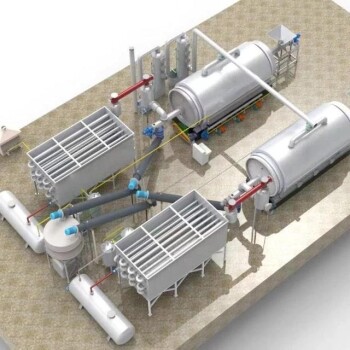
A pyrolysis plant is a complex system designed to thermally decompose organic materials in the absence of oxygen, producing valuable by-products such as biochar, bio-oil, and syngas. The plant typically consists of several key components, including a reactor (or retort), condenser, energy module (furnace), feeding system, discharging system, and emission cleaning systems. These components work together to ensure efficient pyrolysis, energy recovery, and compliance with environmental standards. The design and configuration of the plant may vary depending on the specific goals, such as whether the focus is on solid, liquid, or gaseous products.
Key Points Explained:

-
Reactor (Retort):
- The reactor is the core component where the pyrolysis process occurs. It is designed to withstand high temperatures and facilitate the thermal decomposition of organic materials.
- In batch processes, the reactor is often referred to as a retort. It operates in a sealed environment to prevent oxygen from entering, which is crucial for pyrolysis.
- The reactor's design may vary depending on the scale and type of pyrolysis (e.g., fast, slow, or intermediate pyrolysis).
-
Condenser:
- The condenser is used to cool and condense the vapor-gas mixture produced during pyrolysis into liquid products, such as bio-oil.
- In some designs, the condenser may be excluded if the primary goal is to produce only solid products (e.g., biochar). In such cases, the vapor-gas mixture is often burned in the furnace for energy recovery.
-
Energy Module (Furnace):
- The energy module, typically a furnace, provides the heat required for the pyrolysis process. It can be fueled by external sources or by the combustible gases (syngas) produced during pyrolysis.
- Some designs integrate the reactor and energy module to reduce energy losses, though this requires advanced temperature control and high-quality construction materials.
-
Feeding System:
- The feeding system is responsible for delivering raw materials (e.g., biomass, plastic, or rubber) into the reactor in a fully sealed and automated manner.
- This system ensures a continuous and efficient supply of feedstock, which is critical for maintaining the pyrolysis process.
-
Discharging System:
- The discharging system transports the solid by-products (e.g., carbon black or biochar) from the reactor to a storage or cooling tank.
- In some designs, the discharging system includes water-cooling pipes to cool the solid products before storage.
-
Syn-gas Recycling System:
- The syn-gas recycling system captures and recycles the combustible gases (syngas) produced during pyrolysis.
- These gases can be used to heat the reactor, reducing the need for external energy sources and improving the overall energy efficiency of the plant.
-
De-dusting System (Emission Cleaning Line):
- The de-dusting system purifies the emission gases to remove particulate matter and other pollutants, ensuring compliance with environmental standards (e.g., EU emission standards).
- This system is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of the pyrolysis process.
-
Heating System:
- The heating system provides the necessary thermal energy for the pyrolysis process. It may include burners, heat exchangers, or other heating elements.
- The system is designed to maintain precise temperature control, which is essential for optimizing the pyrolysis reaction.
-
Waste Gas Recovery and Reuse System:
- This system captures and recycles waste gases produced during pyrolysis, further enhancing the plant's energy efficiency.
- The recovered gases can be used to power the heating system or other plant operations.
-
Dust Removal System:
- The dust removal system is responsible for filtering out dust and other particulates from the emission gases.
- This system is critical for maintaining air quality and ensuring that the plant meets regulatory requirements.
In summary, a pyrolysis plant is a sophisticated system composed of multiple interconnected components, each playing a vital role in the efficient and environmentally friendly conversion of organic materials into valuable products. The specific configuration and design of the plant may vary depending on the intended application and the desired output products.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Reactor (Retort) | Core unit for thermal decomposition of organic materials in oxygen-free conditions. |
| Condenser | Cools vapor-gas mixture to produce liquid by-products like bio-oil. |
| Energy Module (Furnace) | Provides heat for pyrolysis, often fueled by syngas or external sources. |
| Feeding System | Delivers raw materials into the reactor in a sealed, automated manner. |
| Discharging System | Transports solid by-products (e.g., biochar) to storage or cooling tanks. |
| Syn-gas Recycling System | Captures and recycles combustible gases to heat the reactor. |
| De-dusting System | Purifies emission gases to meet environmental standards. |
| Heating System | Maintains precise temperature control for optimal pyrolysis. |
| Waste Gas Recovery System | Recycles waste gases to enhance energy efficiency. |
| Dust Removal System | Filters particulates from emission gases to ensure air quality compliance. |
Ready to explore how a pyrolysis plant can transform your organic waste into valuable products? Contact us today for expert guidance!