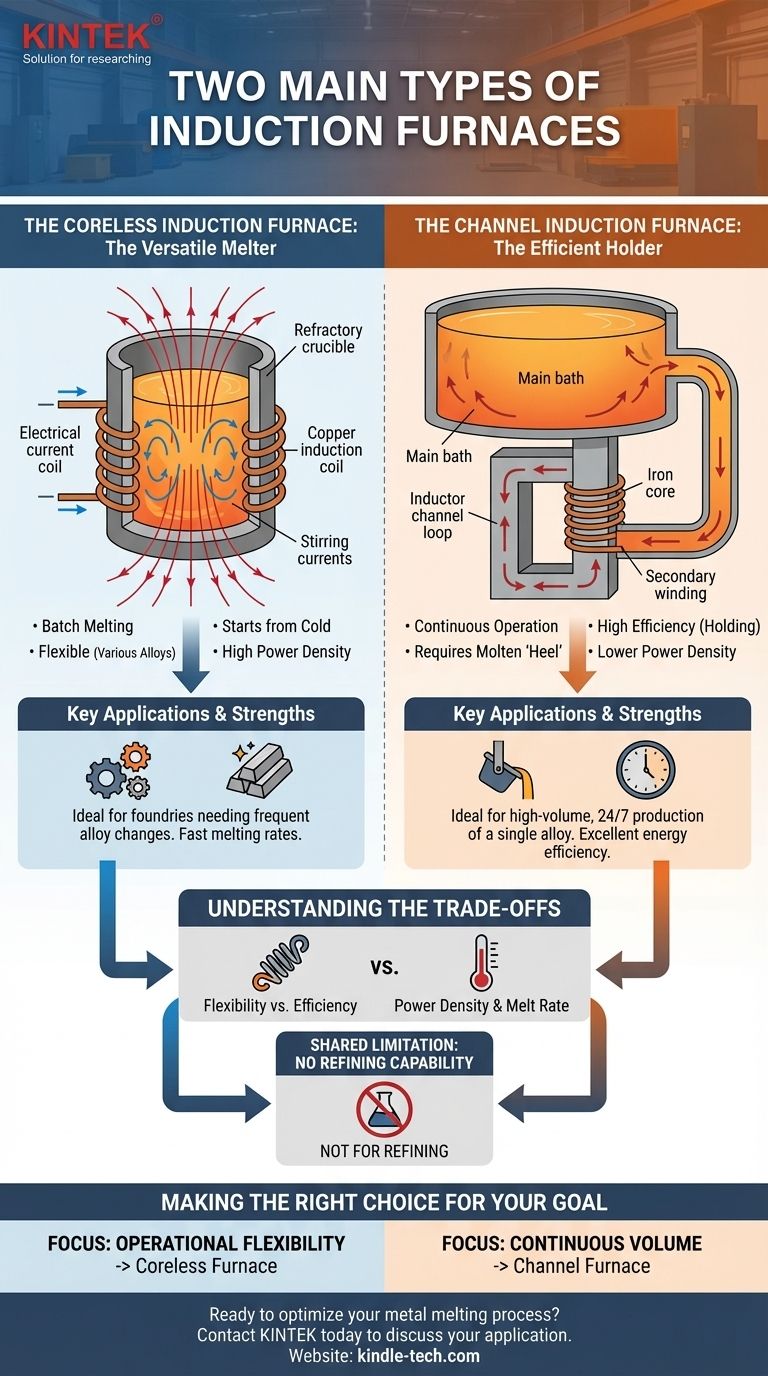
The two primary types of induction furnaces are the coreless induction furnace and the channel induction furnace. While both use electromagnetic induction to melt metal, their internal design dictates their ideal applications. The coreless furnace functions by placing the metal charge inside a crucible surrounded by an electrical coil, making it highly versatile, whereas the channel furnace uses a loop of molten metal as part of a transformer-like circuit, making it exceptionally efficient for holding and continuous melting.
The choice between a coreless and a channel furnace is not about which is superior, but which best aligns with your operational goal. Coreless furnaces provide flexibility for melting various alloys in batches, while channel furnaces deliver high efficiency for holding and continuously processing large volumes of a single alloy.

The Coreless Induction Furnace: The Versatile Melter
A coreless furnace is the most common type found in modern foundries due to its operational flexibility. Its design is straightforward and robust.
How It Works
In a coreless furnace, the metal to be melted is placed into a refractory-lined crucible. This crucible is surrounded by a water-cooled, copper induction coil. When a powerful alternating current is passed through the coil, it generates a strong, reversing magnetic field. This field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal charge, which generates intense heat and causes the metal to melt.
The magnetic field also creates a natural stirring action, which ensures a homogeneous melt and uniform temperature distribution.
Key Applications and Strengths
The primary strength of the coreless furnace is its versatility. Because the entire charge can be melted and emptied, it is excellent for foundries that need to produce different alloys throughout the day.
They are capable of melting a vast range of metals, from aluminum and copper alloys to iron and steel. They are also ideal for starting a melt from a cold, solid charge, providing fast melting rates.
The Channel Induction Furnace: The Efficient Holder
The channel furnace operates on a different principle, functioning more like a traditional transformer. It is a specialized tool for high-volume, continuous operations.
How It Works
A channel furnace has a main furnace body, or "bath," connected to one or more "channels" or "inductors." The inductor contains an iron core with a primary coil. The loop of molten metal within the channel acts as a single-turn secondary winding of the transformer.
Current flowing in the primary coil induces a massive current in the molten metal loop, generating heat. This superheated metal then circulates into the main bath via convection, heating the larger volume of metal. A channel furnace must always maintain a molten "heel" to complete this circuit; it cannot be started from a cold, solid state.
Key Applications and Strengths
Channel furnaces are exceptionally energy-efficient for holding large quantities of molten metal at a specific temperature or for superheating. This makes them ideal for die casting operations or as a holding furnace fed by a primary melting furnace.
They are typically dedicated to a single alloy, such as brass, bronze, or aluminum, and excel in high-volume, 24/7 production environments where stopping and starting is infrequent.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace type is a universal solution. The choice involves clear operational trade-offs that directly impact cost, flexibility, and workflow.
Flexibility vs. Efficiency
The coreless furnace's ability to start from cold and be completely emptied makes it perfect for batch processing and alloy changes. The channel furnace's need for a continuous molten heel makes it rigid but offers superior thermal efficiency for holding and continuous pouring.
Power Density and Melt Rate
Coreless furnaces generally have a much higher power density, allowing them to melt a solid charge very quickly. Channel furnaces have lower power density and are not designed for rapid primary melting, but rather for maintaining and gradually adding to an existing molten bath.
A Shared Limitation: Refining Capability
It is critical to understand that neither furnace type is designed for refining metal. They are melting and holding units. Unlike processes such as an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) or a Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF), induction melting does not remove undesirable elements like sulfur or phosphorus. The quality of the raw material charge directly determines the quality of the final molten metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational requirements will clearly point to the correct furnace technology. The decision hinges on whether your process is built around versatility or continuous volume.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility and melting diverse alloys: The coreless furnace is the clear choice for its ability to handle batch processing, frequent alloy changes, and starting from a cold charge.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous operation or holding a single alloy at temperature: The channel furnace offers unmatched energy efficiency and is the standard for large-scale, dedicated production lines.
Understanding this fundamental distinction between batch flexibility and continuous efficiency is the first step to optimizing your melting process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Furnace | Channel Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Batch melting, alloy changes | Holding, continuous melting |
| Flexibility | High (can start from cold) | Low (requires molten heel) |
| Efficiency | Good for melting | Excellent for holding |
| Ideal For | Diverse alloys, batch processing | High-volume, single alloy production |
Ready to optimize your metal melting process? KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab and industrial equipment for your specific needs. Whether you require the flexibility of a coreless furnace or the high-efficiency holding of a channel furnace, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance your productivity and reduce costs. Contact us today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals



















