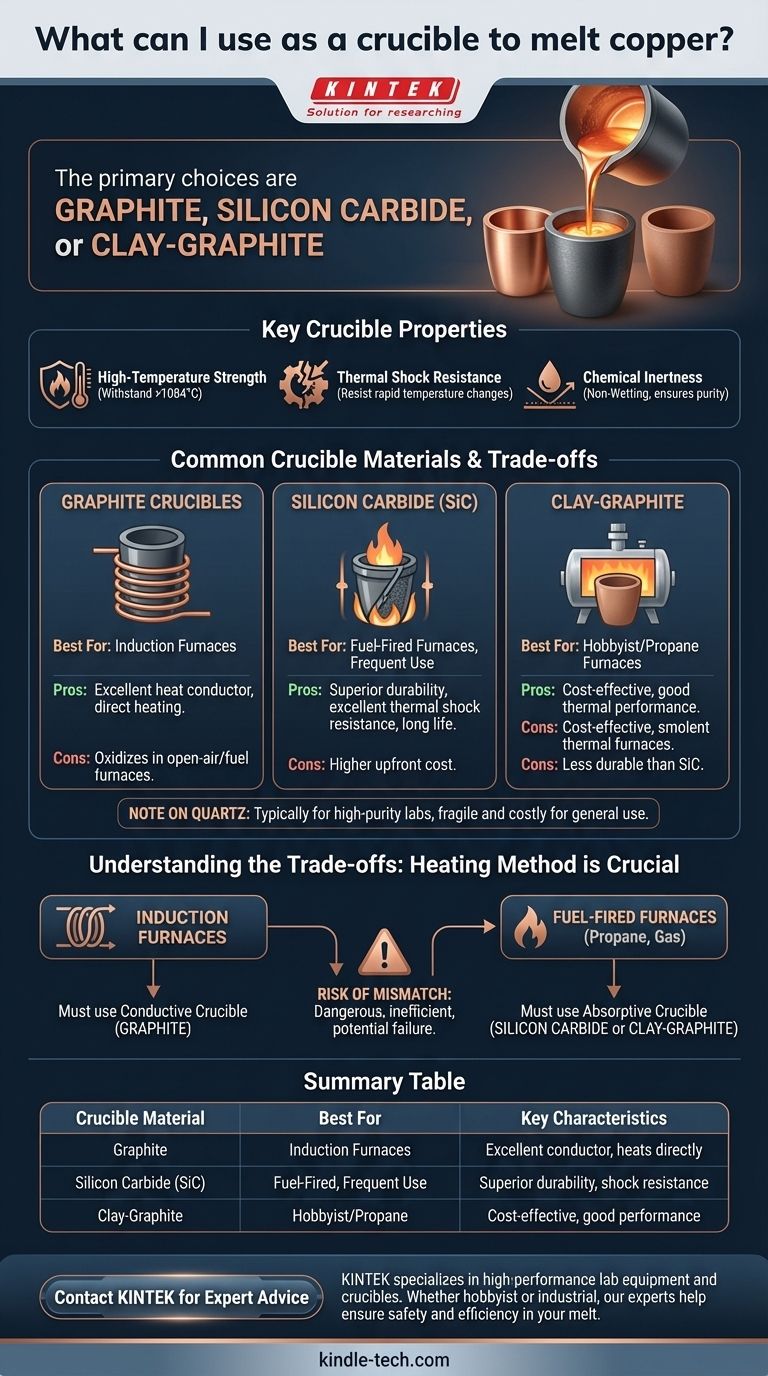
For melting copper, your primary choices for a crucible are graphite, silicon carbide, or a clay-graphite composite. These materials are engineered to withstand the extreme temperatures required, which for copper is 1084°C (1984°F). The best option for you depends directly on your heating method (furnace type), the scale of your work, and your budget.
The ideal crucible for copper doesn't just withstand the heat; it must also resist chemical reactions with the molten metal and survive the thermal shock of rapid heating and cooling. Your choice of material—graphite, silicon carbide, or clay—is a trade-off between cost, durability, and compatibility with your heating source.

What Defines a Good Crucible for Copper?
Before selecting a material, it's essential to understand the properties that make a crucible safe and effective. The wrong choice can lead to a failed casting, a contaminated melt, or a dangerous spill of molten metal.
High-Temperature Strength
The most obvious requirement is that the crucible must not melt or deform at temperatures well above copper's melting point. A quality crucible is rated for the intense heat inside a forge or furnace.
Thermal Shock Resistance
A crucible undergoes immense stress as it goes from room temperature to over 1000°C and back again. Materials with poor thermal shock resistance will crack, leading to catastrophic failure.
Chemical Inertness (Non-Wetting)
A good crucible should be "non-wetting," meaning the molten copper does not stick to or react with its surface. This is achieved with a dense material structure that prevents the liquid metal from seeping into the crucible's walls, ensuring both the purity of your copper and the longevity of your crucible.
Common Crucible Materials for Melting Copper
Each material has a distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications.
Graphite Crucibles
Graphite is an excellent conductor of heat and is the standard choice for induction furnaces. The furnace's magnetic field directly heats the conductive graphite, which in turn efficiently melts the copper inside.
However, pure graphite will oxidize (burn away) in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures, giving it a shorter lifespan in open-air, fuel-fired furnaces.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
Often found as a composite mixed with graphite, silicon carbide offers superior durability, mechanical strength, and excellent resistance to thermal shock.
These crucibles are more expensive upfront but last significantly longer than other types, especially in fuel-fired furnaces. They are a professional-grade choice for serious or frequent use.
Clay-Graphite Crucibles
This is the traditional and most common type of crucible for hobbyists and small-scale founders using fuel-fired (e.g., propane) forges.
They offer a good balance of thermal performance and cost-effectiveness. While not as durable as silicon carbide, they are a reliable and accessible starting point.
A Note on Quartz
While quartz is a possible crucible material, it is typically reserved for high-purity laboratory environments or specialized industrial processes. For general copper melting, its higher cost and relative fragility make graphite, SiC, and clay-graphite composites far more practical choices.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Heating Method is Crucial
The single most important factor influencing your crucible choice is your furnace type. Mismatching the crucible and furnace is a common and dangerous mistake.
For Induction Furnaces
You must use a conductive crucible. Graphite is the ideal material because the furnace works by inducing an electric current directly within the crucible itself, turning it into the heating element. A non-conductive clay crucible would not heat up in an induction furnace.
For Fuel-Fired Furnaces (Propane, Gas, Coal)
Here, the furnace heats the crucible from the outside with a flame. Silicon carbide and clay-graphite crucibles are designed for this. They absorb the external heat and transfer it inward to melt the metal. Using a pure graphite crucible in a flame-fired furnace will cause it to degrade very quickly from oxidation.
The Risk of a Mismatch
Using the wrong crucible for your heating method is not just inefficient—it's dangerous. An improperly heated crucible can fail to reach temperature, or worse, it can crack and fail unexpectedly, spilling molten copper.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your decision should be guided by your equipment and goals.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist work with a propane furnace: Start with a clay-graphite crucible for a proven balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is durability and frequent use in any furnace type: Invest in a silicon carbide (SiC) crucible, as its long life and resistance to wear will pay off over time.
- If your primary focus is using an induction furnace: A graphite crucible is the standard and most effective choice required for this heating method.
Ultimately, matching your crucible material to your heating method is the most critical step for a safe and successful melt.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Induction Furnaces | Excellent heat conductor, heats directly in induction field |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Fuel-Fired Furnaces, Frequent Use | Superior durability, excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Clay-Graphite | Hobbyist/Propane Furnaces | Cost-effective, good thermal performance for small-scale work |
Ready to find the perfect crucible for your copper melting needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles designed for demanding applications. Whether you're a hobbyist or running an industrial lab, our experts can help you select the right graphite, silicon carbide, or clay-graphite crucible to ensure safety, efficiency, and purity in your metal melting processes.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
People Also Ask
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What are the effects of magnetron sputtering? Achieve High-Quality, Durable Thin Films for Your Lab
- What is the fundamental of magnetron sputtering? Master High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is sputtering in plasma treatment? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is a magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















