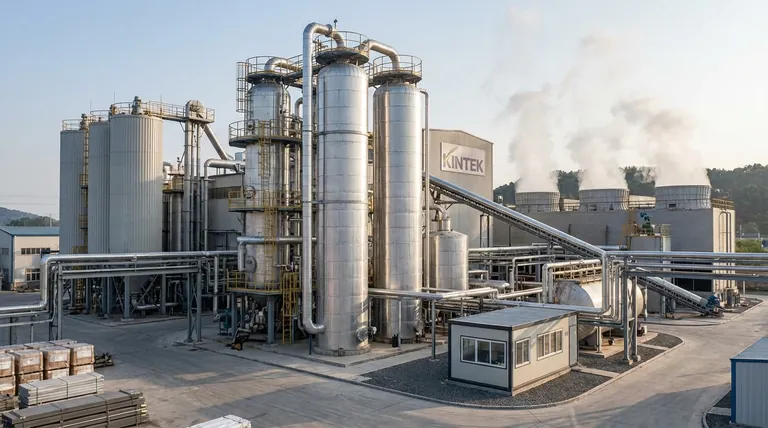
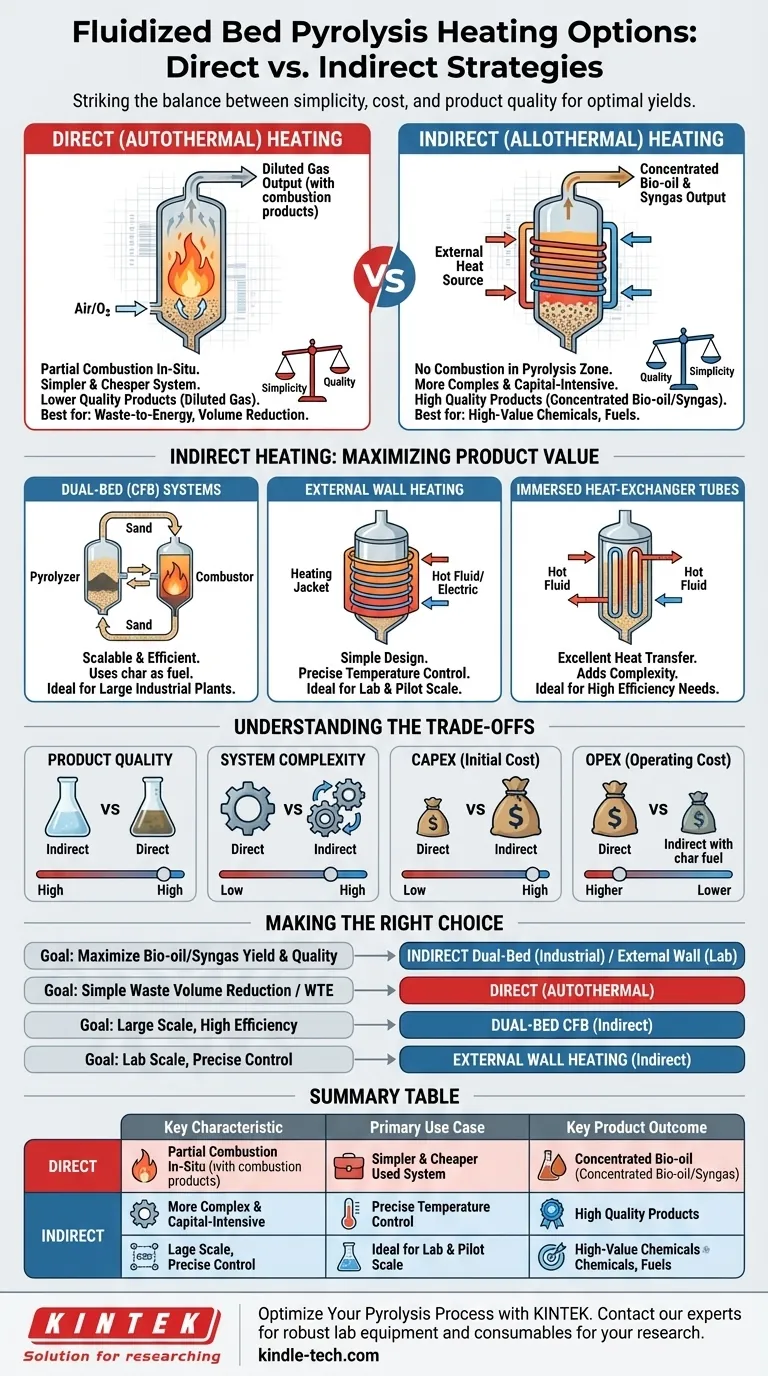
In short, you can heat a fluidized bed for pyrolysis using two primary strategies: direct heating, where a small amount of the feedstock is combusted inside the reactor, or indirect heating, where heat is supplied from an external source without combustion in the pyrolysis zone. Indirect methods are generally preferred for producing high-quality pyrolysis oil and gas, as they prevent dilution of the product with combustion fumes.
The central decision in heating a pyrolysis fluidized bed is a trade-off between process simplicity and product quality. Direct heating is simpler and cheaper but degrades product value, while indirect heating is more complex but maximizes the yield and quality of your desired outputs.

The Two Fundamental Heating Strategies
At its core, the choice of heating method dictates the chemical environment inside your reactor and, therefore, the quality of your final products. The fundamental distinction is whether the heat is generated inside or outside the pyrolysis reaction zone.
Direct (Autothermal) Heating
Direct heating, also known as autothermal pyrolysis, involves introducing a small, controlled amount of an oxidizing agent (typically air or oxygen-enriched air) directly into the fluidized bed.
This process intentionally combusts a portion of the feedstock or the pyrolysis vapors in situ. The heat released from this partial oxidation is what drives the endothermic pyrolysis reactions for the rest of the feedstock.
Indirect (Allothermal) Heating
Indirect heating, or allothermal pyrolysis, keeps the pyrolysis environment completely free of oxygen. Heat is generated externally and then transferred into the fluidized bed.
This separation ensures that the only reactions occurring are related to thermal decomposition (pyrolysis), not combustion. This results in a cleaner, more concentrated, and higher-value product stream.
Indirect Heating: Methods for Maximizing Product Value
Because preserving product quality is often the primary goal, indirect heating methods are more common in applications targeting high-value chemicals or fuels.
Method 1: Dual-Bed (Circulating Fluidized Bed) Systems
This is one of the most effective and scalable industrial methods. The system uses two separate reactors: a pyrolyzer and a combustor.
A solid heat carrier, like sand, is fluidized in the pyrolyzer with the feedstock. The hot sand transfers its heat, driving pyrolysis. The sand, now coated with residual char, is then circulated to the combustor. In the combustor, air is used to burn the char off the sand, reheating it before it is sent back to the pyrolyzer.
Method 2: External Wall Heating
For smaller-scale or pilot reactors, heat can be transferred through the walls of the reactor vessel. This is often called a jacketed reactor.
The heat source can be electric resistance heaters wrapped around the vessel or a jacket through which hot flue gas or a thermal fluid (like molten salt) is circulated. While simple, this method becomes less efficient as the reactor size increases due to an unfavorable surface-area-to-volume ratio.
Method 3: Immersed Heat-Exchanger Tubes
In this design, tubes are placed directly inside the fluidized bed itself. A very hot fluid, such as combustion gas or molten salt, is passed through these tubes.
The excellent heat transfer characteristics of a fluidized bed make this an efficient way to deliver heat. However, it adds mechanical complexity and potential failure points within the highly abrasive and corrosive reactor environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating method is an engineering decision with significant consequences for cost, complexity, and final product.
Product Quality vs. System Complexity
Direct heating is simple but produces a low-calorific-value gas diluted with nitrogen (if using air) and carbon dioxide. This makes downstream upgrading or use as a chemical synthon difficult.
Indirect heating produces a high-quality, energy-dense syngas and maximizes bio-oil yield, but at the cost of a more complex and capital-intensive system (e.g., a dual-bed setup).
Capital Cost (CAPEX) vs. Operating Cost (OPEX)
A direct-heated system has a significantly lower initial CAPEX because it doesn't require a separate furnace, heat exchanger, or complex circulation loop.
An indirect dual-bed system has a very high CAPEX but can have a lower OPEX if the char by-product provides all the necessary process heat, eliminating the need for an external fuel source like natural gas.
Feedstock Flexibility and Scalability
Dual-bed systems are exceptionally flexible, as they are designed to utilize the low-value char as their internal fuel source. They are also highly scalable and are the preferred method for large, industrial plants.
Direct heating scales reasonably well, but managing uniform partial combustion can become challenging in very large reactors. External wall heating does not scale well and is generally limited to pilot or small commercial operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your optimal heating strategy depends entirely on the economic and technical goals of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the yield and quality of bio-oil or syngas: Indirect (allothermal) heating is the only viable path, with dual-bed systems being the standard for industrial scale.
- If your primary focus is simple waste volume reduction or waste-to-energy with minimal capital investment: Direct (autothermal) heating offers a simpler, lower-cost pathway to generate a combustible gas.
- If you are operating at a very large industrial scale and require high thermal efficiency: A dual-bed circulating fluidized bed (CFB) system that uses the product char for fuel is the most efficient and robust solution.
- If you are at the lab or pilot scale and need precise, uniform temperature control for research: An externally heated (jacketed) indirect reactor provides the most stable and easily controlled environment.
Ultimately, aligning your heating strategy with your specific product goals and economic constraints is the key to designing a successful pyrolysis process.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Key Characteristic | Primary Use Case | Key Product Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct (Autothermal) | Partial combustion of feedstock inside reactor | Waste-to-energy, simple volume reduction | Low-calorific-value gas, diluted with combustion gases |
| Indirect (Allothermal) | Heat supplied externally; oxygen-free pyrolysis zone | High-quality bio-oil/syngas production, chemical synthesis | High-quality, concentrated bio-oil and syngas |
| → Dual-Bed System | Circulating solid heat carrier (e.g., sand) between reactors | Large-scale industrial applications, high efficiency | Maximized yield and quality; uses char for process heat |
| → External Wall Heating | Heat transferred through reactor walls/jacket | Lab & pilot-scale R&D, precise temperature control | Stable, controlled environment for research |
| → Immersed Tubes | Heat exchanger tubes inside the fluidized bed | Applications requiring high heat transfer efficiency | Efficient heating; adds mechanical complexity |
Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right heating method is critical to the success of your pyrolysis project, whether you're focused on high-value bio-oil or efficient waste conversion. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to support your research and development in thermal processes like pyrolysis.
Our experts can help you select the right systems to test and scale your heating strategies, ensuring you achieve the product quality and operational efficiency you need.
Ready to enhance your pyrolysis R&D? Contact our team today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can bring precision and reliability to your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output















