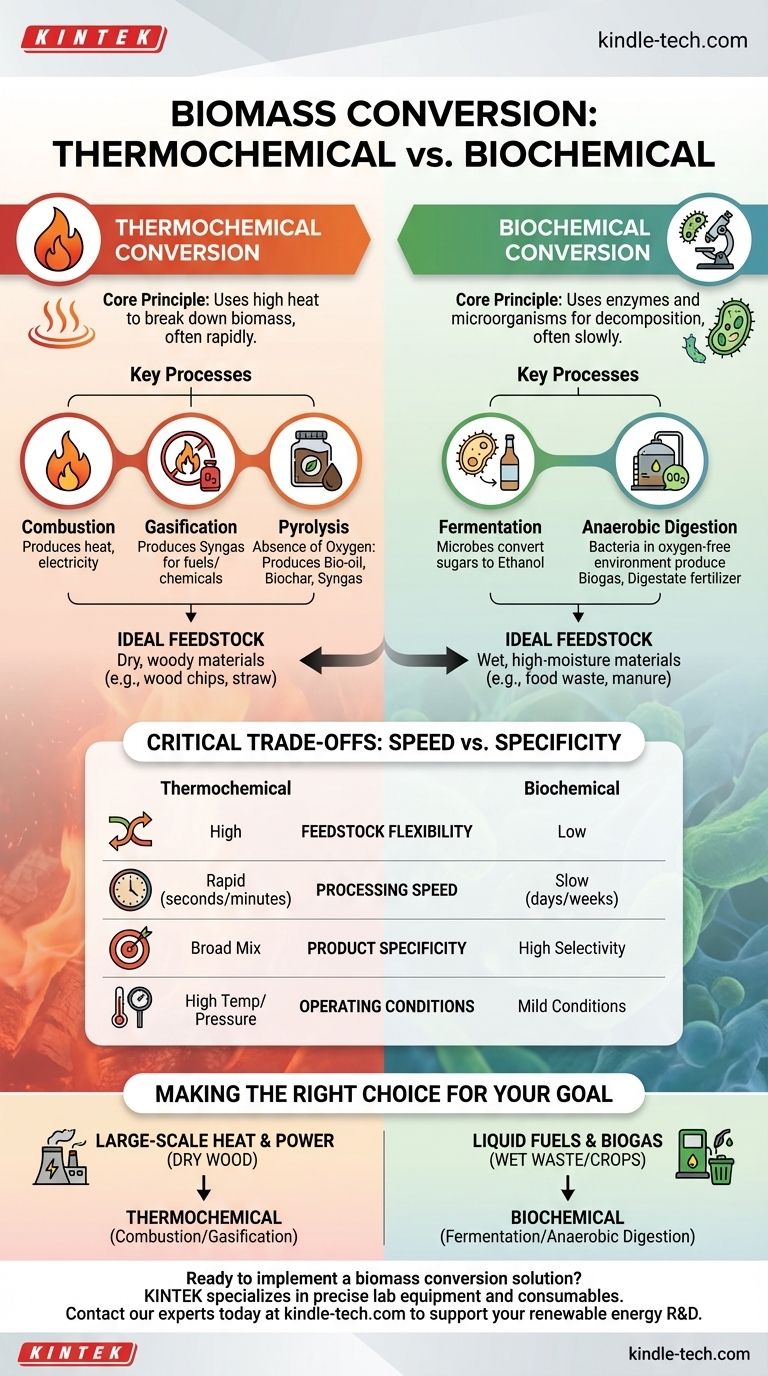
The two primary methods for converting biomass into usable energy are thermochemical conversion and biochemical conversion. Thermochemical processes use heat to break down organic material, while biochemical processes use enzymes and microorganisms to achieve a similar decomposition.
The core distinction lies in the catalyst for change: thermochemical conversion uses high-temperature energy to force a rapid chemical reaction, whereas biochemical conversion leverages the slow, deliberate work of living organisms. Your choice between them is dictated by your starting material and your desired final product.

Understanding Thermochemical Conversion: Harnessing Heat
Thermochemical conversion is a robust and rapid method for breaking down the complex structures within biomass. It is particularly effective for dry, woody materials like wood chips, straw, or other agricultural residues.
The Core Principle
At its heart, this method involves applying high temperatures to biomass, with or without the presence of oxygen, to break down its molecular bonds and release energy or create new chemical compounds.
Key Process: Combustion
Combustion is the most direct and common thermochemical process. It is simply the burning of biomass in the presence of ample oxygen to produce heat, which can then be used directly for heating spaces or to create steam that drives turbines for electricity generation.
Key Process: Gasification
Gasification involves heating biomass with a limited amount of oxygen, preventing full combustion. This process creates a mixture of gases known as synthesis gas, or syngas, which is a valuable intermediate product that can be burned to produce energy or further refined into liquid fuels and chemicals.
Key Process: Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass in the complete absence of oxygen. This process yields three primary products: a liquid known as bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), a solid charcoal-like substance called biochar, and a syngas byproduct. Bio-oil can be upgraded into transportation fuels, while biochar is an excellent soil amendment.
Exploring Biochemical Conversion: The Power of Biology
Biochemical conversion leverages natural biological processes to break down organic matter. It is best suited for feedstocks with high moisture content, such as food waste, animal manure, or dedicated energy crops like corn and sugarcane.
The Core Principle
This method relies on enzymes from bacteria, yeasts, and other microorganisms to digest biomass and convert it into useful products. These processes occur at much lower temperatures and pressures than their thermochemical counterparts.
Key Process: Fermentation
In fermentation, microbes (most commonly yeast) consume the sugars present in biomass and convert them into ethanol. This is the primary pathway for producing bioethanol, a common biofuel blended with gasoline, from crops like corn and sugarcane.
Key Process: Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion uses bacteria in an oxygen-free environment to decompose wet organic waste. The primary output is biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be captured and burned for heat or electricity. The remaining solid material, called digestate, is a nutrient-rich fertilizer.
The Critical Trade-offs: Speed vs. Specificity
Neither conversion pathway is universally superior; they are engineered for different feedstocks and different outcomes. Understanding their inherent trade-offs is key to evaluating their application.
Feedstock Flexibility
Thermochemical processes are generally more versatile. They can handle a wide variety of dry, low-moisture feedstocks, including tough, woody (lignocellulosic) materials that are difficult for microbes to break down.
Processing Speed
A major advantage of thermochemical conversion is speed. Reactions often complete in a matter of seconds or minutes. Biochemical processes, by contrast, are much slower, taking anywhere from several days to multiple weeks to complete.
Product Specificity
Biochemical processes offer high selectivity. Fermentation, for example, is highly optimized to produce a specific molecule like ethanol. Thermochemical processes tend to produce a broader mix of products (e.g., bio-oil, biochar, and syngas from pyrolysis) that often require further refining.
Operating Conditions
Biochemical methods operate under mild conditions—near ambient temperatures and pressures—leading to potentially lower operational energy costs. Thermochemical methods require significant energy input to maintain high temperatures, although well-designed systems can use their own product gases to sustain the reaction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct conversion pathway depends entirely on the resources available and the intended result.
- If your primary focus is large-scale heat and power from dry wood or agricultural waste: Thermochemical conversion, particularly combustion or gasification, is the most direct and established route.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid transportation fuel from sugar or starch crops: Biochemical conversion via fermentation is the industry standard for bioethanol production.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste while generating energy: Biochemical conversion through anaerobic digestion is the ideal solution to create biogas and a valuable fertilizer byproduct.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced biofuels and valuable co-products like biochar: Thermochemical conversion, specifically pyrolysis, offers a flexible platform for producing a portfolio of useful materials.
Understanding this fundamental division between heat and biology is the first step in effectively harnessing the potential of biomass as a renewable resource.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Type | Core Principle | Ideal Feedstock | Primary Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermochemical | Uses high heat to break down biomass | Dry, woody materials (e.g., wood chips, straw) | Heat, Syngas, Bio-oil, Biochar |
| Biochemical | Uses microorganisms/enzymes for decomposition | Wet, high-moisture materials (e.g., manure, food waste) | Bioethanol, Biogas, Digestate (fertilizer) |
Ready to implement a biomass conversion solution in your lab or facility? KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for both thermochemical and biochemical processes. From pyrolysis reactors to fermentation systems, our solutions help you achieve accurate, efficient, and scalable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your renewable energy research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















