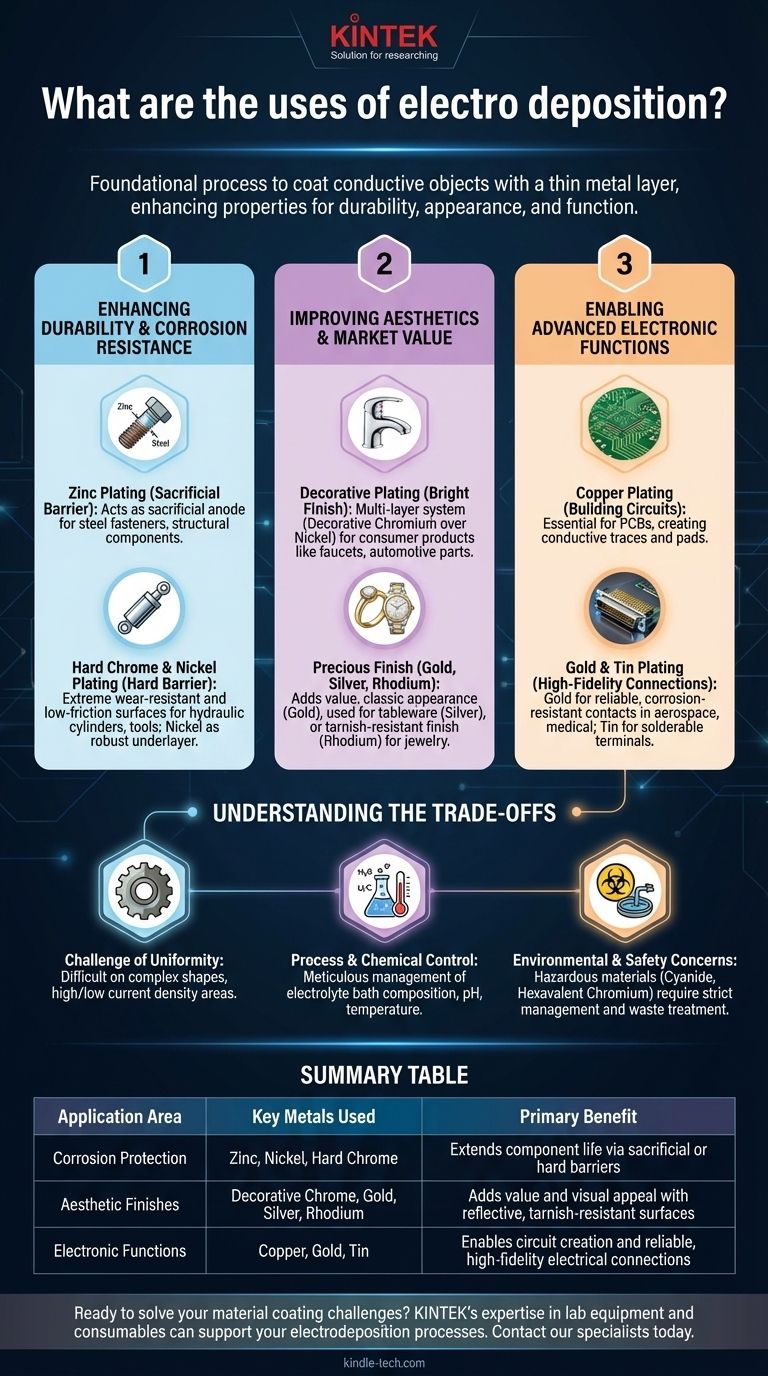
At its core, electrodeposition is a foundational process used across countless industries to coat a conductive object with a thin layer of metal. Its applications range from creating the durable, corrosion-resistant finishes on automotive parts and industrial equipment to applying the delicate, conductive gold layers on high-tech electronic connectors. It is a method for fundamentally changing the surface properties of a material.
The true power of electrodeposition lies in its versatility. It is not just one technique, but a family of processes used to grant materials new properties—enhancing durability, improving appearance, or enabling critical electronic functions that would otherwise be impossible.
Enhancing Durability and Corrosion Resistance
One of the primary drivers for using electrodeposition is to protect a base material, typically steel, from environmental degradation. The process adds a functional barrier that extends the life and reliability of the component.
The Sacrificial Barrier: Zinc Plating
Zinc plating, often called galvanizing, is a workhorse of the industrial world. It is applied to steel fasteners, structural components, and sheet metal.
The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial anode. It is more reactive than the underlying steel, meaning it will corrode first, thereby protecting the steel even if the coating is scratched.
The Hard Barrier: Chrome and Nickel Plating
Hard chrome plating is used to create an extremely hard, wear-resistant, and low-friction surface. It is not for decoration but for function, applied to components like hydraulic cylinders, pistons, and machine tools.
Nickel plating provides a robust layer of corrosion and wear resistance. It often serves as a critical underlayer for decorative chrome, providing the bulk of the corrosion protection beneath the thin, bright chrome finish.
Improving Aesthetics and Market Value
Beyond protection, electrodeposition is essential for creating the beautiful, reflective finishes that define the value of many consumer products.
The Bright Finish: Decorative Plating
When you see a gleaming chrome bumper, faucet, or motorcycle part, you are seeing a multi-layer system. A thin layer of decorative chromium is electrodeposited over a thicker layer of nickel. The nickel provides smoothness and corrosion protection, while the chrome provides the brilliant, blue-white color and tarnish resistance.
The Precious Finish: Gold, Silver, and Rhodium
Electrodeposition is the standard method for plating jewelry, watches, and high-end decorative items with precious metals.
Gold plating adds value and a classic appearance, while silver plating is used for tableware and decorative objects. Rhodium, a platinum-group metal, is often plated over white gold and silver to provide a bright, tanner-proof, and hypoallergenic finish.
Enabling Advanced Electronic Functions
The precision of electrodeposition makes it indispensable in the manufacturing of modern electronics. The ability to deposit pure, thin layers of conductive material is the basis for many components.
Building Circuits: Copper Plating
In Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing, copper is electrodeposited to create the conductive traces, pads, and vias that connect electronic components. This process allows for the creation of complex, multi-layered circuits on a microscopic scale.
High-Fidelity Connections: Gold and Tin Plating
Gold is electrodeposited onto electrical connectors, switch contacts, and bonding pads. Its high conductivity and supreme resistance to corrosion ensure a reliable electrical connection over the long term, which is critical in aerospace, medical, and telecommunications hardware.
Tin plating is widely used on terminals and component leads to provide a corrosion-resistant and highly solderable surface, facilitating the assembly of electronic devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, electrodeposition is a complex chemical process with significant challenges. Understanding these limitations is key to its successful application.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Achieving a perfectly uniform coating thickness is difficult, especially on complex shapes. High-current-density areas, like sharp edges and corners, tend to receive a thicker deposit, while low-current-density areas, like holes and recesses, receive a thinner one. This is known as the "throwing power" of the plating bath.
Process and Chemical Control
The electrodeposition bath, or electrolyte, is a complex chemical soup that must be meticulously maintained. The concentration of metal salts, additives, pH, and temperature must be kept within tight tolerances to ensure a quality coating.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
Many traditional plating processes involve hazardous materials, such as cyanide in some gold and copper baths or hexavalent chromium in chrome plating. Managing these chemicals and treating the resulting wastewater is a significant environmental and regulatory challenge for the industry.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your choice of electrodeposited coating depends entirely on the primary problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection for industrial parts: Zinc plating is your most cost-effective solution for sacrificial protection, while hard chrome is the choice for superior wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is a high-value decorative finish: A nickel-chromium system provides the classic "chrome" look, while gold, silver, or rhodium are the standard for jewelry and luxury goods.
- If your primary focus is electronic functionality: Copper is essential for creating circuit pathways on PCBs, while gold is the premier choice for ensuring long-term reliability in critical connectors.
Electrodeposition is the unseen technology that makes the objects around us more durable, beautiful, and functional.

Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Metals Used | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Protection | Zinc, Nickel, Hard Chrome | Extends component life via sacrificial or hard barriers |
| Aesthetic Finishes | Decorative Chrome, Gold, Silver, Rhodium | Adds value and visual appeal with reflective, tarnish-resistant surfaces |
| Electronic Functions | Copper, Gold, Tin | Enables circuit creation and reliable, high-fidelity electrical connections |
Ready to solve your material coating challenges? Whether you need to protect industrial parts, enhance product aesthetics, or ensure electronic reliability, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can support your electrodeposition processes. Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior surface properties and performance for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity



















