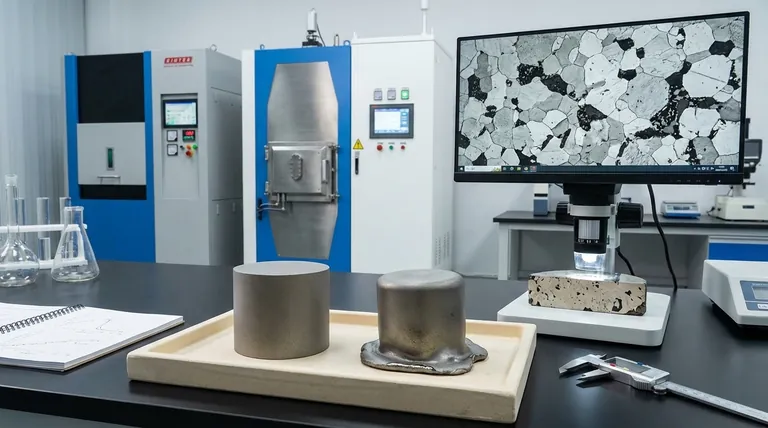
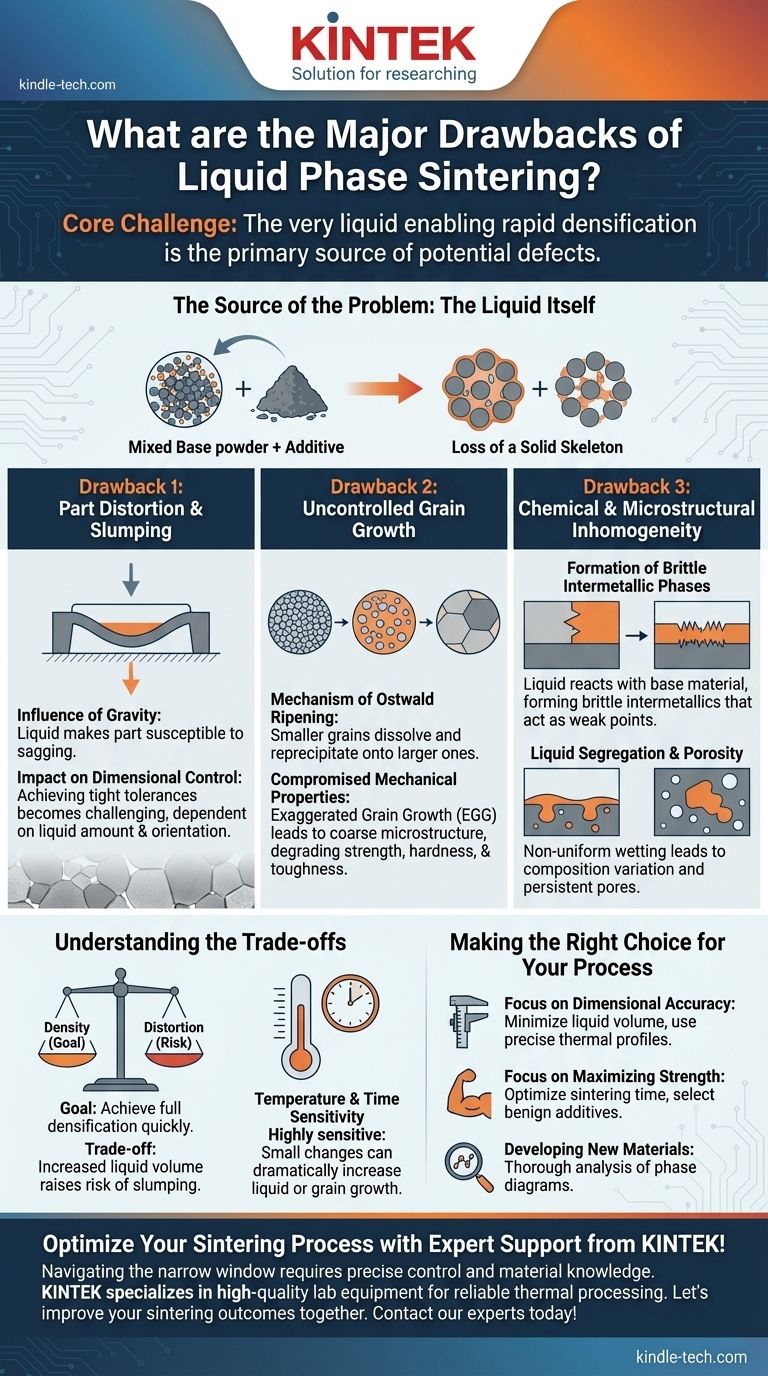
While highly effective for densification, the liquid phase sintering process introduces significant risks that are not present in solid-state methods. The primary drawbacks are the potential for part distortion or slumping, uncontrolled grain growth that degrades mechanical properties, and chemical reactions that can form brittle, undesirable phases within the final component.
The core challenge of liquid phase sintering is that the very same liquid that enables rapid densification is also the primary source of potential defects. Successfully using this process depends entirely on precisely controlling the amount, distribution, and behavior of this liquid phase.

The Source of the Problem: The Liquid Itself
To understand the drawbacks, we must first understand the mechanism. Liquid phase sintering involves mixing a base powder with a small amount of an additive that has a lower melting point.
How the Liquid Phase Works
When heated, this additive melts before the primary material, creating a liquid that wets the solid particles. This liquid pulls the particles together through capillary action, fills the pores between them, and provides a fast path for atomic diffusion, leading to rapid densification at lower temperatures than solid-state sintering.
The Loss of a Solid Skeleton
The critical moment occurs when the liquid forms. The previously rigid structure of packed powder particles is now partially supported by a liquid. This loss of a rigid, solid skeleton is the root cause of the major drawbacks.
Drawback 1: Part Distortion and Slumping
The most immediate risk in liquid phase sintering is the loss of the component's shape.
The Influence of Gravity
Once the liquid is present, the part is susceptible to gravitational forces. If too much liquid forms or if the solid particles are not arranged to provide sufficient support, the component can sag, slump, or distort under its own weight.
Impact on Dimensional Control
This makes achieving tight dimensional tolerances a significant challenge. The final shape becomes highly dependent on the precise amount of liquid, heating rates, and even the part's orientation in the furnace.
Drawback 2: Uncontrolled Grain Growth
The liquid provides a high-speed pathway for material transport, which can lead to rapid and sometimes undesirable changes in the microstructure.
The Mechanism of Ostwald Ripening
This process, known as Ostwald ripening, causes larger grains to grow at the expense of smaller grains, which dissolve into the liquid and reprecipitate onto the larger ones.
Compromised Mechanical Properties
If this process is not controlled, it can lead to exaggerated grain growth (EGG), where a few grains become abnormally large. This creates a coarse, non-uniform microstructure that can severely degrade mechanical properties like strength, hardness, and fracture toughness.
Drawback 3: Chemical and Microstructural Inhomogeneity
The interaction between the liquid additive and the solid base material is a complex chemical process that can produce unintended consequences.
Formation of Brittle Intermetallic Phases
The liquid can react with the solid particles to form new chemical phases, known as intermetallics. These phases are often brittle and can act as internal weak points, compromising the integrity of the final part. Careful material selection based on phase diagrams is essential to avoid this.
Liquid Segregation and Porosity
If the liquid does not uniformly "wet" the solid particles, it can pool in certain areas, a phenomenon called segregation. Upon cooling, these pools solidify with a different composition than the rest of the matrix. In other areas, poor wetting can leave behind persistent pores, defeating the goal of full densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Success with liquid phase sintering requires navigating a narrow processing window and balancing competing factors.
Density vs. Distortion
The goal is to use enough liquid to achieve full densification quickly. However, increasing the liquid volume fraction also increases the risk of slumping and distortion. This is the central trade-off of the process.
Temperature and Time Sensitivity
The process is extremely sensitive to temperature and time. A slightly higher temperature or a longer hold time can dramatically increase the amount of liquid or the extent of grain growth, pushing a successful process into a failed one.
Material Compatibility Is Non-Negotiable
The choice of the liquid-forming additive is critical. It must melt at the right temperature, wet the solid particles effectively, and, most importantly, not form brittle phases upon reacting with the base material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
You must evaluate these drawbacks in the context of your specific material and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: Prioritize minimizing the liquid volume fraction and implementing precise, repeatable thermal profiles to prevent slumping.
- If your primary focus is maximizing mechanical strength: Concentrate on preventing exaggerated grain growth by optimizing the sintering time and carefully selecting additives known to have benign interactions with the base material.
- If you are developing a new material system: Your first step must be a thorough analysis of the relevant phase diagrams to predict and avoid the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds.
By understanding these potential drawbacks, you can strategically control the liquid phase to harness its benefits while mitigating its inherent risks.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Primary Cause | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Part Distortion/Slumping | Loss of rigid solid skeleton due to liquid formation | Poor dimensional control and tolerances |
| Uncontrolled Grain Growth | Ostwald ripening facilitated by liquid phase | Degraded strength, hardness, and toughness |
| Chemical Inhomogeneity | Reaction between liquid additive and base material | Formation of brittle intermetallic phases |
Optimize your sintering process with expert support from KINTEK!
Liquid phase sintering is a powerful but complex technique. Navigating the narrow processing window between achieving full densification and avoiding defects like slumping or grain growth requires precise control and deep material knowledge. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for reliable thermal processing. Our expertise can help you select the right materials and fine-tune your parameters to mitigate these risks and achieve consistent, high-performance results.
Let's improve your sintering outcomes together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control



















