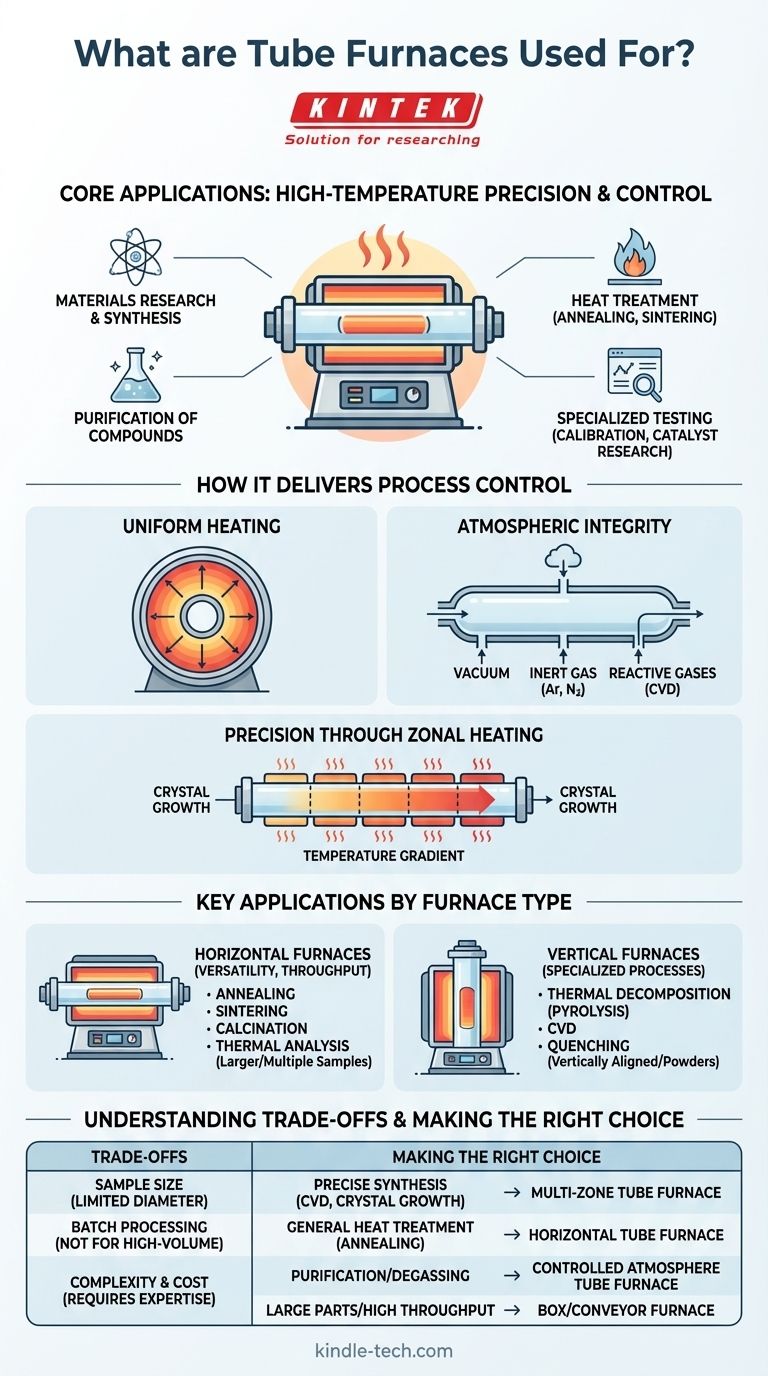
At its core, a tube furnace is used for a wide range of high-temperature thermal processes requiring exceptional precision and atmospheric control. Applications span materials research and production, including the synthesis of new materials, heat treatment like annealing and sintering, purification of compounds, and specialized testing such as thermocouple calibration or catalyst research.
The primary reason to use a tube furnace is not simply to achieve high temperatures, but to do so with exceptional uniformity inside a tightly controlled atmosphere. This control over the processing environment is what makes it indispensable for sensitive and advanced applications.

How a Tube Furnace Delivers Process Control
A tube furnace's value comes from its unique design, which facilitates a level of control that standard box furnaces or ovens cannot match. This control is centered on two key principles: temperature uniformity and atmospheric integrity.
The Principle of Uniform Heating
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical chamber, typically made of ceramic or quartz, that is surrounded by heating elements. This configuration ensures that heat radiates evenly toward the center of the tube from all directions.
This design results in a highly uniform hot zone, which is critical for processes where every part of the sample must experience the exact same temperature. It also enables rapid heat-up and cool-down cycles, improving efficiency in laboratory and production settings.
The Critical Role of Atmospheric Control
The defining feature of a tube furnace is its sealed tube. This containment allows you to completely dictate the gaseous environment surrounding your sample.
You can create a vacuum to remove reactive gases, introduce a flow of inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, or use specific reactive gases for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD). This atmospheric control is non-negotiable for purifying materials, growing crystals, or synthesizing advanced coatings.
Precision Through Zonal Heating
More advanced tube furnaces are configured with multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube.
This zonal heating allows you to create precise temperature gradients, which is essential for specialized work like crystal growth or certain types of chemical transport reactions.
Key Applications by Furnace Type
While all tube furnaces share the same basic principles, their orientation—horizontal or vertical—makes them better suited for different tasks.
Horizontal Furnaces: For Versatility and Throughput
Horizontal furnaces are the most common type. Their orientation makes it easy to load and unload samples, making them well-suited for general-purpose heat treatment.
They are widely used for processes like annealing, sintering, calcination, and thermal analysis. They can often handle larger or multiple samples, and in some cases, can be adapted for continuous processing.
Vertical Furnaces: For Specialized Processes
Vertical furnaces are used when gravity can aid the process or when samples must be kept from touching the tube walls.
They excel at applications like thermal decomposition (pyrolysis), CVD, and dropping a sample into a quench tank after heating. They are particularly effective for experiments on vertically aligned samples or powders that need uniform heating without being spread out.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Sample Size and Geometry
The most obvious limitation is the diameter of the process tube. Tube furnaces are inherently designed for smaller samples that can fit within this confined space, making them unsuitable for large, bulky parts.
Batch Processing Nature
Most tube furnace applications are batch processes, where one sample or a small group of samples is processed at a time. While some continuous systems exist, they are not typically designed for high-volume manufacturing in the way a conveyor furnace is.
Increased Complexity and Cost
The features that provide precision—gas mixing systems, vacuum pumps, multi-zone controllers—add significant complexity and cost compared to a simple box furnace. These features require more user expertise to operate safely and effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing tool depends entirely on the requirements of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is precise material synthesis (like CVD or crystal growth): A multi-zone tube furnace with advanced atmospheric control is the correct and necessary tool.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment (like annealing or hardening): A horizontal tube furnace offers an ideal balance of thermal uniformity and operational flexibility.
- If your primary focus is purifying materials or degassing samples: The ability of a tube furnace to operate under a controlled inert atmosphere or vacuum is its defining advantage.
- If your primary focus is processing large parts or achieving high throughput: A box furnace or conveyor furnace is likely a more suitable and cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, choosing a tube furnace is a decision to prioritize absolute control over the processing environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Heating Chamber | Uniform hot zone for consistent results | Annealing, Sintering |
| Sealed Tube Design | Controlled atmosphere (vacuum, inert gas) | Purification, CVD |
| Multi-Zone Heating | Precise temperature gradients | Crystal Growth, Research |
| Horizontal/Vertical Orientation | Flexibility for different sample types | General heat treatment, Pyrolysis |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise thermal processing?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance tube furnaces designed for your specific laboratory needs. Whether you are synthesizing new materials, conducting heat treatment, or requiring advanced atmospheric control, our equipment delivers the accuracy and reliability you demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK tube furnace can optimize your research and production processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab



















