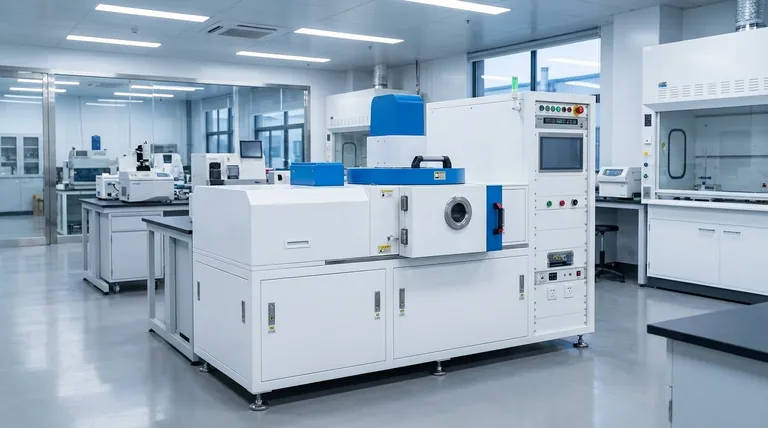
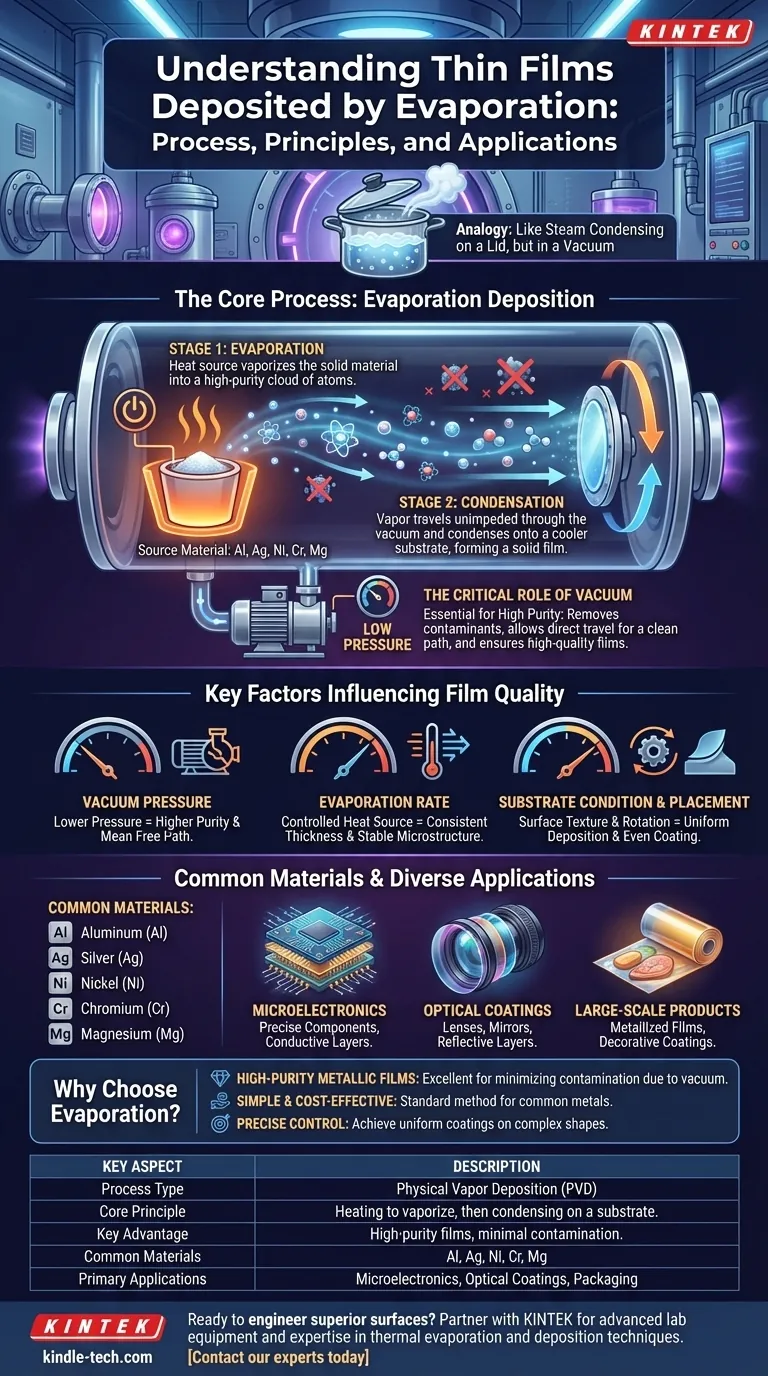
In essence, thin films deposited by evaporation are ultra-thin layers created by heating a source material in a vacuum until it turns into a vapor. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, forming a solid, high-purity film. The entire process is analogous to the way steam from a boiling pot condenses as water droplets on a cooler lid.
This technique is a cornerstone of materials science, valued for its direct and effective method of creating high-quality coatings. It operates on a simple principle: transforming a solid material into a gas and back into a solid, all within a controlled vacuum environment to ensure purity.

The Core Principles of Evaporation Deposition
Evaporation is a form of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), a category of techniques where a material is vaporized and then deposited onto a surface. The process is governed by two fundamental stages happening in a specific environment.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. This vacuum is not a trivial detail; it is essential for success.
A vacuum removes unwanted air and water vapor, preventing these particles from contaminating the final film. It also allows the evaporated material to travel directly to the substrate without colliding with other gas molecules, ensuring a clean and direct deposition path.
Stage 1: The Evaporation Process
To begin, a source material—such as a piece of aluminum or silver—is heated. The energy supplied by a heat source causes the material to evaporate (or sublimate, turning directly from a solid to a gas).
This transforms the solid source into a cloud of vaporized particles within the vacuum chamber.
Stage 2: The Condensation Process
The vaporized particles travel unimpeded through the vacuum until they strike the substrate. The substrate is kept at a cooler temperature than the source.
Upon contact with this cooler surface, the particles lose energy and condense back into a solid state. This gradual buildup of condensed particles is what forms the thin film.
Key Factors Influencing Film Quality
The final quality and uniformity of an evaporated thin film are not accidental. They are the result of carefully controlling several process variables.
Vacuum Pressure
A higher degree of vacuum (lower pressure) directly improves the film's purity. It minimizes the chance of background gases getting trapped in the film and increases the "mean free path," allowing source particles a clearer journey to the substrate.
Evaporation Rate
The speed at which the source material evaporates is determined by the temperature of the heat source. Controlling this rate is crucial for achieving consistent film thickness and a stable microstructure.
Substrate Condition and Placement
The state of the substrate surface can impact the final film. A rough surface may lead to non-uniform deposition.
Furthermore, rotating the substrate holder during deposition is a common technique used to ensure the vapor coats the surface evenly from all angles.
Common Materials and Applications
One of the great advantages of thermal evaporation is its compatibility with a wide variety of materials.
A Versatile Material Palette
Many elements can be effectively deposited using this method. Common examples include:
- Aluminum (Al)
- Silver (Ag)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Magnesium (Mg)
This versatility makes the technique suitable for numerous industries and applications.
From Microfabrication to Macro Products
Evaporation is used to produce everything from highly precise components in microelectronics to large-scale commercial products.
You can find its application in creating conductive layers on circuits, optical coatings on lenses, and even the reflective layers on metallized plastic films used in food packaging and decorations.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding the core principles allows you to see where this technique excels.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metallic films: Evaporation is an excellent choice due to the high-vacuum environment that minimizes contamination from unwanted gases.
- If your primary focus is creating simple, reflective, or conductive coatings: This is a standard, cost-effective method for depositing materials like aluminum, silver, and chrome onto various substrates.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex shape uniformly: You must consider system design, especially the use of substrate rotation and precise source-to-substrate distance, to achieve an even deposition.
Ultimately, evaporation is a powerful and foundational technique for engineering surfaces at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Principle | Heating a material in a vacuum to vaporize it, then condensing it onto a cooler substrate. |
| Key Advantage | High-purity metallic films with minimal contamination. |
| Common Materials | Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), Nickel (Ni), Chromium (Cr) |
| Primary Applications | Microelectronics, optical coatings, reflective layers for packaging. |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces with high-purity thin films?
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need to master thermal evaporation and other deposition techniques. Whether you are developing next-generation microchips, precision optics, or advanced packaging, our expertise ensures your laboratory operates at peak performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can support your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing



















