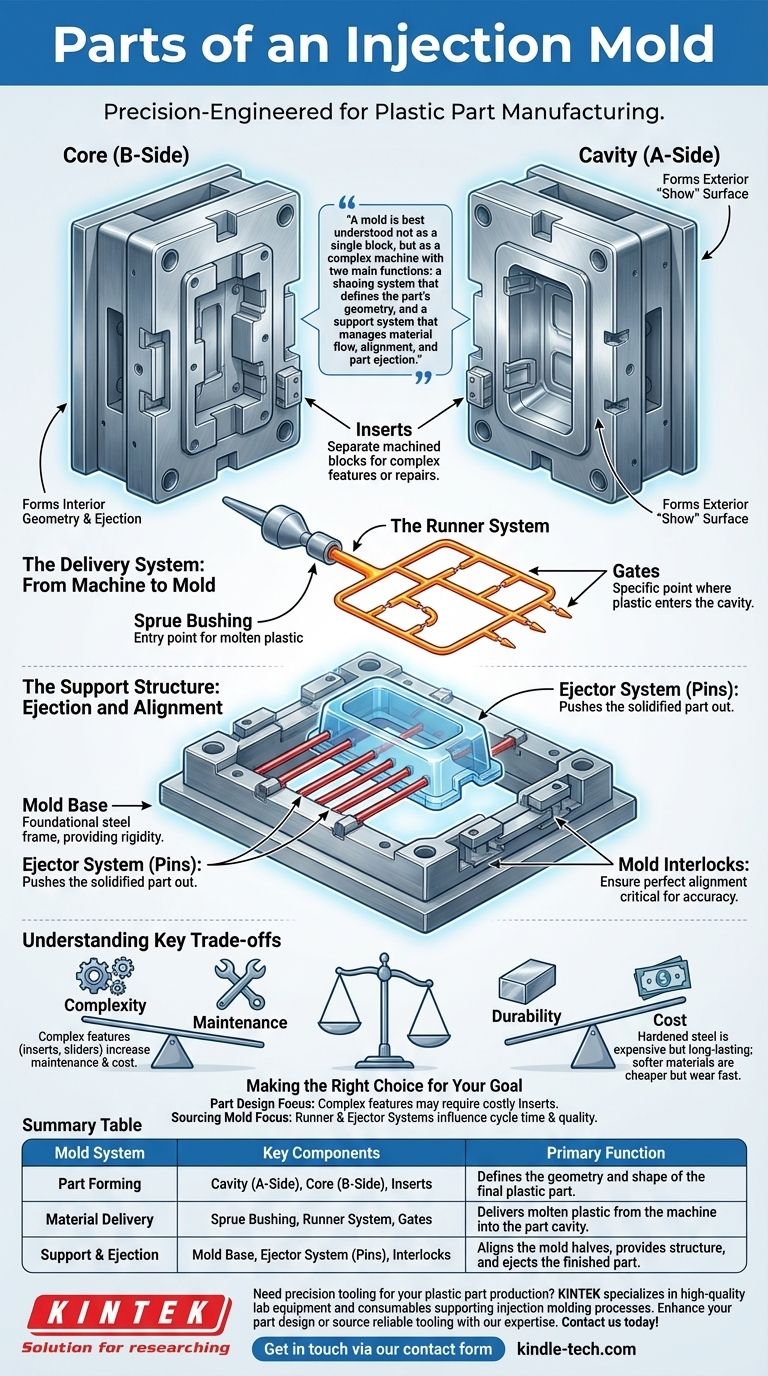
At its core, an injection mold is a precision-engineered steel tool composed of two primary halves—the Core and the Cavity—which form the negative space of the final plastic part. These are housed within a standardized Mold Base and supported by several critical systems that deliver molten plastic, cool the part, and safely eject it.
A mold is best understood not as a single block, but as a complex machine with two main functions: a shaping system that defines the part's geometry, and a support system that manages material flow, alignment, and part ejection.

The Heart of the Mold: Forming the Part
The components that directly shape the molten plastic are the most critical for determining the final part's quality, appearance, and function. These parts are located on the two halves of the mold.
The Cavity (A-Side)
The Cavity is the half of the mold that typically forms the exterior, or "show" surface, of a part. It is often the less complex half and is usually mounted on the stationary platen of the molding machine.
The Core (B-Side)
The Core is the other half of the mold that forms the interior geometry of the part. It is typically mounted on the moving platen and also contains the ejector system needed to push the finished part out.
Inserts
Inserts are separate, machined blocks of steel that are fitted into pockets within the core or cavity. They are used to create complex features, facilitate easier repairs, or allow for different versions of a part to be made from the same base mold.
The Delivery System: From Machine to Mold
Before the plastic can be shaped, it must travel from the injection molding machine into the cavity. This is handled by a network of channels.
Sprue Bushing
The Sprue Bushing is the entry point for the molten plastic. It is a hardened steel nozzle that seats against the nozzle of the molding machine's barrel, creating a sealed path for material to enter the mold.
The Runner System
The Runner System is a series of channels machined into the mold face that distributes the plastic from the sprue to the individual part cavities. The design of the runner is critical for ensuring all cavities fill evenly.
Gates
The Gate is the specific point where the plastic leaves the runner and enters the part cavity. The size, type, and location of the gate have a major impact on the part's final cosmetic appearance and structural integrity.
The Support Structure: Ejection and Alignment
These components do not shape the plastic but are essential for the mold to function cycle after cycle with high precision.
The Mold Base
The Mold Base is the foundational steel frame that holds the core, cavity, and all other components together. It acts as the chassis, providing rigidity and the mounting points for installation into the molding machine.
The Ejector System
The Ejector System is the mechanism that pushes the solidified part out of the core half of the mold after it opens. Its most common components are Ejector Pins, which are round rods that press against the part to force its release.
Mold Interlocks
Interlocks are precision-machined features on each mold half that engage as the mold closes. They ensure perfect alignment between the core and cavity, which is critical for maintaining consistent wall thickness and part accuracy.
Understanding Key Trade-offs
A mold's design is a series of engineering compromises that balance performance, longevity, and cost.
Complexity vs. Maintenance
Adding components like inserts, sliders for undercuts, or complex hot runner systems enables more intricate part designs. However, each addition increases the initial cost and introduces a potential point of failure or required maintenance.
Durability vs. Cost
The choice of steel is a primary cost driver. A mold made from softer pre-hardened steel or aluminum is much cheaper and faster to machine but will wear out quickly. A fully hardened tool steel mold is expensive but can produce millions of parts reliably.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these components empowers you to make better decisions whether you are designing a product or sourcing tooling.
- If your primary focus is part design: Pay close attention to how your geometry will be formed by the Core and Cavity, as complex features may require costly Inserts or side-actions.
- If your primary focus is sourcing a mold: Scrutinize quotes to understand the proposed Runner System and Ejector System, as these heavily influence cycle time and part quality.
Ultimately, viewing the mold as an integrated system of specialized components is the first step toward successful plastic part manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Mold System | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Part Forming | Cavity (A-Side), Core (B-Side), Inserts | Defines the geometry and shape of the final plastic part. |
| Material Delivery | Sprue Bushing, Runner System, Gates | Delivers molten plastic from the machine into the part cavity. |
| Support & Ejection | Mold Base, Ejector System (Pins), Interlocks | Aligns the mold halves, provides structure, and ejects the finished part. |
Need precision tooling for your plastic part production?
KINTEK specializes in supplying the high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support advanced manufacturing processes like injection molding. Whether you're optimizing your part design or sourcing reliable tooling, our expertise can help you achieve superior results and efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and manufacturing needs. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Stirring Bar Recovery Rod
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Performance Lab Homogenizer for Pharma Cosmetics and Food R&D
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
People Also Ask
- What are the two structures of molds? Understanding Hyphae and Mycelium
- What is mould in manufacturing? Unlock Mass Production with Precision Tooling
- What are three-plate molds? Precision Injection Molding for Complex Parts
- What is a pressing die? The Precision Tool for Shaping Powder into Solid Pellets
- What are the different types of molds? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process for Your Product









