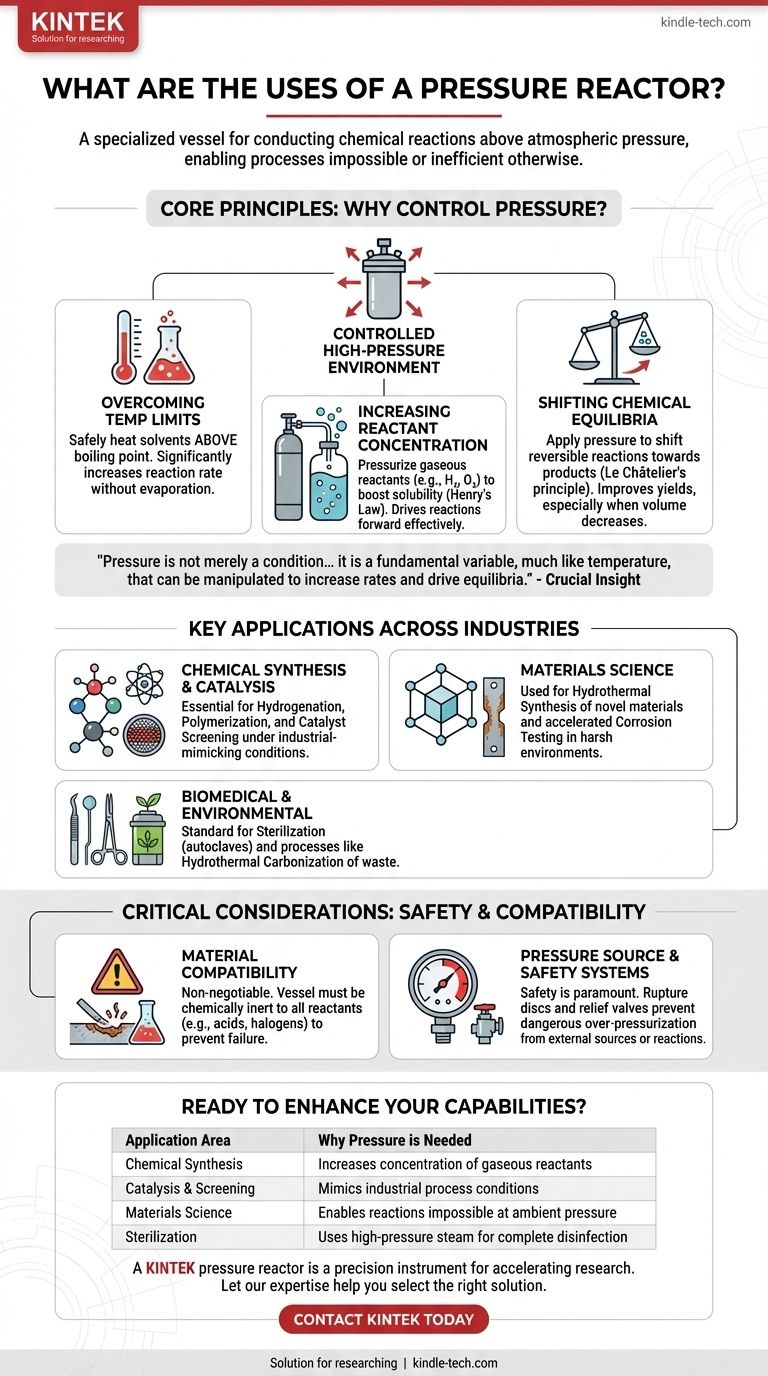
At its core, a pressure reactor is a specialized vessel for conducting chemical reactions above atmospheric pressure. These devices are essential tools in chemistry, materials science, and engineering, used for a wide range of applications including chemical synthesis like hydrogenation and polymerization, catalyst screening, materials testing, and high-pressure sterilization. The primary function is to create a controlled, high-pressure environment that enables reactions or processes that are otherwise impossible or inefficient.
The crucial insight is that pressure is not merely a condition to be contained; it is a fundamental variable, much like temperature, that can be manipulated. A pressure reactor gives you direct control over this variable, allowing you to increase reaction rates, work with volatile substances, and drive chemical equilibria toward desired products.
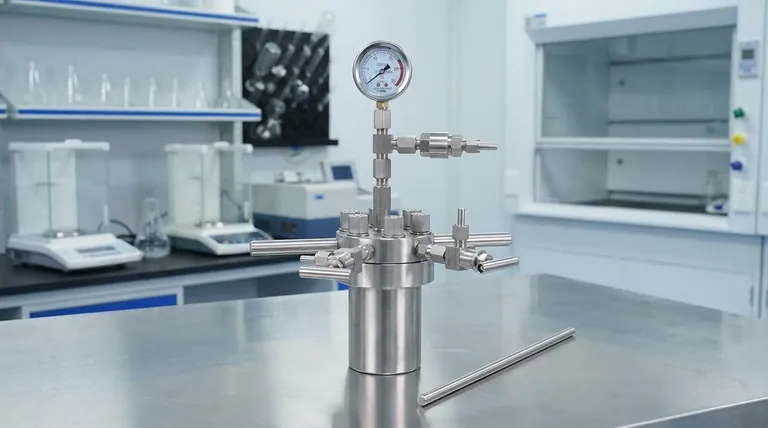

Why Control Pressure? The Core Principles
Understanding why you would use a pressure reactor is more important than simply listing its applications. The decision to use one is based on fundamental chemical and physical principles.
Overcoming Temperature Limitations
Many chemical reactions are painfully slow at room temperature. A common way to speed them up is by heating the solvent.
A pressure reactor allows you to safely heat a solvent far above its normal boiling point. This significantly increases the reaction rate without losing the solvent to evaporation, a common limitation of standard laboratory glassware.
Increasing Reactant Concentration
For reactions involving gaseous reactants, like hydrogen (H₂), oxygen (O₂), or carbon monoxide (CO), their low solubility in liquids can be a major bottleneck.
By pressurizing the reactor with the gas, you dramatically increase its concentration in the liquid phase, as described by Henry's Law. This higher concentration drives the reaction forward much more efficiently, which is the principle behind catalytic hydrogenation.
Shifting Chemical Equilibria
Many reactions are reversible, meaning they do not go to completion but instead reach a chemical equilibrium.
According to Le Châtelier's principle, if a reaction results in a decrease in the number of gas molecules (a reduction in volume), applying high pressure will shift the equilibrium to favor the formation of products. This is a powerful tool for improving yields.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to control pressure unlocks capabilities across a diverse range of scientific and industrial fields.
Chemical Synthesis & Catalysis
This is the most common domain for pressure reactors. They are indispensable for screening new catalysts under conditions that mimic industrial processes.
Specific reactions like hydrogenation (adding hydrogen across a molecule) and polymerization (linking monomers into long chains) often require elevated pressure and temperature to proceed effectively.
Materials Science
Pressure reactors, also known as autoclaves, are used to synthesize novel materials like zeolites or certain nanomaterials through hydrothermal or solvothermal processes.
They are also used for accelerated aging and corrosion testing, where materials are exposed to high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive environments to simulate long-term performance.
Biomedical and Environmental
In the medical field, autoclaves are the standard for sterilizing surgical instruments, lab equipment, and other materials using high-pressure steam.
In environmental applications, they are used for processes like hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of wet biomass or wastewater sludge. This process can be used to create sterile soil conditioners or solid fuels.
Understanding the Critical Considerations
While powerful, pressure reactors introduce complexities that must be managed. Objectivity requires acknowledging these trade-offs.
Material Compatibility is Non-Negotiable
The reactor vessel must be chemically inert to your reaction mixture under high pressure and temperature. While stainless steel is common, it is not universally resistant.
Aggressive acids, halogens, or other reactants can corrode the vessel, leading to reaction failure and catastrophic safety risks. Always verify the chemical resistance of the reactor material and seals against all components in your system.
Pressure Source and Safety Systems
Pressure can be generated by an external source (e.g., a gas cylinder) or by the reaction itself as temperature increases. This stored energy makes safety paramount.
Modern reactors are engineered with critical safety features like rupture discs or pressure relief valves that prevent over-pressurization. Bypassing or failing to understand these systems is extremely dangerous.
Operational Complexity and Cost
Compared to standard glassware, pressure reactors are significantly more expensive and complex to operate. They require careful assembly, leak testing, and proper handling procedures. This investment in equipment and training must be factored into any project plan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a pressure reactor is the right tool, align your choice with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is accelerating slow organic reactions: Use a pressure reactor to safely heat solvents well above their atmospheric boiling point, drastically reducing reaction times.
- If your primary focus is working with gaseous reagents: A pressure reactor is essential for increasing the concentration of gases like hydrogen or oxygen to drive reactions like hydrogenations or oxidations.
- If your primary focus is materials synthesis or catalysis: An autoclave allows you to mimic industrial conditions or use hydrothermal methods to create unique materials and test catalyst performance.
- If your primary focus is sterilization: An autoclave is the industry-standard tool for using high-pressure steam to ensure complete disinfection of equipment and media.
By understanding its underlying principles, a pressure reactor becomes a precision instrument for solving specific chemical challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use Case | Why Pressure is Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Synthesis | Hydrogenation, Polymerization | Increases concentration of gaseous reactants (e.g., H₂) |
| Catalysis & Screening | Testing new catalysts | Mimics industrial process conditions for accurate results |
| Materials Science | Hydrothermal synthesis, Corrosion testing | Enables reactions and aging tests impossible at ambient pressure |
| Sterilization | Medical & lab equipment disinfection | Uses high-pressure steam to ensure complete sterility |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities?
A pressure reactor from KINTEK is more than just a vessel; it's a precision instrument for accelerating research and development. Whether you are synthesizing new compounds, screening catalysts, developing advanced materials, or ensuring sterile conditions, controlling pressure is key to achieving your goals efficiently and safely.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories worldwide. Let our expertise help you select the right pressure reactor to drive your projects forward.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research
- What role does an autoclave play in simulating PWR conditions? Advanced Material Validation for Nuclear Safety
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS



















