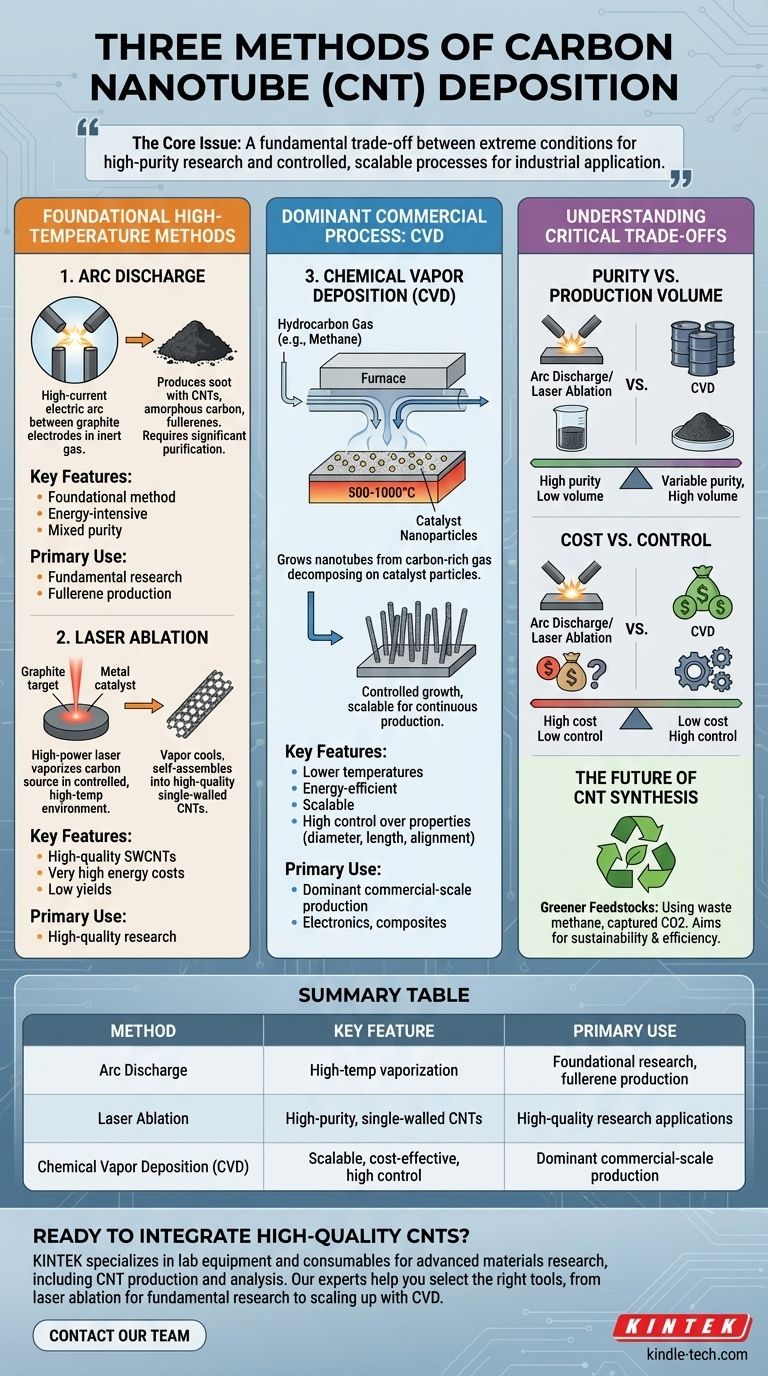
The three primary methods for producing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are arc discharge, laser ablation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). While arc discharge and laser ablation were foundational in the discovery and study of CNTs, chemical vapor deposition has since become the dominant process for commercial-scale production due to its superior control and scalability.
The core issue isn't simply knowing the three methods, but understanding the fundamental trade-off they represent: a choice between the extreme conditions required for high-purity research and the controlled, scalable processes needed for industrial application.

The Foundational High-Temperature Methods
The first two methods discovered for creating CNTs rely on vaporizing a solid carbon source at extremely high temperatures. They are energy-intensive and are now used primarily in research settings.
Arc Discharge
The arc discharge technique was the first method used to produce carbon nanotubes. It involves creating a high-current electric arc between two graphite electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere.
As the current passes, the anode is consumed, and the resulting carbon vapor cools and condenses to form a soot-like deposit. This deposit contains a mixture of CNTs, amorphous carbon, and other fullerenes that requires significant downstream purification.
Laser Ablation
In the laser ablation process, a high-power laser beam is aimed at a graphite target, which often contains a small amount of metal catalyst. The intense heat from the laser vaporizes the carbon source.
As the vaporized carbon cools in a controlled, high-temperature environment, it self-assembles into carbon nanotubes. This method is known for producing high-quality single-walled CNTs but suffers from low yields and very high energy costs.
The Dominant Commercial Process: CVD
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) has emerged as the most important method for producing CNTs at scale due to its cost-effectiveness and process control.
How Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Works
The CVD process "grows" nanotubes from a carbon-rich gas. A hydrocarbon gas (such as methane or ethylene) is introduced into a furnace and passed over a substrate coated with tiny metal catalyst nanoparticles.
At temperatures between 500-1000°C, the hydrocarbon gas decomposes, and the carbon atoms attach to the catalyst particles, growing into hollow tubes. It is analogous to growing fibers from metallic "seeds."
Why CVD Is the Industry Standard
CVD offers unparalleled advantages for commercial production. It operates at lower temperatures than arc discharge or laser ablation, is more energy-efficient, and can be scaled up for continuous production.
Crucially, CVD allows for significant control over the final CNT properties, such as diameter, length, and even alignment on the substrate, making it ideal for integration into electronic and composite material applications.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Each synthesis method presents a different balance of quality, cost, and production volume. Selecting the right one depends entirely on the end goal.
Purity vs. Production Volume
Arc discharge and laser ablation can produce highly crystalline nanotubes, but they are generated in small batches mixed with significant impurities. These methods prioritize quality over quantity.
CVD, on the other hand, is a master of volume. It can produce kilograms of CNTs cost-effectively, though the quality can be more variable, and residual catalyst material can be a concern for sensitive applications like electronics.
Cost vs. Control
Laser ablation is by far the most expensive method due to the cost of the lasers and the high energy consumption. Arc discharge is also an energy-intensive process.
CVD represents the most cost-effective path to large-scale CNT production. Its true advantage, however, lies in control—the ability to tailor nanotube characteristics for specific commercial products.
The Future of CNT Synthesis
Modern research is focused on making existing processes, particularly CVD, more sustainable and efficient.
Greener Feedstocks and Processes
Emerging strategies aim to replace traditional hydrocarbon feedstocks with more environmentally friendly sources. This includes using waste methane from pyrolysis or even using captured carbon dioxide as the carbon source via electrolysis in molten salts. These innovations promise to lower the cost and environmental footprint of CNT production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best method is the one that aligns with your specific objectives for quality, scale, and cost.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or producing the highest-purity single-walled CNTs: Laser ablation remains a valuable, albeit expensive, laboratory technique.
- If your primary focus is exploring historical methods or creating specific fullerene structures: Arc discharge is the foundational method, though it requires significant post-processing.
- If your primary focus is scalable, cost-effective production for commercial applications: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the undisputed industry standard due to its balance of control, volume, and cost.
Ultimately, understanding these core processes allows you to select the synthesis path that best aligns with your specific technical and commercial objectives.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | High-temperature vaporization | Foundational research, fullerene production |
| Laser Ablation | High-purity, single-walled CNTs | High-quality research applications |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Scalable, cost-effective, high control | Dominant commercial-scale production |
Ready to integrate high-quality carbon nanotubes into your research or product development?
The choice of synthesis method is critical to achieving your goals for purity, volume, and cost. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced materials research, including CNT production and analysis.
Our experts can help you select the right tools for your specific application, whether you're exploring fundamental research with laser ablation or scaling up with CVD. Let us support your innovation with reliable equipment and technical expertise.
Contact our team today to discuss your project needs and discover how KINTEK can be your partner in advanced materials science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is chemical deposition different from physical deposition? A Guide to Coating Complex Shapes vs. Precision
- What is the application of DC sputtering? A Guide to Cost-Effective Metal Coating
- What is chemical vapor deposition of coatings? Grow Superior, Conformal Films on Complex Parts
- What is Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) and why is it critical for advanced CMOS? Master Nanoscale Precision
- How do the growth patterns of HPHT, CVD, and natural diamonds differ? Uncover the Morphology of Lab vs. Mined Gems
- What are the applications of Apcvd? High-Speed, Cost-Effective Thin-Film Deposition Solutions
- What is the formula for deposition rate of thin film? Master the Key Variables for Your Process
- What is the function of a high-temperature CVD reactor in TiN/TiC coating? Optimize Tool Durability and Hardness



















