're optimizing battery electrodes or creating flexible electronics, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your innovation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Magnetic Stirring Bar
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- What are the advantages of nickel foam? Unlock Superior Performance in Energy & Catalysis
- How to check the power of a lithium-ion battery? Master the difference between charge level and battery health.
- How will carbon nanotubes change the world? Powering the Green Revolution with Superior Materials
















