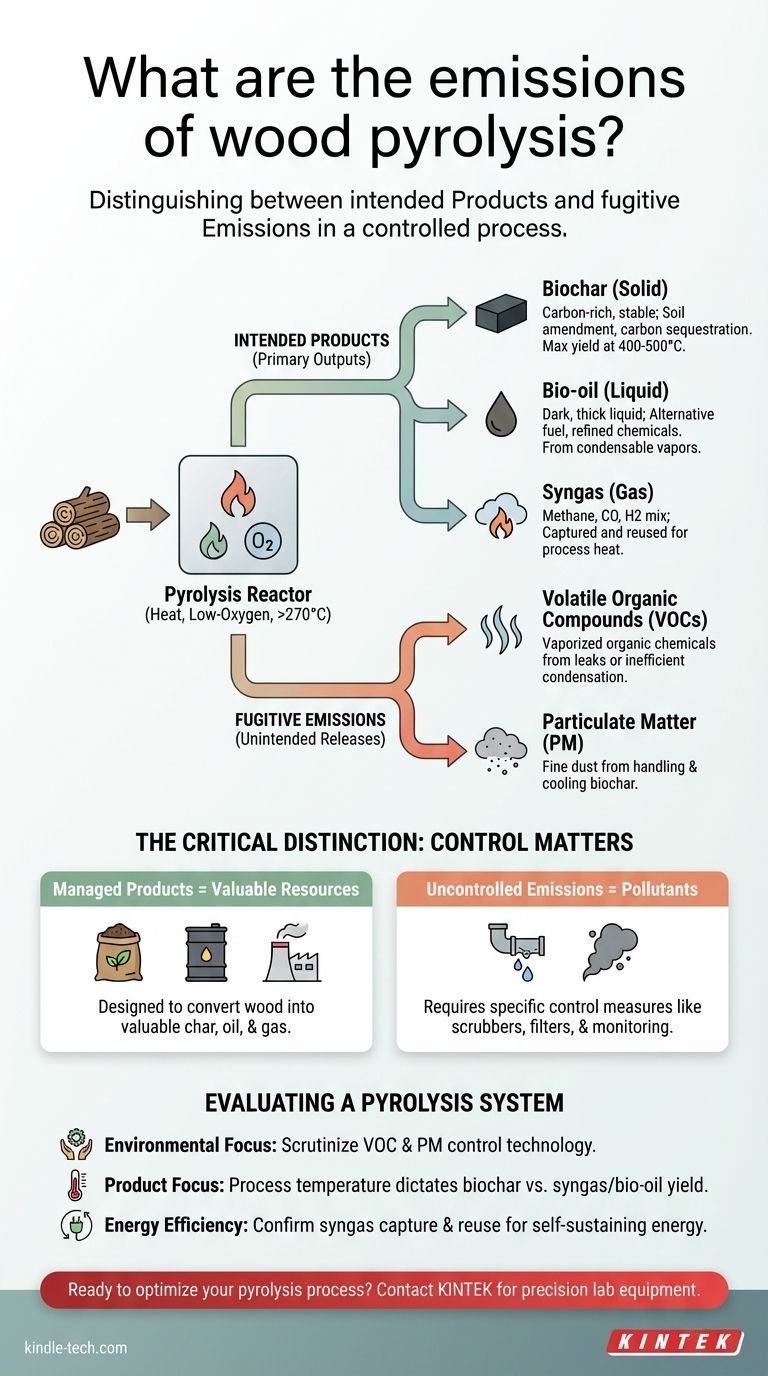
In practice, wood pyrolysis produces three primary outputs: biochar (a solid), bio-oil (a liquid), and syngas (a gas). These are the intended, valuable products of the process. However, the term "emissions" also includes unintended or fugitive releases of pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter, which must be managed by a properly designed system.
The core distinction to understand is between the desired products of pyrolysis and the unintended emissions. While the process is designed to convert wood into valuable char, oil, and gas, it can also release pollutants if not equipped with effective control and capture technologies.

Understanding the Primary Outputs of Pyrolysis
Wood pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes wood at high temperatures (typically above 270°C) in a low-oxygen environment. This controlled decomposition yields three distinct product streams rather than just ash from burning.
The Solid Product: Biochar
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after pyrolysis. It is analogous to charcoal but is often produced with specific agricultural or environmental goals in mind.
The yield of biochar is highly dependent on temperature. Lower process temperatures, generally in the 400–500°C range, maximize the production of this solid material. Its primary uses include soil amendment, carbon sequestration, and as a raw material for activated carbon.
The Liquid Product: Bio-oil
As the wood decomposes, a complex mixture of condensable vapors is produced. When cooled, these vapors form a dark, thick liquid known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
This liquid fraction contains water, wood vinegar, tars, and hundreds of organic compounds. It can be used as an alternative boiler fuel or further refined to produce transportation fuels and specialty chemicals.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
The third output is a stream of non-condensable gases, collectively known as synthesis gas or syngas.
This gas mixture primarily consists of methane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen. In most modern pyrolysis plants, this syngas is not released but is captured and used to provide the heat required to run the pyrolysis process itself, creating a partially self-sustaining energy loop.
The Critical Distinction: Products vs. Fugitive Emissions
A well-engineered pyrolysis system is designed to capture the three primary products cleanly. However, "emissions" in an environmental context refers to any substance released into the atmosphere, which requires specific control measures.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
The process generates VOCs, which are organic chemicals that can vaporize into the air. If the system has leaks or an inefficient condensation process for the bio-oil, these compounds can escape.
Particulate Matter
Particulate matter (fine dust) can become an emission source, particularly during the handling, cooling, and transport of the finished biochar. Effective filtration and dust management systems are required to prevent its release.
Process By-products
Gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor are inherent by-products of the chemical reactions occurring during pyrolysis. While water is harmless, the management of CO2 is a key part of the system's overall carbon footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Evaluating a pyrolysis system requires looking beyond its intended outputs and assessing how it manages its entire operational footprint. The technology's sustainability is defined by its efficiency and its ability to control emissions.
The Myth of "Zero Emissions"
No industrial process is truly free of emissions. The goal of a modern pyrolysis plant is to minimize and control fugitive emissions through robust engineering, not to eliminate them entirely. A system's environmental performance is a direct result of its design quality.
The Central Role of Control Systems
To be considered environmentally sound, a pyrolysis plant must have an effective emission control system. This includes components like scrubbers, filters, and continuous monitoring equipment to capture potential pollutants before they are released.
How Process Conditions Dictate Outputs
Operators can influence the product ratio by adjusting the process temperature. Higher temperatures (above 700°C) favor the production of syngas and bio-oil, while lower temperatures (400-500°C) maximize the yield of biochar. This choice has significant downstream effects on both the economics and the emission profile of the operation.
Evaluating a Pyrolysis System
To assess the true environmental impact of a wood pyrolysis operation, you must look at the complete system, from feedstock input to the management of all outputs.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Scrutinize the design of the emission control systems, specifically the technology used to manage VOCs and particulate matter.
- If your primary focus is maximizing a specific product: Understand that the process temperature is the key variable that determines the yield of either biochar, bio-oil, or syngas.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Confirm that the system captures and reuses its own syngas to power the process, which significantly reduces external energy demand.
Ultimately, a pyrolysis system's emissions are a direct reflection of its engineering quality and operational discipline.
Summary Table:
| Emission/Product | Type | Key Characteristics | Management/Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar | Solid Product | Carbon-rich, stable solid; yield maximized at 400-500°C | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration, activated carbon |
| Bio-oil | Liquid Product | Dark, thick liquid from condensed vapors; contains water, tars, and organics | Boiler fuel, refined for chemicals/transport fuels |
| Syngas | Gaseous Product | Mix of methane, CO, CO2, H2; non-condensable | Captured and reused to heat the pyrolysis process |
| VOCs | Fugitive Emission | Organic chemicals that vaporize; released via leaks or inefficient condensation | Controlled with scrubbers, filters, and monitoring systems |
| Particulate Matter | Fugitive Emission | Fine dust from biochar handling and cooling | Managed with dust control and filtration systems |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process with precision equipment? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're focusing on maximizing biochar yield, refining bio-oil, or ensuring environmental compliance with advanced emission control, our solutions help you achieve efficient, reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's pyrolysis needs and drive your sustainability goals forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis



















