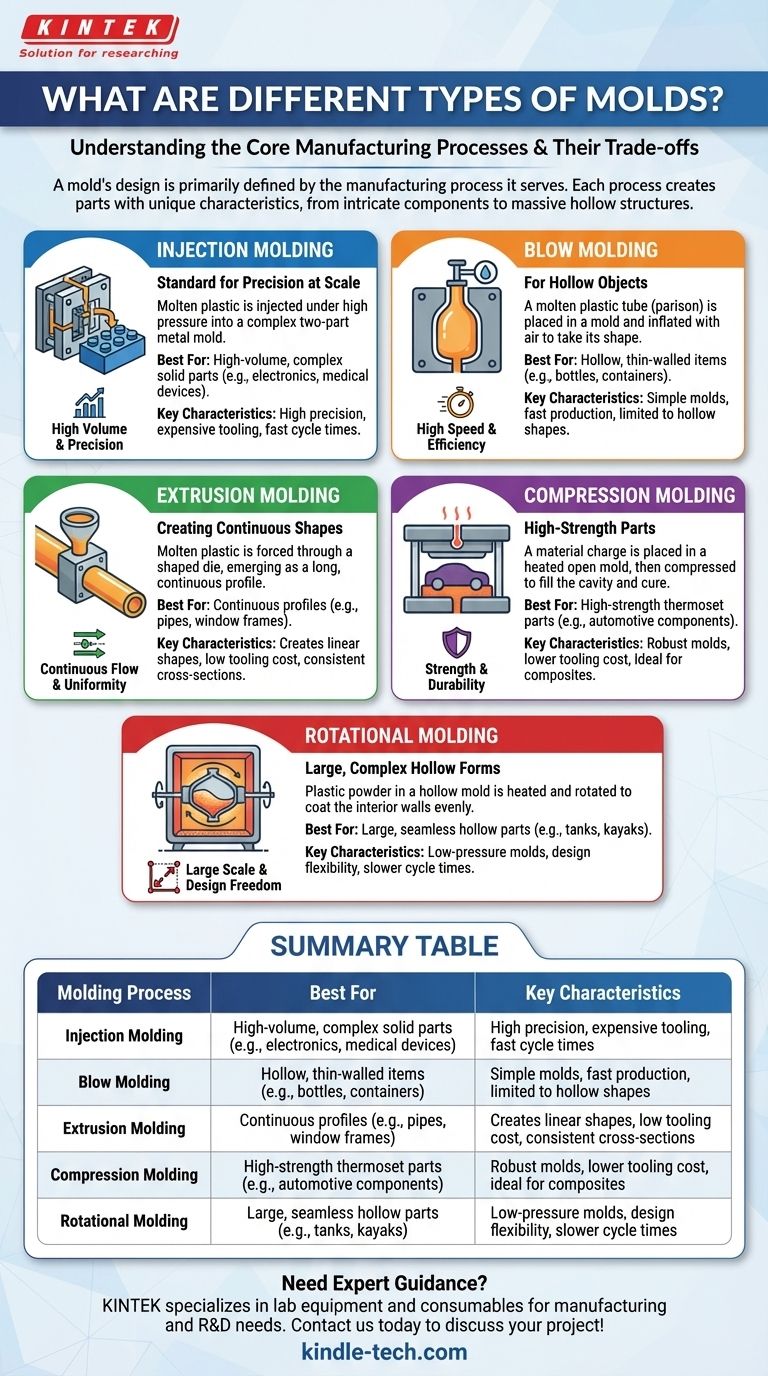
At the heart of modern manufacturing, a "mold" is rarely a single concept but is instead defined by its process. The most common types of molds correspond to the five primary plastic molding processes: injection molding, blow molding, extrusion molding, compression molding, and rotational molding. Each process is engineered to create parts with specific characteristics, from tiny, intricate components to massive, hollow structures.
The type of mold you need is fundamentally tied to the manufacturing process you choose. Understanding the goal—such as production volume, part complexity, and material—is the key to selecting the right method, as each offers a distinct balance of cost, speed, and capability.

Understanding the 5 Core Molding Processes
Each molding process uses a unique tool (the mold) and a distinct method to shape raw material, typically plastic pellets or powder, into a finished product.
1. Injection Molding: The Standard for Precision at Scale
Injection molding works by injecting molten plastic under high pressure into a precisely machined two-part metal mold. The plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected.
The molds (or tools) are highly complex and expensive to create but can produce millions of identical parts with extreme precision.
This process is the backbone of mass production for solid parts like LEGO bricks, electronic enclosures, car interior components, and medical devices.
2. Blow Molding: For Hollow Objects
Blow molding begins with a hollow tube of molten plastic called a "parison." This parison is placed inside a mold, which then closes around it. Air is blown into the parison, inflating it like a balloon until it takes the shape of the mold cavity.
The mold itself is a relatively simple hollow cavity that defines the final exterior shape.
This method is used almost exclusively for manufacturing hollow, thin-walled items like water bottles, milk jugs, and chemical drums.
3. Extrusion Molding: Creating Continuous Shapes
Unlike other methods that create discrete parts, extrusion creates continuous linear shapes. Molten plastic is forced through a shaped die (the mold), emerging as a long profile that is then cooled and cut to length.
Think of it like squeezing toothpaste from a tube; the shape of the opening determines the shape of the toothpaste stream.
Extrusion is ideal for products with a consistent cross-section, such as pipes, drinking straws, window frames, and plastic decking.
4. Compression Molding: High-Strength Parts
In compression molding, a pre-measured amount of molding material (a "charge") is placed directly into a heated, open mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to force the material to fill the cavity and cure.
The mold is typically simpler and more robust than an injection mold, often resembling a high-tech waffle iron.
This process is excellent for high-strength thermoset plastics and is used to make electrical components, automotive parts, and durable composite dinnerware.
5. Rotational Molding: Large, Complex Hollow Forms
Also known as rotomolding, this process involves placing plastic powder into a hollow mold. The mold is then heated and slowly rotated on two axes, allowing the melting plastic to tumble and coat the interior walls evenly.
The molds can be very large but are relatively low-cost compared to injection molds because they do not need to withstand high pressure.
Rotational molding is the go-to method for creating large, seamless, and stress-free hollow parts like kayaks, large water tanks, and playground equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Volume vs. Geometry
Choosing a molding process is an engineering decision based on critical trade-offs. No single method is universally best.
Tooling Cost vs. Part Cost
Injection molding has an extremely high upfront tooling cost but produces parts for pennies, making it economical only at very high volumes.
Rotational and compression molding have much lower tooling costs, making them suitable for lower-volume production. However, the cost per part is higher due to slower cycle times.
Production Volume and Speed
Injection and extrusion molding are incredibly fast, capable of producing thousands or millions of units efficiently.
Rotational molding is the slowest process, with cycle times measured in minutes or hours rather than seconds. It is inherently a low-volume process.
Part Geometry and Complexity
Injection molding excels at producing complex, solid parts with intricate features and tight tolerances.
Blow and rotational molding are exclusively for hollow parts. Rotational molding can handle more complex shapes and produce much larger parts than blow molding.
Extrusion is limited to continuous 2D profiles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
Your final decision depends entirely on your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is mass production and high precision for solid parts: Injection molding is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is creating commodity hollow items like bottles: Blow molding offers unmatched speed and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is producing large, durable, and complex hollow parts: Rotational molding provides design freedom and low tooling costs.
- If your primary focus is creating long, continuous profiles like pipes or trim: Extrusion molding is the only logical choice.
- If your primary focus is strong, simple parts from thermoset or composite materials: Compression molding delivers strength and durability.
Understanding these fundamental processes and their associated molds empowers you to make informed decisions that align your manufacturing method with your product's design and business goals.
Summary Table:
| Molding Process | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | High-volume, complex solid parts (e.g., electronics, medical devices) | High precision, expensive tooling, fast cycle times |
| Blow Molding | Hollow, thin-walled items (e.g., bottles, containers) | Simple molds, fast production, limited to hollow shapes |
| Extrusion Molding | Continuous profiles (e.g., pipes, window frames) | Creates linear shapes, low tooling cost, consistent cross-sections |
| Compression Molding | High-strength thermoset parts (e.g., automotive components) | Robust molds, lower tooling cost, ideal for composites |
| Rotational Molding | Large, seamless hollow parts (e.g., tanks, kayaks) | Low-pressure molds, design flexibility, slower cycle times |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right mold and equipment for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for your manufacturing and R&D needs. Whether you're prototyping with compression molding or scaling up with injection molding, our team ensures you get the right tools for precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are molds used for? Unlock Mass Production of Precision Parts
- How do high-precision molds contribute to Li6PS5Cl electrolyte membrane formation? Achieve Perfect Density and Thickness
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) improve W-Cu densification? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density with High Pressure
- How do steel molds and hydraulic equipment collaborate for high-density molding? Optimize WC/Cu FGM Green Body Prep
- What is mould in manufacturing? Unlock Mass Production with Precision Tooling















