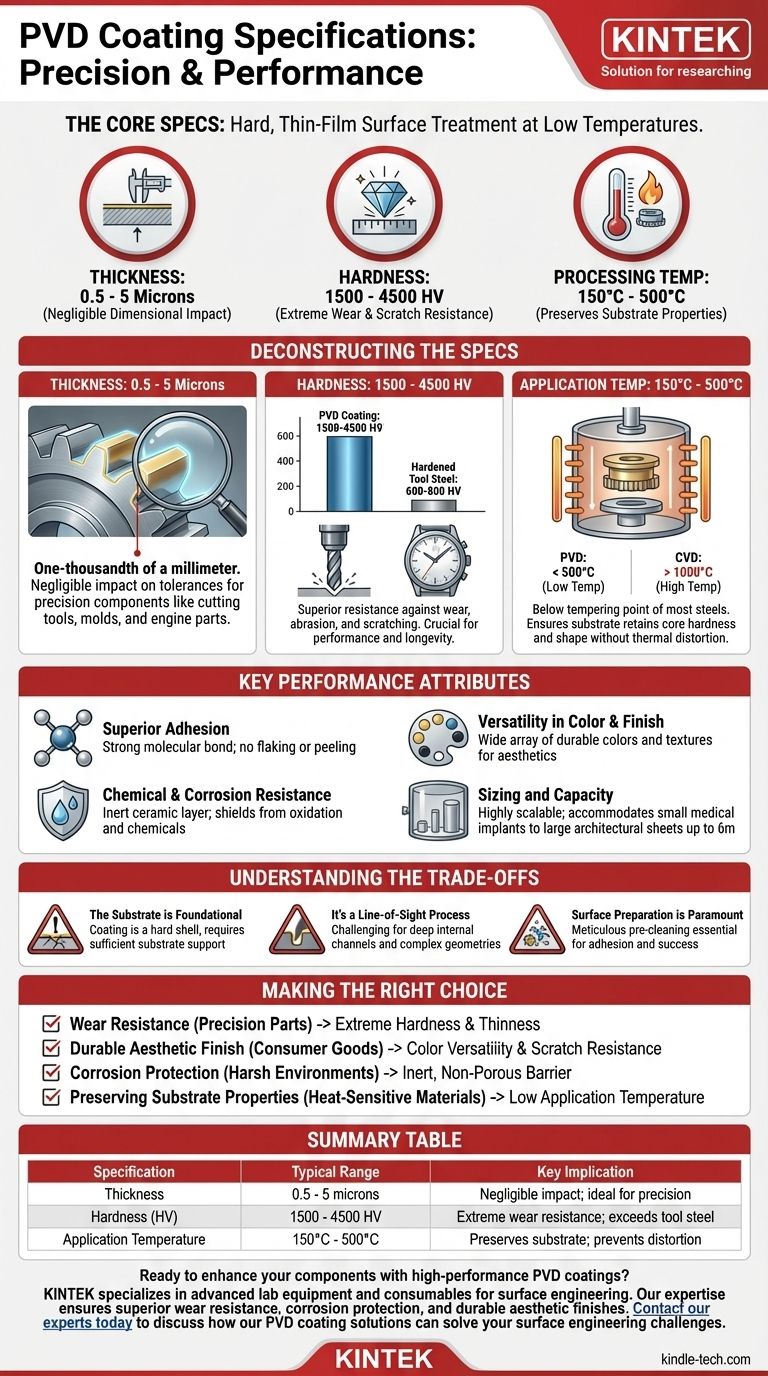
The core specifications for PVD coating define it as an extremely hard, thin-film surface treatment applied at low temperatures. Key specs include a thickness of 0.5 to 5 microns, a hardness between 1500 and 4500 HV (Hardness Vickers), and a processing temperature range of 150°C to 500°C. These characteristics make it a high-performance finish that enhances a part's surface properties without altering its underlying structure or critical dimensions.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is less a single "coating" and more a sophisticated surface engineering process. Its specifications reveal a method designed to add exceptional surface durability (wear, scratch, and corrosion resistance) to a component while having a minimal, predictable impact on its size and core material properties.
Deconstructing the Core Specifications
To truly evaluate PVD, you must understand the practical implications of its primary technical specs. These numbers dictate where and why the process is uniquely effective.
Thickness: 0.5 to 5 Microns
The most defining feature of a PVD coating is that it is incredibly thin. A micron (μm) is one-thousandth of a millimeter.
This minimal thickness is a significant advantage, as it has a negligible impact on the dimensional tolerances of precision components. Parts like cutting tools, injection molds, and engine components can be coated without requiring re-machining.
Hardness: 1500 to 4500 HV
This range places PVD coatings among the hardest synthetic materials available. For context, hardened tool steel is typically in the 600-800 HV range.
This extreme hardness directly translates to superior resistance against wear, abrasion, and scratching. It is the primary reason PVD is used on cutting tools, dies, and high-end watches, where maintaining a pristine surface is critical for performance and longevity.
Application Temperature: 150°C to 500°C
PVD is fundamentally a low-temperature process compared to other high-performance coatings like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which can exceed 1000°C.
This low-temperature application is crucial because it occurs below the tempering or annealing point of most steels and alloys. This ensures the substrate material retains its core hardness, strength, and shape without risk of thermal distortion or damage.
Key Performance Attributes
Beyond the numbers, these specifications create a set of powerful functional benefits that solve specific engineering and design challenges.
Superior Adhesion
Modern PVD processes utilize systems that create a strong molecular bond between the coating and the substrate. The coating doesn't just sit on the surface like paint; it becomes an integral part of the component. This results in a finish that will not flake, peel, or blister under stress.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
PVD coatings are typically ceramic in nature (e.g., Titanium Nitride, Chromium Nitride), making them dense and chemically inert. This forms a protective barrier on the substrate's surface, shielding it from oxidation, corrosion, and attack from most chemicals.
Versatility in Color and Finish
While rooted in industrial performance, PVD also offers a wide array of decorative options. The process can produce a variety of rich, durable colors—such as black, blue, gold, and bronze—with different textures. This makes it a preferred choice for architectural fixtures, jewelry, and luxury consumer goods.
Sizing and Capacity
The PVD process is highly scalable. Coating chambers can range in size to accommodate everything from small medical implants to large stainless steel architectural sheets (e.g., 1500mm x 4000mm) and long tubes (up to 6 meters).
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect. An objective evaluation of PVD requires acknowledging its operational constraints.
The Substrate is Foundational
A PVD coating is a hard shell on a component; it does not enhance the core strength of the substrate material. If a soft base metal is subjected to a heavy impact, it can deform, causing the extremely hard (but brittle) coating to crack. The substrate must have sufficient hardness to support the coating.
It's a Line-of-Sight Process
In PVD, the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the component. This makes it challenging to evenly coat deep internal channels, complex interior geometries, or heavily shadowed areas. Parts often require complex rotation and fixturing to ensure uniform coverage.
Surface Preparation is Paramount
The high adhesion of PVD is entirely dependent on an atomically clean surface. The process requires meticulous pre-cleaning to remove any oils, oxides, or contaminants. This critical step is essential for coating success and adds to the overall process time and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PVD specifications align with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance on precision parts: The combination of extreme hardness and minimal thickness is ideal for protecting cutting edges and maintaining tight tolerances.
- If your primary focus is a durable aesthetic finish: The versatility of color options combined with superior scratch resistance makes PVD perfect for consumer goods that must withstand daily use.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection in a harsh environment: The inert, non-porous ceramic layer provides an excellent protective barrier for medical, marine, or chemical applications.
- If your primary focus is preserving substrate properties: The low application temperature ensures that heat-treated or stress-sensitive materials will not be compromised during the coating process.
Understanding these technical specifications empowers you to leverage PVD not just as a finish, but as a deliberate tool for advanced surface engineering.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Typical Range | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.5 - 5 microns | Negligible impact on part dimensions; ideal for precision components. |
| Hardness (HV) | 1500 - 4500 HV | Extreme wear, abrasion, and scratch resistance; far exceeds tool steel. |
| Application Temperature | 150°C - 500°C | Low-temperature process preserves substrate hardness and prevents distortion. |
Ready to enhance your components with high-performance PVD coatings?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our expertise ensures your laboratory can achieve superior wear resistance, corrosion protection, and durable aesthetic finishes. Let us help you select the right PVD solution for your specific application—from precision tools to decorative finishes.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD coating solutions can solve your surface engineering challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure



















