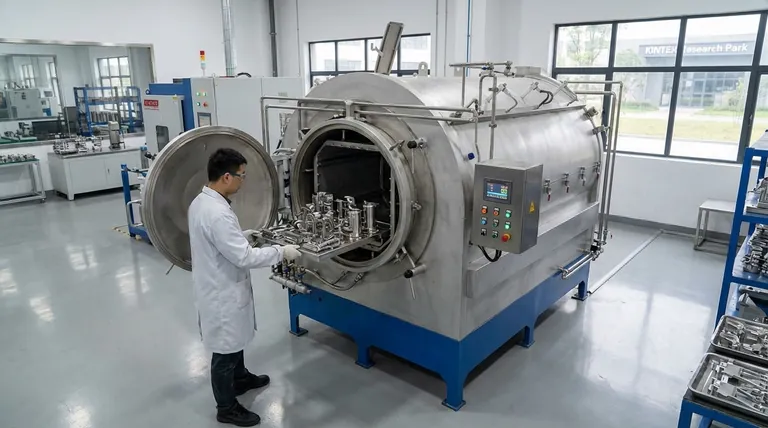
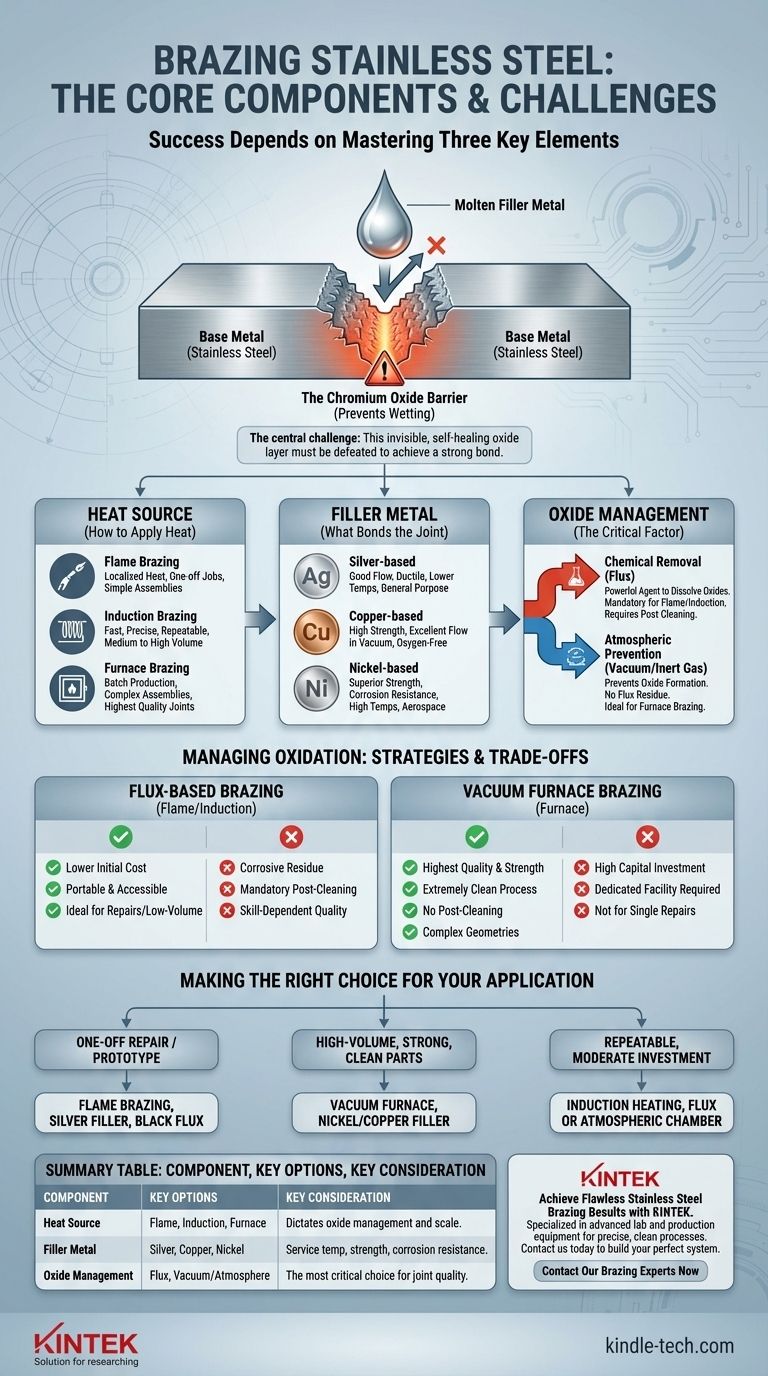
To successfully braze stainless steel, you need three core components: an appropriate heat source, a compatible filler metal, and a method to manage the stubborn oxide layer that forms on the steel's surface. The method for handling this oxide—either by chemically removing it with flux or by preventing its formation in a controlled atmosphere—is the most critical factor determining the success of your joint.
The central challenge in brazing stainless steel is not the metal itself, but the invisible, self-healing layer of chromium oxide on its surface. Your entire brazing strategy, from filler metal choice to heating method, must be built around defeating this barrier to achieve a strong, reliable bond.

The Core Challenge: The Oxide Layer
Brazing works by flowing a molten filler metal into a joint through capillary action. For this to happen, the filler must "wet" the surfaces of the base metals. The primary obstacle with stainless steel is a chemical layer that prevents this wetting.
The Role of Chromium Oxide
Stainless steel is "stainless" because it contains chromium, which reacts with oxygen in the air to form a very thin, stable, and passive layer of chromium oxide.
This layer is excellent for preventing rust, but it is a major problem for brazing. The molten filler metal cannot bond to this oxide; it will bead up and refuse to flow, much like water on a waxed car.
Overcoming the Barrier
To create a successful braze joint, you must overcome this oxide layer. There are two primary strategies:
- Chemical Removal: Using a powerful chemical agent, known as flux, to dissolve and displace the oxide layer, allowing the filler metal to contact and bond with the raw steel beneath.
- Atmospheric Prevention: Placing the parts in a high-purity vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere. By removing the oxygen, the oxide layer cannot form during heating, allowing the filler metal to wet the surface freely.
Essential Components for Brazing Stainless Steel
With the core challenge understood, choosing your specific tools and materials becomes a logical process.
Choosing a Heat Source
The method used to apply heat depends on the scale of your operation and the complexity of the part.
- Flame Brazing: Uses a torch. This is best for one-off jobs, simple assemblies, or repairs where localized heat is sufficient. It almost always requires the use of flux.
- Induction Brazing: Uses an electromagnetic coil to generate heat directly within the part. It is fast, precise, and repeatable, making it excellent for medium to high-volume production. It is often used with flux but can be adapted for atmospheric brazing.
- Furnace Brazing: Heats the entire assembly in a controlled environment. This is the ideal method for batch production, complex assemblies, and achieving the highest quality joints, as it is most often done in a vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
Selecting the Right Filler Metal
The choice of filler metal depends on the service temperature, strength requirements, and corrosive environment the final part will face. Common families include:
- Silver-based fillers: Excellent general-purpose choice with good flow characteristics and ductility. They braze at relatively low temperatures.
- Copper-based fillers: Often used in vacuum furnace brazing for their high strength and excellent flow in oxygen-free environments. Pure copper is a common choice.
- Nickel-based fillers: Provide superior strength and corrosion resistance, especially at high temperatures. They are a standard choice for aerospace and other demanding applications, almost exclusively used in vacuum furnaces.
Managing Oxidation: Flux vs. Atmosphere
This is the most critical decision and is directly tied to your heating method.
- Brazing with Flux: When flame or induction heating in open air, a flux is mandatory. A special flux for stainless steel (often called "black flux" due to its color) is required to be aggressive enough to dissolve the chromium oxides.
- Brazing in a Vacuum: When using a furnace, pulling a high vacuum removes the oxygen. This not only prevents oxidation but can also cause the existing thin oxide layer to dissociate, or break down, at high temperatures. This results in an exceptionally clean, strong joint without any corrosive flux residue.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each approach to managing oxidation comes with distinct advantages and disadvantages that dictate its best use case.
Flux-Based Brazing
This method, typically using a flame or induction coil, is accessible but requires significant operator skill.
- Advantages: Lower initial equipment cost and portability make it ideal for repairs and low-volume work.
- Disadvantages: Flux residue is highly corrosive and must be completely removed after brazing to prevent future joint failure. The final joint quality is highly dependent on operator skill and may not be as clean or strong as a furnace-brazed joint.
Vacuum Furnace Brazing
This method is the gold standard for quality and repeatability but requires significant capital investment.
- Advantages: Produces the highest quality, strongest, and most aesthetically pleasing joints. The process is extremely clean, requiring no post-braze cleaning of flux. It is ideal for complex geometries and mission-critical components.
- Disadvantages: The equipment is extremely expensive and requires a dedicated facility. The process is not suitable for single repairs or low-volume prototyping due to long cycle times and high operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select your method based on your project's specific goals for quality, volume, and cost.
- If your primary focus is a one-off repair or simple prototype: Use flame brazing with a silver-based filler and the correct black flux for stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of strong, clean parts: Invest in vacuum furnace brazing with a nickel or copper-based filler for the most reliable and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is repeatable production with moderate investment: Consider induction heating, which offers more control than a flame and can be used with flux or integrated into an atmospheric chamber.
Ultimately, your success hinges on selecting a complete system—heat, filler, and oxide management—that directly addresses the unique chemical properties of stainless steel.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Options | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Flame, Induction, Furnace | Dictates oxide management method and production scale. |
| Filler Metal | Silver-based, Copper-based, Nickel-based | Chosen for service temperature, strength, and corrosion resistance. |
| Oxide Management | Flux (Chemical Removal), Vacuum/Atmosphere (Prevention) | The most critical choice for joint quality and cleanliness. |
Achieve flawless stainless steel brazing results with KINTEK.
Whether you are developing prototypes in an R&D lab or scaling up for high-volume production, selecting the right equipment is crucial for overcoming the challenge of chromium oxide. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab and production equipment, including induction heating systems and vacuum furnaces designed for precise, clean brazing processes.
Let our experts help you build the perfect brazing system for your specific application, ensuring strong, reliable, and repeatable joints. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing capabilities.
Contact Our Brazing Experts Now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for pyrolysis? Optimize for Biochar, Bio-oil, or Syngas
- How much more efficient are electric arc furnaces? Achieve 90% Energy Savings in Steel Production
- What are the benefits of using an inert gas to prevent oxidation in welding? Ensure Weld Strength and Integrity
- What role does a benchtop incubator shaker play during antimicrobial activity assessment? Ensure Precise Results
- How do Ultra-Low Temperature freezers contribute to public health? Preserving Vaccines and Research for a Healthier World
- Is pyrolysis a green technology? Unlocking Sustainable Waste-to-Value Solutions
- What is the lifespan of a filter media? Understand the 3 Types for Optimal Filtration
- What is the high temperature of quartz? Key Thresholds for Crystalline vs. Fused Silica



















