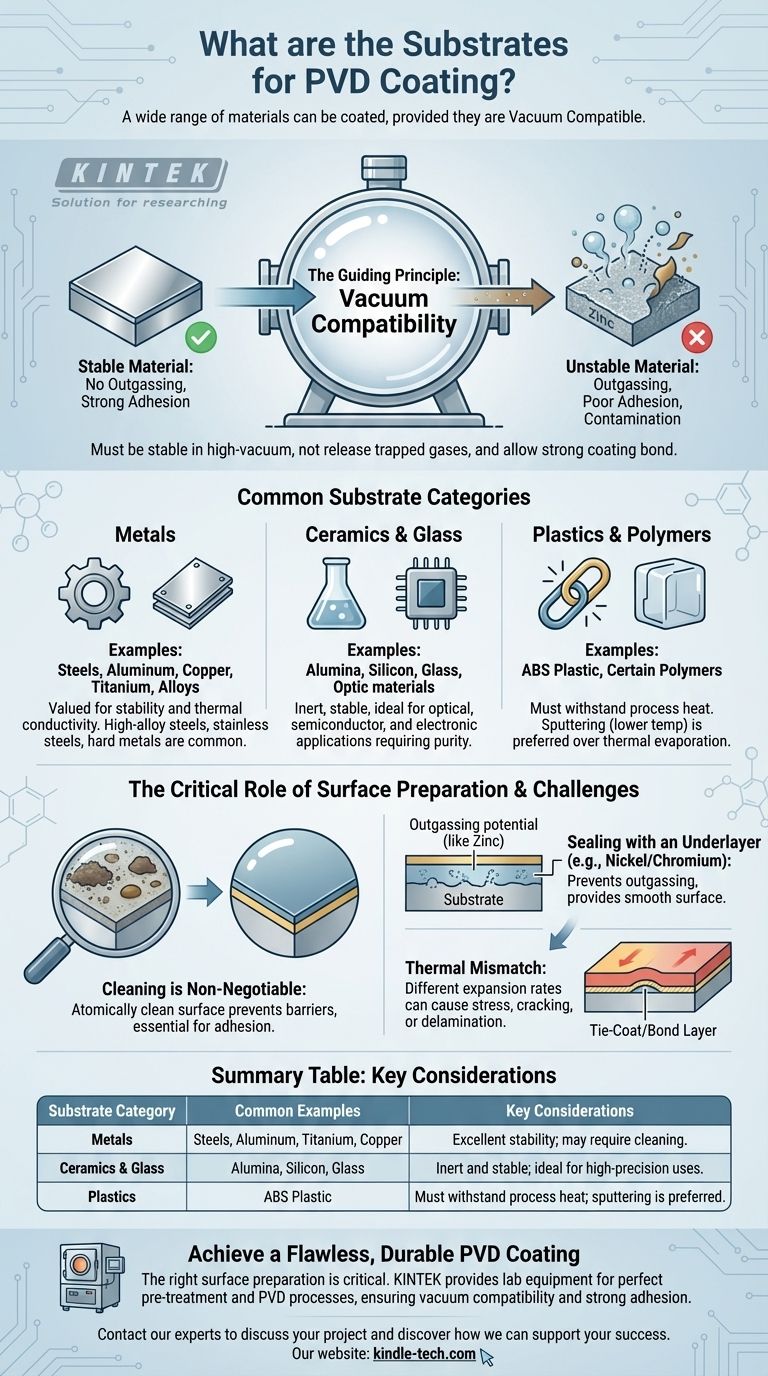
In short, an extremely wide range of materials can serve as substrates for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating. This includes nearly all metals such as steels, aluminum, copper, and titanium, as well as ceramics, glass, and even certain polymers like ABS plastic. The defining characteristic is not the material class itself, but its ability to remain stable in a high-vacuum environment and allow for strong adhesion of the coating material.
The suitability of a substrate for PVD coating is determined less by its specific material type and more by its vacuum compatibility. Any material that can remain stable and not release gases or contaminants under vacuum can be coated, often requiring specific pre-treatments to ensure a flawless, adhesive finish.

The Guiding Principle: Vacuum Compatibility
What "Vacuum Compatible" Means
PVD processes take place inside a high-vacuum chamber. This pristine environment is necessary for the coating atoms to travel from the source to the substrate without colliding with air molecules.
A suitable substrate, therefore, must not "outgas"—that is, it cannot release trapped gases, water vapor, or volatile elements when exposed to the vacuum. Outgassing contaminates the chamber, interferes with the coating process, and results in poor adhesion and film quality.
Why Some Materials Are Challenging
Materials with high vapor pressure elements are problematic. For example, galvanized steel is unsuitable because the zinc coating will vaporize in the vacuum.
Similarly, certain alloys like brass (which contains zinc) can outgas, compromising the process. This is why such materials often require a sealing layer before they can be coated.
Common Substrate Categories
Metals
Metals are the most common substrates for PVD, valued for their stability and thermal conductivity.
Nearly all metal families are suitable, including high-alloy steels, stainless steels, hard metals, aluminum, copper, titanium, and their alloys.
Ceramics and Glass
Due to their inertness and stability under vacuum, ceramics and glass are excellent substrates.
They are frequently used for functional coatings in optical, semiconductor, and electronic applications where precision and purity are paramount.
Plastics and Polymers
Certain plastics, most notably ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), can be PVD coated.
The main limitation is temperature. The substrate must be able to withstand the heat generated during the PVD process. Processes like sputtering are conducted at lower temperatures than thermal evaporation, making them more suitable for heat-sensitive materials.
The Critical Role of Surface Preparation
Cleaning is Non-Negotiable
The substrate surface must be atomically clean. Any trace of oils, oxides, dust, or other contaminants will act as a barrier, preventing the coating from adhering directly to the substrate and causing it to fail.
Sealing with an Underlayer
For materials that tend to outgas (like zinc or brass) or for decorative applications requiring a brilliant finish, pre-treatment is essential.
Substrates are often electroplated with layers of nickel and chromium first. This plating serves two purposes: it seals the substrate to prevent outgassing and provides a smooth, stable, and highly receptive surface for the PVD coating to bond to.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adhesion Strength Varies
The bond strength of a PVD coating is highly dependent on the substrate material. The interaction between a coating and a steel substrate is fundamentally different from its interaction with a plastic one.
To manage this, engineers often use thin "bond layers" or "tie-coats" to improve the interface between the substrate and the final functional coating.
Thermal Mismatch Can Cause Stress
The substrate and the coating material expand and contract at different rates when heated. This difference, known as the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), can create immense stress in the coating.
If the mismatch is too great, it can lead to cracking or delamination of the coating, especially in applications with significant temperature fluctuations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct substrate and preparation method is foundational to a successful coating outcome.
- If your primary focus is durability and performance (e.g., cutting tools): Stable metal substrates like high-alloy steels or hard metals are ideal, as they require minimal pre-treatment beyond rigorous cleaning.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish (e.g., faucets, jewelry): Substrates like ABS plastic, zinc, or brass are common but will almost certainly require an electroplated underlayer to ensure a flawless finish and strong adhesion.
- If your primary focus is optical or electronic applications: Glass and ceramic substrates are the industry standard due to their inherent stability, smoothness, and inert chemical properties.
Ultimately, a successful PVD outcome depends on treating the substrate and its preparation with the same importance as the coating itself.
Summary Table:
| Substrate Category | Common Examples | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Steels, Aluminum, Titanium, Copper | Excellent stability; may require cleaning. |
| Ceramics & Glass | Alumina, Silicon, Glass | Inert and stable; ideal for high-precision uses. |
| Plastics | ABS Plastic | Must withstand process heat; sputtering is preferred. |
Ready to achieve a flawless, durable PVD coating on your specific substrate?
The right surface preparation is critical for coating adhesion and performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed for perfect pre-treatment and PVD processes. Whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or plastics, our solutions help ensure vacuum compatibility and strong adhesion for your laboratory's applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















