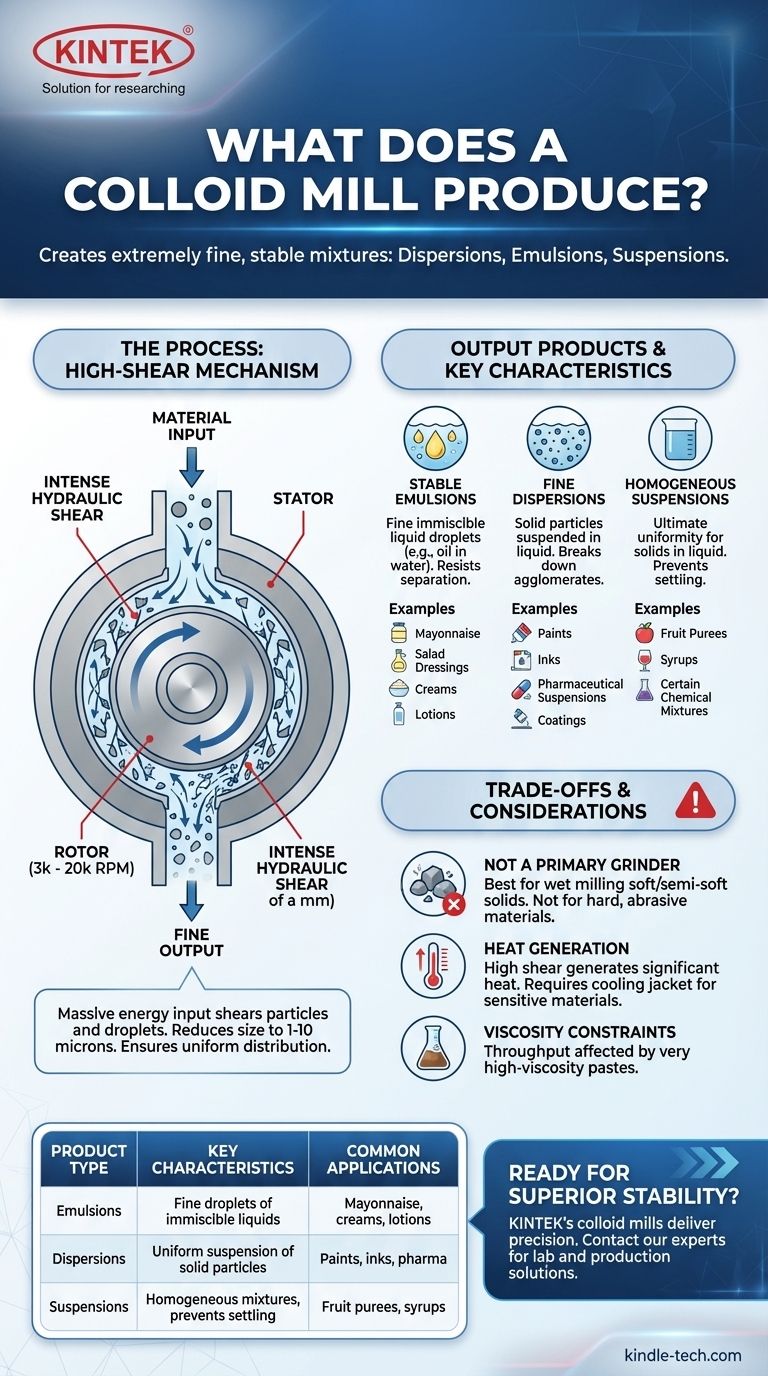
In essence, a colloid mill produces extremely fine and stable mixtures known as dispersions, emulsions, and suspensions. It achieves this by subjecting materials to intense mechanical shearing forces, breaking down particles or liquid droplets to a microscopic scale and distributing them uniformly within a liquid base.
A colloid mill is not simply a mixer. Its primary function is to use high-shear forces to reduce the size of soft particles or droplets within a liquid, resulting in a highly stable, homogenous final product that resists separation over time.

How a Colloid Mill Achieves This Result
The output of a colloid mill is a direct result of its unique mechanical design. It excels at applying massive amounts of energy to a fluid in a controlled way.
The Rotor-Stator Principle
At the heart of every colloid mill is a rotor that spins at very high speeds (often 3,000 to 20,000 RPM) within a stationary outer casing, the stator.
The clearance, or gap, between the rotor and stator is extremely small and precisely adjustable, often measured in fractions of a millimeter.
The Force of High Shear
As material is fed into the mill, it is forced into this narrow gap. The high rotational speed of the rotor creates a zone of intense hydraulic shear.
This action subjects the material to tremendous tearing, crushing, and accelerating forces, effectively ripping apart particles and liquid droplets.
Particle Size Reduction and Homogenization
This intense energy input reduces the size of suspended solid particles or droplets of an immiscible liquid. The final particle size typically falls in the range of 1 to 10 microns.
Simultaneously, the powerful turbulence ensures these newly reduced particles are distributed perfectly evenly throughout the liquid carrier, creating a homogenous final product.
The Key Characteristics of the Output
A colloid mill transforms coarse, unstable mixtures into refined, high-performance products with specific physical properties.
Stable Emulsions
An emulsion is a mixture of two liquids that normally don't mix, like oil and water. A colloid mill produces incredibly fine oil droplets, allowing them to remain suspended in water for a very long time without separating.
This is the principle behind products like mayonnaise, salad dressings, creams, and lotions.
Fine Dispersions
A dispersion is a system of solid particles suspended in a liquid. The mill breaks down agglomerates (clumps of particles) and reduces the size of individual soft particles.
This creates products like paints, inks, pharmaceutical suspensions, and coatings with smooth textures and uniform color.
Homogeneous Suspensions
For materials that are already solids in a liquid, the mill ensures ultimate uniformity. It prevents the settling of solids and guarantees a consistent product from top to bottom.
This is critical for applications like fruit purees, syrups, and certain chemical mixtures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a colloid mill is a specialized tool and not the right choice for every task. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not a Primary Grinder
Colloid mills are designed for wet milling and are best suited for reducing the size of soft or semi-soft solids. They are not effective for grinding hard, abrasive, or crystalline materials from a large to a small size.
For hard materials, a different type of mill (like a ball mill) is typically required for initial size reduction before a colloid mill can be used for final dispersion.
Significant Heat Generation
The immense mechanical energy applied by the mill is converted into heat. This can be problematic for heat-sensitive materials like certain pharmaceuticals or food products.
Most industrial colloid mills are equipped with a cooling jacket around the stator to dissipate this heat and maintain a controlled processing temperature.
Viscosity Constraints
The performance of a colloid mill can be highly dependent on the viscosity of the material. Very high-viscosity pastes may be difficult to pump through the narrow rotor-stator gap, limiting throughput and efficiency.
Is a Colloid Mill Right for Your Process?
Choosing the right processing equipment depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is creating stable emulsions (e.g., lotions, sauces, dressings): A colloid mill is an excellent choice for achieving the fine droplet size necessary for long-term stability.
- If your primary focus is dispersing soft solids or deagglomerating powders in a liquid (e.g., inks, ointments): The high shear of a colloid mill is ideal for breaking down clumps and ensuring a smooth, uniform texture.
- If your primary focus is grinding hard, crystalline solids: You should first consider other equipment like a ball mill or hammer mill, as a colloid mill is not a primary grinder.
A colloid mill is a powerful tool for anyone needing to create exceptionally fine and uniform liquid-based products.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Emulsions | Fine droplets of immiscible liquids (e.g., oil in water) | Mayonnaise, creams, lotions, salad dressings |
| Dispersions | Uniform suspension of solid particles in a liquid | Paints, inks, pharmaceutical suspensions |
| Suspensions | Homogeneous mixtures preventing solid settling | Fruit purees, syrups, chemical mixtures |
Ready to achieve superior product stability and uniformity? KINTEK's colloid mills are engineered for precision and reliability in your lab or production line. Whether you're developing pharmaceuticals, food products, or specialty chemicals, our equipment delivers consistent, high-shear results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your emulsion and dispersion needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Micro Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a high-energy ball mill? Master Nano-Nickel Synthesis and Material Refinement
- What is the primary use of an agate mortar for NaSICON samples? Optimize Cold Sintering Pre-Treatment
- What is the role of a 3-dimensional mixer in glass raw material pretreatment? Enhance Chemical Consistency
- What is the role of a high-energy ball mill in the preparation of Li2S–GeSe2–P2S5 sulfide solid electrolytes?
- What is the purpose of using a grinding bowl? Achieve Perfect Electrode Slurry Homogeneity
- What is a mortar and pestle used for in a lab? A Guide to Precision Grinding and Mixing
- How does a ball mill machine work? Master Impact and Attrition for Precise Grinding
- What is the milling process? A Guide to Shaping & Particle Reduction



















