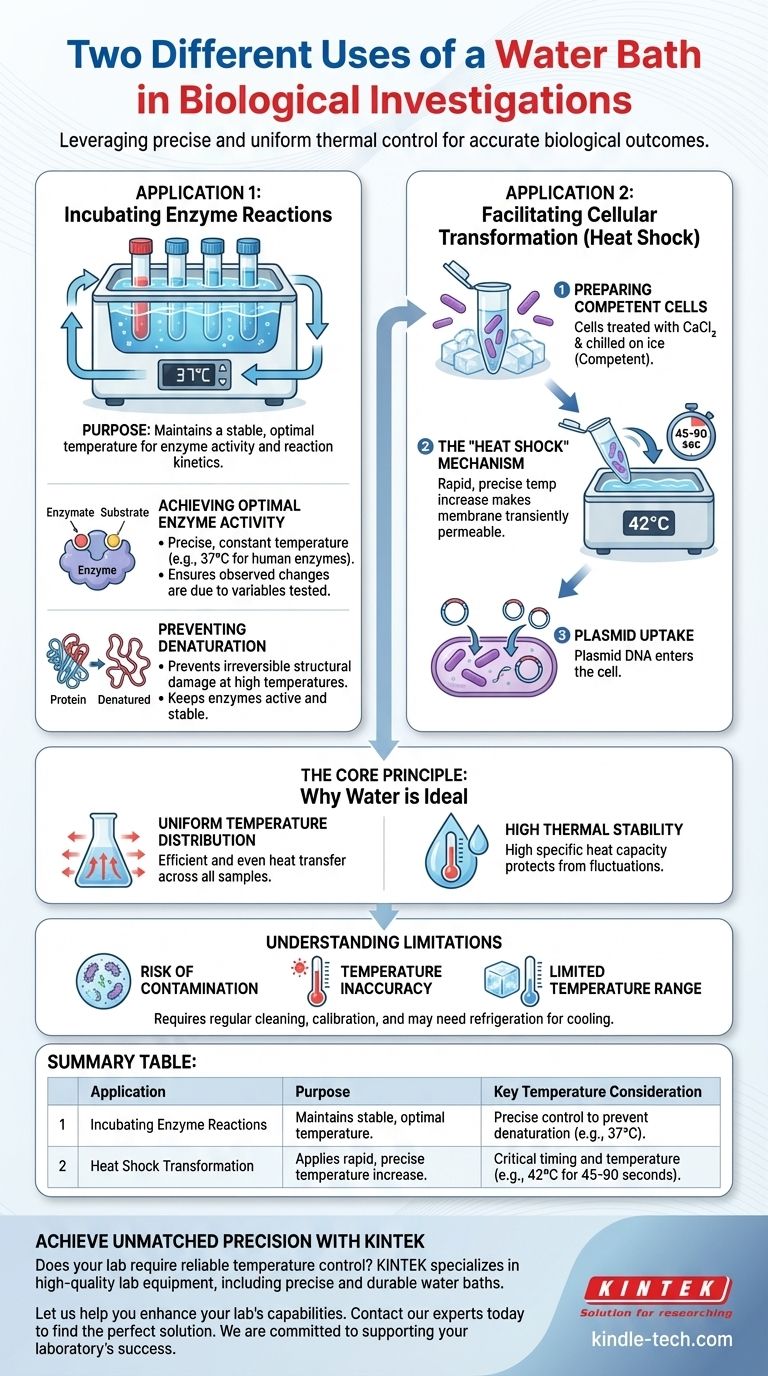
In biological investigations, a water bath is most commonly used for two distinct purposes: incubating samples at a constant, specific temperature for processes like enzyme reactions, and applying a rapid, precise temperature change to cells, known as "heat shock," to facilitate genetic transformation. These functions leverage water's ability to maintain and transfer heat uniformly.
The fundamental role of a water bath is to provide a highly stable and uniform thermal environment. This precision is not a convenience but a requirement for ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of countless temperature-sensitive biological experiments.

The Core Principle: Why Water is the Ideal Medium
Before examining its uses, it's crucial to understand why water is the medium of choice. Unlike a dry incubator or heat block, which can have hot spots, circulating water provides a superior environment for temperature control.
Uniform Temperature Distribution
Water transfers heat more efficiently and evenly than air. This ensures that every sample submerged in the bath, regardless of its position, is exposed to the exact same temperature.
High Thermal Stability
Water has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it can absorb a lot of heat without a significant change in its own temperature. This property creates a thermal buffer, protecting sensitive biological samples from an unstable ambient environment and rapid temperature fluctuations.
Application 1: Incubating Enzyme Reactions
One of the most fundamental uses of a water bath is to study enzyme kinetics, which is the rate at which an enzyme catalyzes a reaction. This process is profoundly dependent on temperature.
Achieving Optimal Enzyme Activity
Every enzyme has an optimal temperature at which it functions most efficiently. A water bath allows a researcher to set and maintain this precise temperature (e.g., 37°C for most human enzymes) throughout an experiment.
This ensures that any observed change in reaction rate is due to the variable being tested (like substrate concentration), not a hidden fluctuation in temperature.
Preventing Denaturation
If the temperature rises even slightly above the optimal range, an enzyme's delicate three-dimensional structure can begin to unravel. This process, called denaturation, is often irreversible and permanently inactivates the enzyme.
A water bath provides the control needed to keep the enzyme active and stable, preventing denaturation from compromising the experimental results.
Application 2: Facilitating Cellular Transformation (Heat Shock)
A second, completely different application is in genetic engineering, specifically for introducing foreign DNA (like a plasmid) into bacteria. This technique is known as heat shock transformation.
Preparing Competent Cells
First, bacteria are treated with a solution of calcium chloride and chilled on ice. This makes their cell membranes "competent"—primed to accept foreign DNA.
The "Heat Shock" Mechanism
The competent cells are mixed with the desired plasmid DNA and remain on ice. They are then briefly moved into a water bath set to a very specific temperature, typically 42°C, for a short, timed period (e.g., 45-90 seconds).
This rapid temperature shift creates a thermal imbalance that is believed to make the bacterial membrane transiently permeable, allowing the plasmid DNA to enter the cell. The precise temperature and timing are critical for success.
Understanding the Limitations
While indispensable, water baths are not without their operational challenges. Awareness of these issues is key to maintaining experimental integrity.
Risk of Contamination
Standing, warm water is an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, algae, and fungi. Without regular cleaning and the use of algaecides, the water bath can become a significant source of contamination for your samples.
Temperature Inaccuracy
The temperature displayed on the unit may not perfectly match the actual water temperature. It is critical to periodically calibrate the water bath with a certified thermometer to ensure accuracy, especially for highly sensitive procedures.
Limited Temperature Range
A standard water bath cannot cool below the ambient room temperature. For experiments requiring temperatures below this (e.g., 4°C), a refrigerated or circulating water bath is necessary.
Matching the Technique to the Biological Goal
Your specific experimental goal will dictate how you use the water bath.
- If your primary focus is studying reaction kinetics or metabolic pathways: Use the water bath to provide a long-term, stable incubation at the optimal temperature for your enzyme or organism.
- If your primary focus is genetic engineering: Use the water bath to deliver a precise, short-duration heat shock to competent cells for efficient bacterial transformation.
- If your primary focus is cell culture: Use the water bath to gently warm media and other reagents to body temperature (37°C) before adding them to live cells, preventing cellular shock.
Ultimately, mastering the use of a water bath is about leveraging its capacity for precise thermal control to achieve reliable and repeatable biological outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Temperature Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Incubating Enzyme Reactions | Maintains a stable, optimal temperature for enzyme activity and reaction kinetics. | Precise control to prevent denaturation (e.g., 37°C). |
| Heat Shock Transformation | Applies a rapid, precise temperature increase to introduce DNA into bacterial cells. | Critical timing and temperature (e.g., 42°C for 45-90 seconds). |
Achieve Unmatched Precision in Your Biological Investigations
Does your lab require reliable temperature control for sensitive experiments like enzyme kinetics or genetic transformation? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including precise and durable water baths designed to meet the rigorous demands of biological research. Our products ensure uniform heating and thermal stability, which are critical for the accuracy and reproducibility of your work.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to find the perfect water bath solution for your specific application. We are committed to supporting your laboratory's success with equipment you can trust.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 100L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- How does a thermostatic water bath function in ODS steel corrosion tests? Ensure Precise Bio-Simulation Accuracy
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the working temperature range of a high-temperature oil bath? Optimize Your High-Heat Lab Processes
- Why is a recirculating thermostatic bath required for high-precision CV testing? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Data
- What is the primary role of a constant temperature water bath in biomass washing? Optimize Poplar Pretreatment.



















