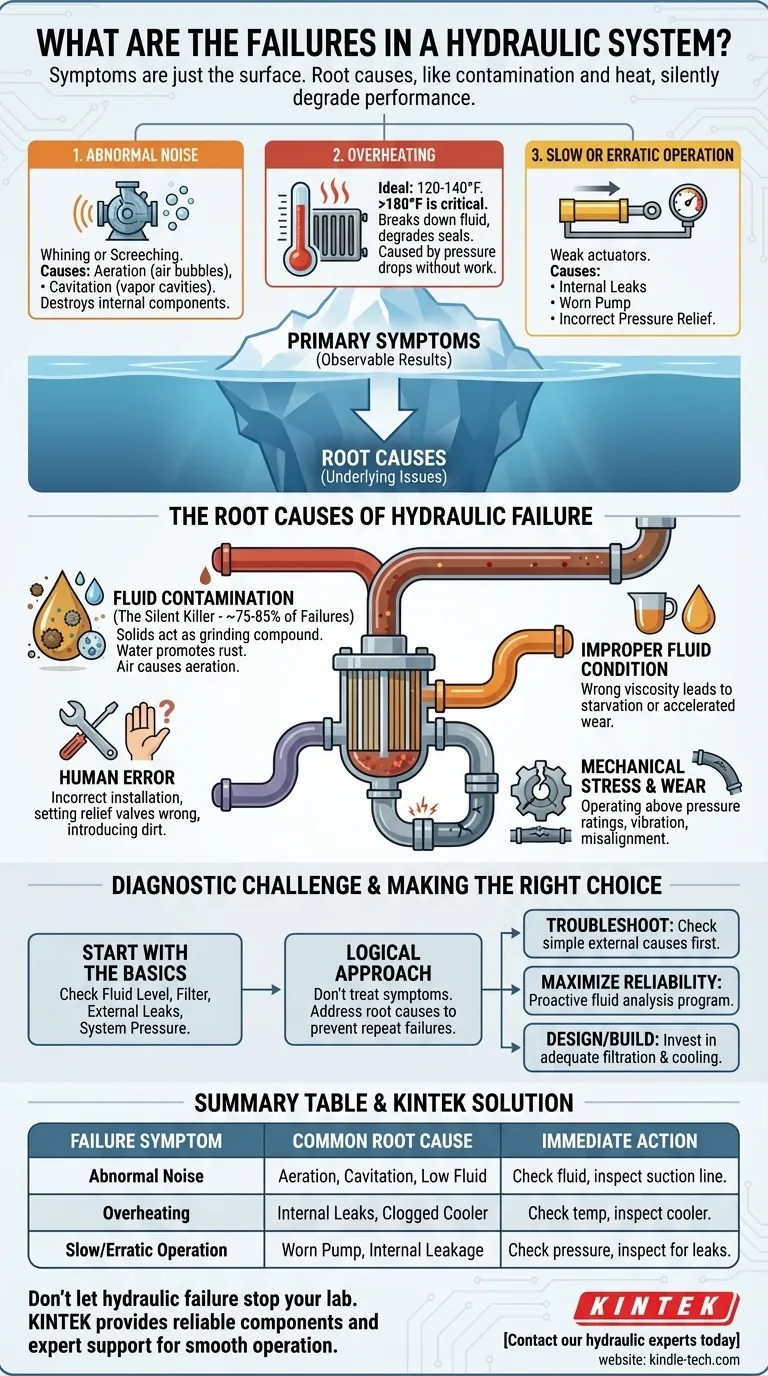
In practice, hydraulic system failures almost always manifest as one of three primary symptoms: abnormal noise, excessive heat, or incorrect speed and operation. These are not the root problems themselves, but are instead the observable results of underlying issues, most often related to the hydraulic fluid's condition and the presence of contamination.
The vast majority of hydraulic system failures are not sudden, catastrophic events. They are the predictable outcome of progressive issues, with fluid contamination and heat being the primary culprits that quietly degrade system performance until a noticeable failure occurs.
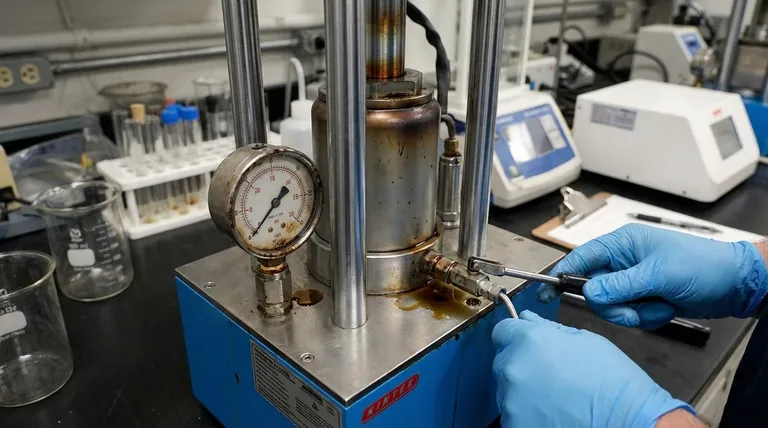

The Three Primary Failure Symptoms
When a hydraulic system begins to fail, it will communicate the problem through its performance. Understanding these symptoms is the first step in diagnosing the root cause.
1. Abnormal Noise
Unusual noise is a clear indicator that something is mechanically or hydraulically wrong. It is never normal and should be investigated immediately.
The most common sources of noise are aeration and cavitation. Aeration is caused by air bubbles being drawn into the system, often from a low fluid level or a leak on the pump's inlet side. Cavitation occurs when the pump starves for fluid, creating vapor cavities that collapse violently under pressure.
Both conditions produce a distinct whining or screeching sound and are extremely destructive, rapidly eroding internal pump components.
2. Overheating (Excessive Heat)
Heat is the enemy of a hydraulic system. An ideal operating temperature is typically between 120-140°F (50-60°C). Consistently running hotter than 180°F (82°C) is a serious problem.
Excessive heat breaks down the hydraulic fluid, reducing its lubricity and causing it to form sludge and varnish. It also degrades seals and hoses, leading to leaks.
Heat is generated anytime there is a significant pressure drop without useful work being done. This can be caused by a relief valve opening constantly, internal leakage in a pump or cylinder, or a clogged cooler.
3. Slow or Erratic Operation
This symptom points directly to a problem with either fluid flow or pressure. A system's actuators (cylinders and motors) will move slowly if they are not receiving the required volume of fluid (flow).
They may be weak or stall if the system cannot build the necessary pressure. Common causes include internal leaks where high-pressure fluid bypasses a component, a worn and inefficient pump, or an incorrectly set pressure relief valve.
The Root Causes of Hydraulic Failure
Symptoms tell you something is wrong, but the root causes are what you must fix to ensure long-term reliability. Nearly all failures can be traced back to one of these fundamental issues.
Fluid Contamination: The Silent Killer
This is the single greatest cause of hydraulic system failure, responsible for an estimated 75-85% of all problems. Contaminants come in three forms: solids (dirt, metal particles), liquids (water), and gases (air).
These particles act like a liquid grinding compound, causing abrasive wear on the tight tolerances inside pumps, valves, and actuators. Water contamination promotes rust and fluid breakdown, while air leads to the destructive forces of aeration.
Improper Fluid Condition
Using the wrong type of hydraulic fluid or failing to maintain it is a direct path to failure. The fluid's viscosity (its resistance to flow) is critical.
If viscosity is too high, the pump may starve, leading to cavitation. If it's too low (often due to excessive heat), it won't provide an adequate lubricating film, leading to accelerated component wear.
Mechanical Stress and Wear
Even in a clean system, components eventually wear out. However, this process is dramatically accelerated by operational stress.
Operating a system above its designed pressure rating, subjecting components to excessive vibration or shock, or mechanical misalignment can all cause premature failure.
Human Error
A significant number of failures are introduced during maintenance or repair activities. Incorrectly installing a component, failing to properly set a relief valve, or introducing dirt into the system during a filter change are common examples.
Understanding the Diagnostic Challenge
Diagnosing a hydraulic system requires a logical approach. Jumping to conclusions is a common and costly mistake.
A Single Symptom, Multiple Causes
It is critical to understand that a symptom like "slow operation" does not have one single cause. It could be a worn pump, an internal leak in a cylinder, a relief valve set too low, or even a partially clogged suction strainer.
The Danger of Treating Symptoms, Not Causes
Replacing a failed component without addressing the root cause is a recipe for repeat failure. If a pump fails due to contamination, simply installing a new pump without flushing the system and improving filtration will ensure the new pump also fails prematurely.
Overlooking the Basics
Before disassembling complex components, always start with the simplest checks. Verify the fluid level in the reservoir, check the filter condition indicator, look for obvious external leaks, and check system pressure with a gauge. These basic steps can often solve the problem or point you directly to the cause.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to hydraulic system failure should be dictated by your primary objective, whether it's immediate troubleshooting or long-term prevention.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a current problem: Start by identifying the main symptom (noise, heat, or speed) and then systematically check the simple, external causes first before suspecting major component failure.
- If your primary focus is maximizing reliability: Implement a proactive maintenance program centered on fluid cleanliness. Regular fluid analysis is the most effective tool for preventing unplanned downtime.
- If your primary focus is designing or building a system: Invest in adequate filtration and cooling from the start. Sizing these components correctly for the application is far cheaper than dealing with the consequences of failure later.
Ultimately, understanding that hydraulic fluid is the lifeblood of the system is the key to achieving consistent performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Failure Symptom | Common Root Cause | Immediate Action |
|---|---|---|
| Abnormal Noise | Aeration, Cavitation, Low Fluid Level | Check fluid level, inspect suction line for leaks |
| Overheating | Internal Leaks, Clogged Cooler, Relief Valve Stuck Open | Check fluid temperature, inspect cooler, verify relief valve setting |
| Slow/Erratic Operation | Worn Pump, Internal Leakage, Low System Pressure | Check system pressure with a gauge, inspect for internal leaks |
Don't let hydraulic failure stop your lab. The symptoms of noise, heat, and slow operation often point to deeper issues like fluid contamination. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable hydraulic components and expert support to keep your systems running smoothly and efficiently.
Contact our hydraulic experts today to discuss your specific application and ensure maximum uptime for your laboratory operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- Why is a hydraulic press used for pre-deformation treatment? Enhance Coating Hardness & Thermal Stability
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic hot press play in rice husk-based composite boards? Achieve Structural Density
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for nanocomposites? Ensure Precise Material Characterization
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.














