At its core, induction heating is an advanced, non-contact method for rapidly and precisely heating electrically conductive materials. Its primary industrial applications include the surface hardening of machine components like gears and shafts, the pre-heating of metal billets for forging or extrusion, and the high-purity melting of metals in foundries.
Induction heating's value in industry stems from its ability to deliver precise, localized, and rapid heat directly within a material. This control results in superior product quality, higher process speeds, and greater energy efficiency compared to traditional furnace-based methods.
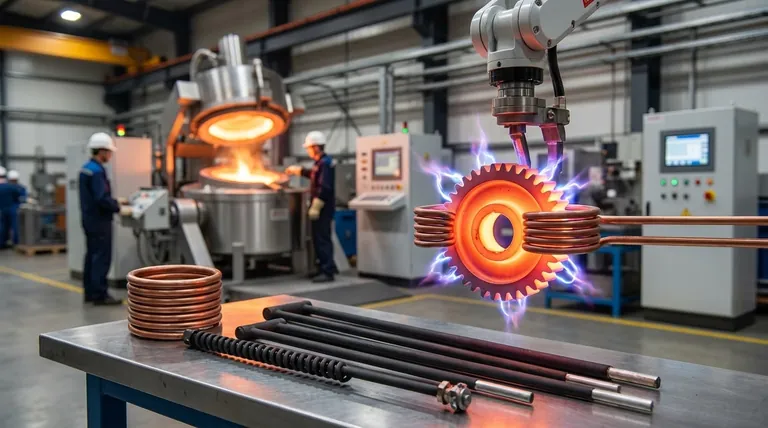

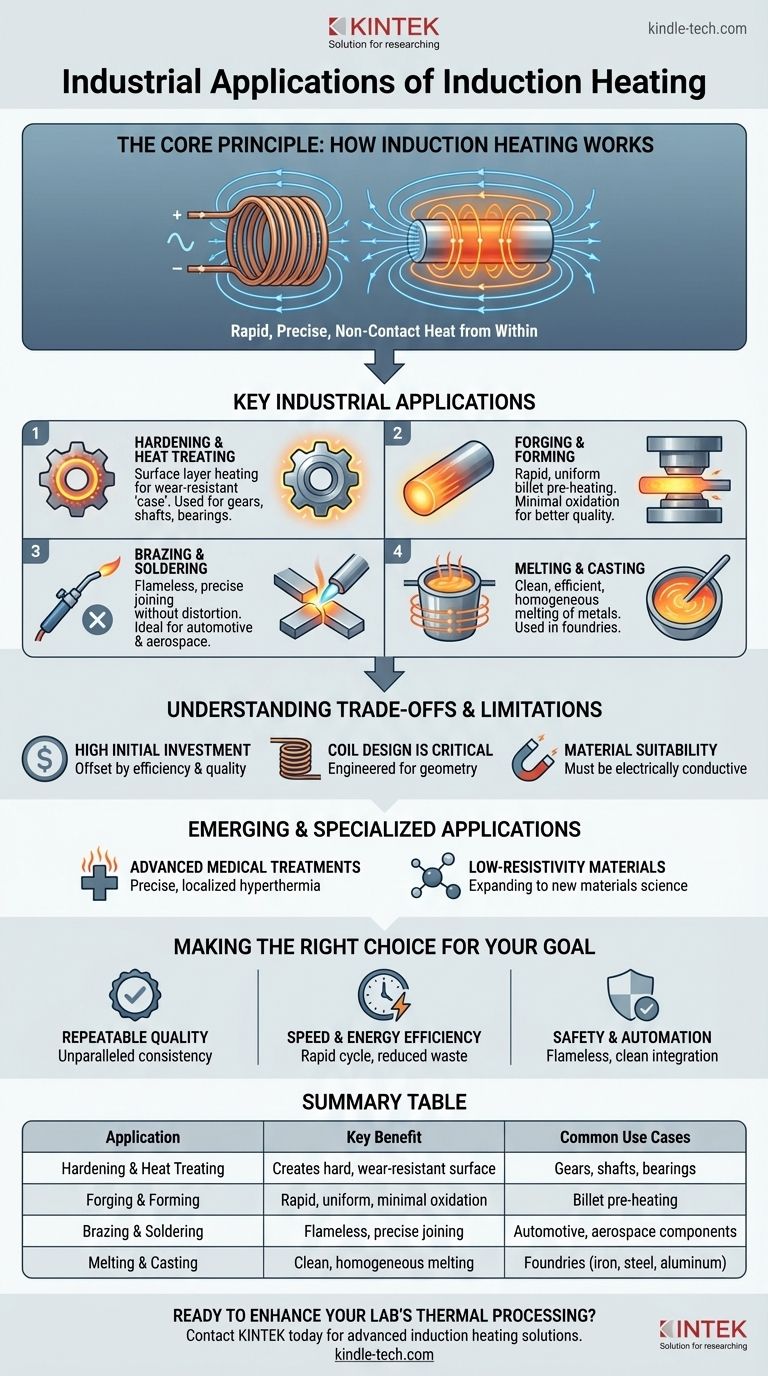
The Core Principle: How Induction Heating Works
Induction heating is fundamentally a process of transforming electrical energy into thermal energy without any physical contact. It operates on the principles of electromagnetism.
An Alternating Magnetic Field
An induction coil, typically made of copper tubing, is energized by a high-frequency alternating current (AC). This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around and within the workpiece placed near the coil.
Generating Internal Heat
This magnetic field induces circulating electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the conductive workpiece. The material's natural resistance to the flow of these currents generates immense and instantaneous heat from within. For magnetic materials like steel, additional heat is generated through a process called hysteresis loss.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique characteristics of induction heating—speed, precision, and control—make it indispensable across a range of demanding industrial processes.
Hardening and Heat Treating
This is one of the most common applications. By heating only the surface layer of a part, induction can create a hard, wear-resistant "case" while leaving the core tough and ductile. This is critical for parts like gears, bearings, axles, and shafts that experience high stress and wear.
Forging and Forming
Before metal can be forged, pressed, or extruded, it must be heated to a malleable temperature. Induction rapidly heats entire metal billets through to their core with minimal oxidation (scale), improving the final product quality and reducing material waste compared to gas furnaces.
Brazing and Soldering
Induction provides a flameless, repeatable method for joining components. It precisely heats the joint area, allowing brazing or soldering alloys to flow and create a strong bond without overheating or distorting the surrounding parts. This is widely used in manufacturing automotive and aerospace components.
Melting and Casting
In foundries, induction furnaces are used to melt metals ranging from iron and steel to aluminum, copper, and precious metals. The process is clean, contained, and efficient. The stirring action created by the magnetic field also ensures a homogenous, high-quality molten alloy before casting.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to its successful implementation.
High Initial Investment
The initial capital cost for induction heating systems, including the power supply and custom coils, is typically higher than that of conventional furnaces. However, this is often offset by lower operating costs, higher throughput, and improved part quality.
Coil Design is Critical
An induction system's effectiveness is entirely dependent on the coil design. The coil must be carefully engineered to match the geometry of the part to ensure uniform and efficient heating. This often requires specialized expertise.
Material Suitability
Induction heating only works on materials that are electrically conductive. It is highly effective for metals like steel, iron, copper, and aluminum but cannot be used to directly heat non-conductive materials like plastics, ceramics, or glass.
Emerging and Specialized Applications
Enabled by modern solid-state power supplies, the core technology of induction is expanding beyond traditional heavy industry.
Advanced Medical Treatments
The ability to generate precise, localized heat is being explored for medical uses. This includes hyperthermia treatments for cancer therapy, where heat is used to target and damage biological tissues with high precision.
Low-Resistivity Materials
Technological advancements are also expanding induction's use for heating materials with very low electrical resistance. This opens up new possibilities in materials science and specialized manufacturing processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating method depends entirely on your process priorities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable quality: Induction's precise control over heating depth and temperature ensures unparalleled consistency from part to part.
- If your primary focus is process speed and energy efficiency: The rapid, on-demand heating cycle of induction dramatically reduces startup times and energy waste compared to always-on furnaces.
- If your primary focus is workplace safety and automation: The flameless, clean nature of induction heating improves air quality and integrates seamlessly into automated production lines.
Ultimately, induction heating is a modern thermal processing tool that offers a superior level of control for demanding industrial challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening & Heat Treating | Creates a hard, wear-resistant surface | Gears, shafts, bearings |
| Forging & Forming | Rapid, uniform heating with minimal oxidation | Billet pre-heating for forging/extrusion |
| Brazing & Soldering | Flameless, precise joining without distortion | Automotive, aerospace components |
| Melting & Casting | Clean, homogeneous melting of metals | Foundries for iron, steel, aluminum, copper |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems, to help you achieve superior product quality, higher throughput, and greater energy efficiency. Our solutions are tailored for laboratories focused on materials testing, metallurgy, and R&D.
Contact us today to discuss how our induction heating technology can meet your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes

















