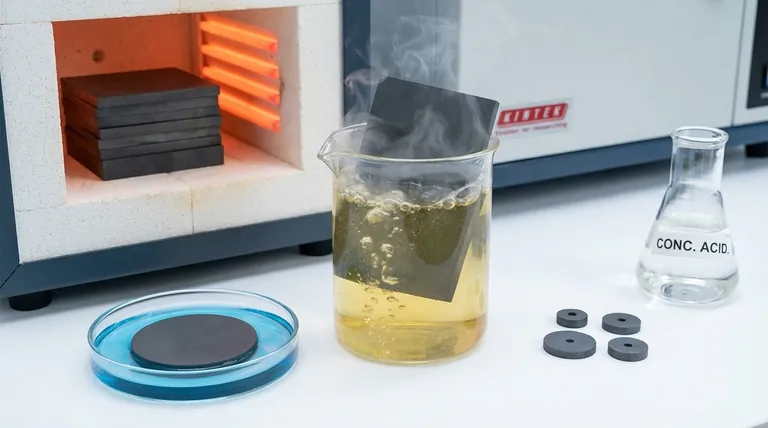
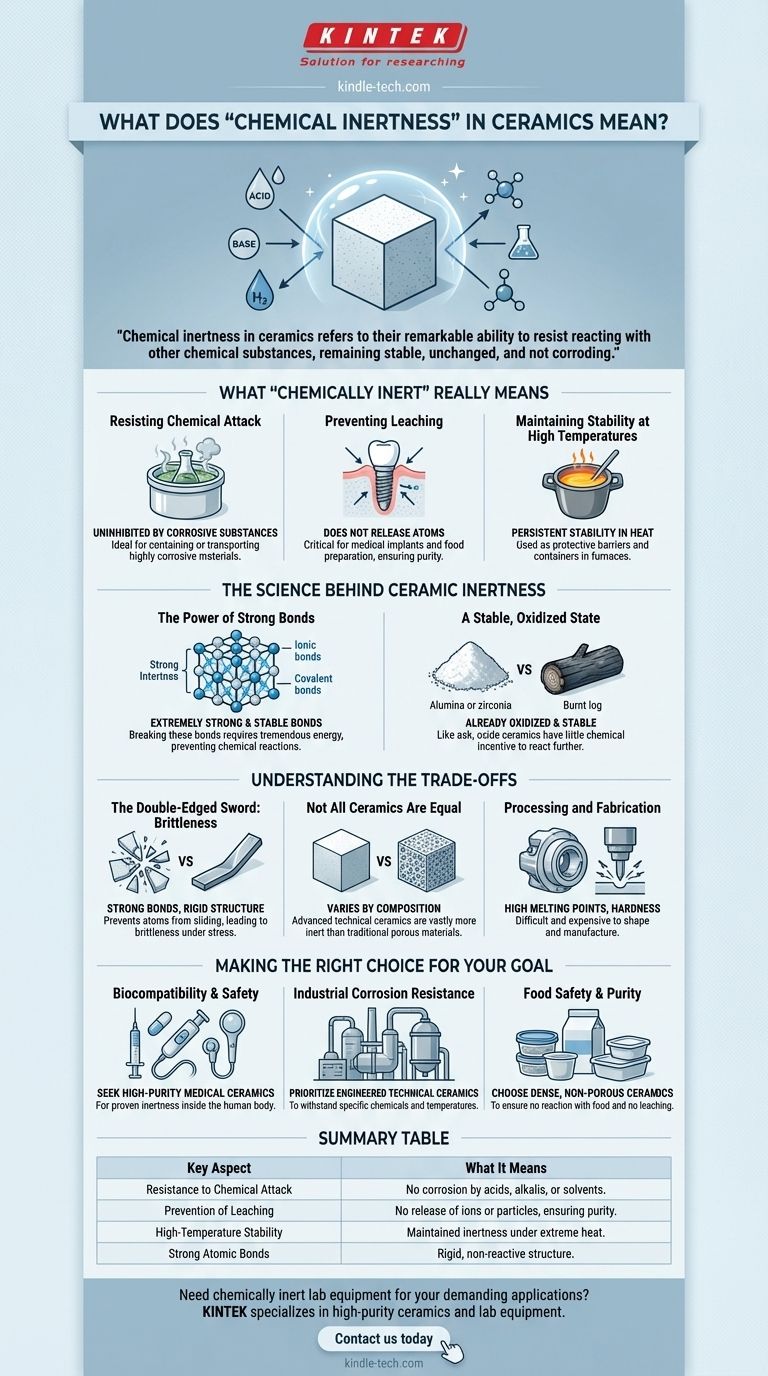
In the world of materials, chemical inertness in ceramics refers to their remarkable ability to resist reacting with other chemical substances. This means that when a ceramic material comes into contact with acids, alkalis, solvents, or even biological tissue, it remains stable, unchanged, and does not corrode or dissolve.
Chemical inertness is the property that makes ceramics uniquely stable and non-reactive in harsh environments. This resistance to chemical attack is not a minor detail; it is the fundamental reason ceramics are trusted in applications demanding extreme purity and durability, from medical implants to industrial chemical processing.

What "Chemically Inert" Really Means
To truly grasp this concept, we need to break down what non-reactivity looks like in practice. It’s more than just a material not dissolving.
Resisting Chemical Attack
The most direct meaning of inertness is resistance to corrosion. While metals can rust (oxidize) or be eaten away by acids, most technical ceramics are unaffected.
This makes them ideal for containing or transporting highly corrosive materials that would destroy lesser substances.
Preventing Leaching and Contamination
Inert materials do not release their own atoms or molecules into their surroundings. This is called leaching.
For applications in medicine or food preparation, this is critical. A chemically inert ceramic implant will not leach ions into the body, and a ceramic bowl will not impart any taste or harmful substances into your food.
Maintaining Stability at High Temperatures
Many materials become more reactive as temperature increases. Ceramics are an exception.
Their chemical stability often persists even at very high temperatures, allowing them to be used as containers (crucibles) for molten metal or as protective barriers in engines and furnaces.
The Science Behind Ceramic Inertness
This exceptional stability isn't magic; it's rooted in the fundamental atomic structure of ceramic materials.
The Power of Strong Bonds
Ceramics are characterized by extremely strong and stable ionic and covalent bonds. These bonds hold the atoms together in a rigid, tightly locked crystal lattice.
Breaking these bonds requires a tremendous amount of energy. A chemical reaction is essentially a process of breaking old bonds and forming new ones, so substances with weak bonds react easily. Because ceramic bonds are so strong, they are highly resistant to being broken by chemical agents.
A Stable, Oxidized State
Many common ceramics, such as alumina (Al₂O₃) or zirconia (ZrO₂), are oxides. This means they have already reacted with oxygen and exist in a very low-energy, stable state.
Think of it like a burnt log. The wood has already undergone its primary chemical reaction (combustion) and is now ash, a far more stable material that cannot be burned again. Similarly, these oxide ceramics have little chemical incentive to react further.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The very properties that make ceramics chemically inert also introduce significant challenges.
The Double-Edged Sword: Brittleness
The strong, rigid atomic bonds that prevent chemical reactions also prevent the atoms from sliding past one another. This is what makes ceramics brittle.
While a metal will bend or deform under stress, a ceramic will absorb that energy until it reaches its breaking point and then shatter catastrophically. The strength of the bonds resists both chemical attack and physical flexibility.
Not All Ceramics Are Equal
"Ceramic" is a vast category. Advanced technical ceramics like silicon carbide and aluminum nitride are incredibly inert.
However, traditional pottery or earthenware can be porous and may contain impurities, making them far less chemically resistant. The degree of inertness is highly dependent on the specific chemical composition and manufacturing process.
Processing and Fabrication
The high melting points and hardness that contribute to a ceramic's stability also make it difficult and expensive to shape and manufacture.
Machining ceramics is a specialized, energy-intensive process, unlike the relative ease of casting or forming metals and plastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding chemical inertness allows you to select the right material for a specific, demanding job. It's about matching the unique stability of ceramics to an application that requires it.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and safety: Seek out high-purity, medical-grade ceramics like zirconia or alumina for their proven inertness inside the human body.
- If your primary focus is industrial corrosion resistance: Prioritize technical ceramics specifically engineered to withstand the exact chemicals and temperatures in your process.
- If your primary focus is food safety and purity: Choose dense, non-porous ceramics or high-quality ceramic coatings to ensure no reaction with acidic foods and no leaching of unwanted substances.
Ultimately, understanding chemical inertness allows you to leverage the unique stability of ceramics for applications demanding safety, purity, and long-term durability.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect of Chemical Inertness | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Resistance to Chemical Attack | Ceramics do not corrode when exposed to acids, alkalis, or solvents. |
| Prevention of Leaching | They do not release ions or particles, ensuring purity in medical and food contexts. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Inertness is maintained even under extreme heat, ideal for furnaces and molten materials. |
| Strong Atomic Bonds | Ionic and covalent bonds provide a rigid, non-reactive structure. |
Need chemically inert lab equipment for your demanding applications? KINTEK specializes in high-purity ceramics and lab equipment that offer unmatched chemical stability, ensuring safety, durability, and contamination-free results in medical, industrial, and research settings. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- What are the characteristics of SiC? Unlock High-Temp, Hard, and Chemically Inert Performance
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength



















