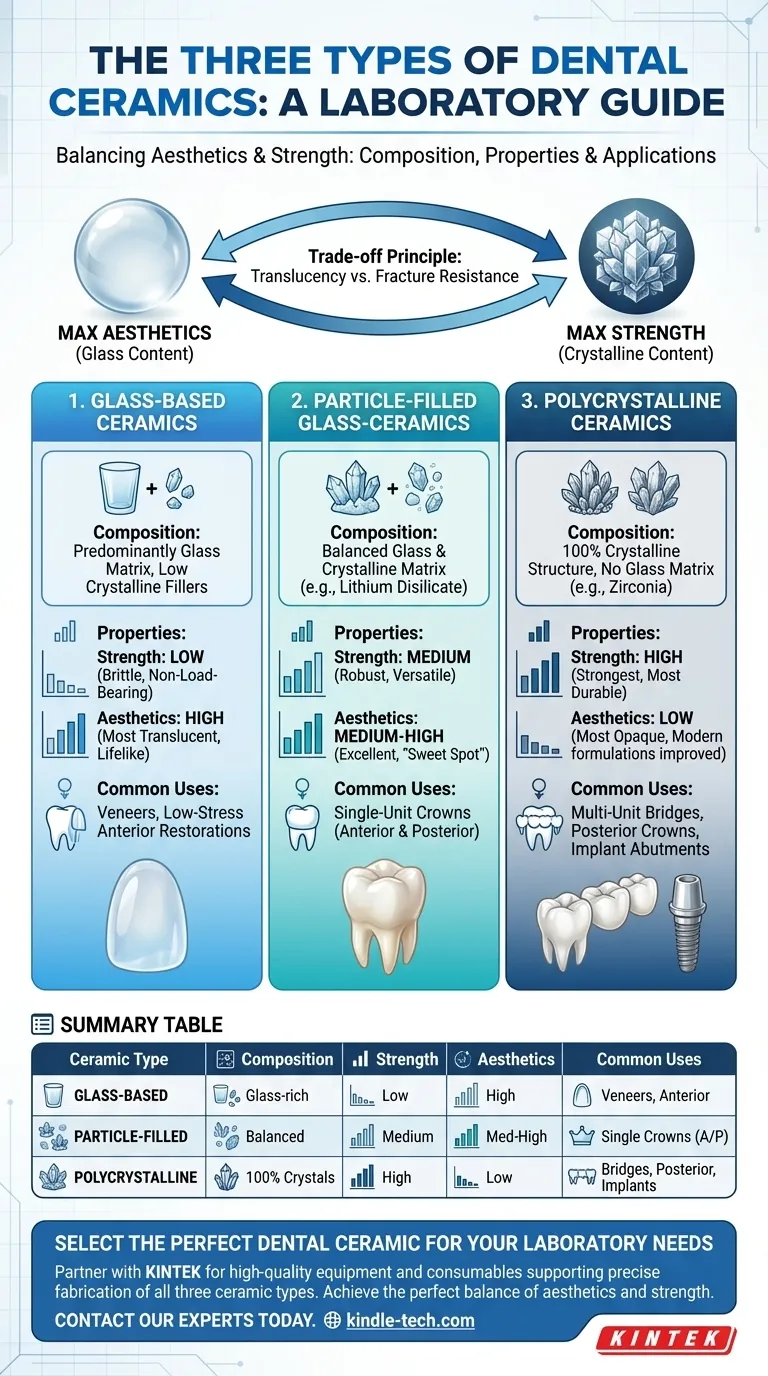
In modern dentistry, restorative materials are broadly classified into three fundamental types of dental ceramics. These categories are distinguished by their composition and the ratio of glass to crystalline structures, which directly dictates their strength and aesthetic properties. The three primary groups are glass-based ceramics, particle-filled glass-ceramics, and polycrystalline ceramics.
The core principle to understand is that the choice of a dental ceramic is always a deliberate trade-off between optical beauty (translucency) and mechanical strength (fracture resistance). No single material is perfect for every situation.

Understanding the Core Components: Glass vs. Crystals
To grasp the differences between the three ceramic types, you must first understand their two main ingredients and the role each plays.
The Role of Glass
The glass matrix is the primary component responsible for a ceramic's aesthetics. Its amorphous, non-crystalline structure allows light to pass through, mimicking the translucency of a natural tooth.
The Role of Crystalline Fillers
Crystalline structures are added to the glass matrix to increase mechanical strength. These particles act as reinforcements, impeding crack propagation and making the material more durable and fracture-resistant.
The Fundamental Trade-off
There is an inverse relationship between these components. As the percentage of crystalline fillers increases to enhance strength, the overall glass content decreases. This, in turn, reduces the material's translucency, making it more opaque.
The Three Classes of Dental Ceramics
This balance between glass and crystals gives us our three distinct functional categories.
1. Glass-Based Ceramics (e.g., Feldspathic Porcelain)
These materials are predominantly glass with a low amount of crystalline fillers. This composition makes them the most aesthetically pleasing and translucent option available.
Their low strength, however, restricts their use to non-load-bearing applications. They are the ideal choice for aesthetic veneers on front teeth where appearance is the highest priority.
2. Particle-Filled Glass-Ceramics (e.g., Lithium Disilicate)
This category represents the "sweet spot" for many common restorations. It contains a significantly higher volume of crystalline fillers (like lithium disilicate) embedded within a glass matrix.
This balanced composition provides good strength, suitable for single-unit crowns on both anterior and posterior teeth, while maintaining excellent aesthetic properties. It is arguably the most versatile and widely used ceramic class today.
3. Polycrystalline Ceramics (e.g., Zirconia)
Polycrystalline ceramics contain no glass matrix at all. They are composed of densely packed, high-strength crystals, making them the strongest and most fracture-resistant dental ceramic available.
This strength comes at the cost of translucency, as their dense crystalline structure makes them inherently more opaque. They are the material of choice for high-stress applications like multi-unit bridges, posterior crowns under heavy biting forces, and implant abutments.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Aesthetics vs. Strength
Choosing the right ceramic requires a clear understanding of the clinical goal, as each material class sits on a spectrum of optical and mechanical properties.
The Translucency Spectrum
Aesthetics follow the glass content. Glass-based ceramics are the most translucent and lifelike. Particle-filled glass-ceramics offer a very good compromise. Polycrystalline ceramics (zirconia) are the most opaque, though modern formulations have improved their translucency.
The Strength Spectrum
Strength follows the crystalline content. Polycrystalline ceramics are the strongest and most durable. Particle-filled glass-ceramics offer robust strength for most single-tooth situations. Glass-based ceramics are the most brittle and have the lowest fracture resistance.
Clinical Implications of Material Choice
This trade-off directly dictates clinical use. A highly visible front tooth that needs a veneer demands the aesthetics of a glass-based ceramic. A molar crown requires the durability of a particle-filled or polycrystalline ceramic. A long-span bridge can only be fabricated from high-strength polycrystalline ceramic.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
Your final material selection must align with the specific demands of the restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics for a low-stress area (e.g., an anterior veneer): A glass-based ceramic is the superior choice for its unmatched translucency.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and appearance (e.g., a single crown): A particle-filled glass-ceramic like lithium disilicate provides the ideal blend of durability and beauty.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for a high-stress area (e.g., a multi-unit bridge): A polycrystalline ceramic like zirconia is the only option that can withstand the required forces.
Understanding this classification empowers you to select the precise material that delivers the ideal balance of beauty and performance for any clinical need.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Key Composition | Primary Strength | Primary Aesthetics | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass-Based | Predominantly glass, low crystals | Low | High (Most Translucent) | Veneers, low-stress anterior restorations |
| Particle-Filled | Balanced glass & crystal matrix | Medium (Versatile) | Medium-High (Excellent) | Single-unit crowns (anterior & posterior) |
| Polycrystalline | 100% crystals, no glass | High (Strongest) | Low (Most Opaque) | Multi-unit bridges, posterior crowns, implant abutments |
Select the Perfect Dental Ceramic for Your Laboratory Needs
Choosing the right material is critical for the success of every dental restoration. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables that support the precise fabrication of all three ceramic types. Whether you're crafting delicate feldspathic veneers, versatile lithium disilicate crowns, or robust zirconia bridges, having reliable materials and equipment is paramount.
Let us help you achieve the perfect balance of aesthetics and strength in your dental lab. Our products are trusted by professionals to deliver consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can be your partner in dental excellence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API
- Why are high-precision vacuum sintering furnaces preferred over traditional methods for biofunctional dental ceramics?
- What temperature is porcelain fired at? A Guide to Precise Dental Firing Cycles
- What is the function of a porcelain furnace? Precision Firing for Lifelike Dental Restorations
- Why is a 1000°C+ furnace needed for LLZO/LLTO? Mastering High-Temperature Sintering for Ceramic Electrolytes



















