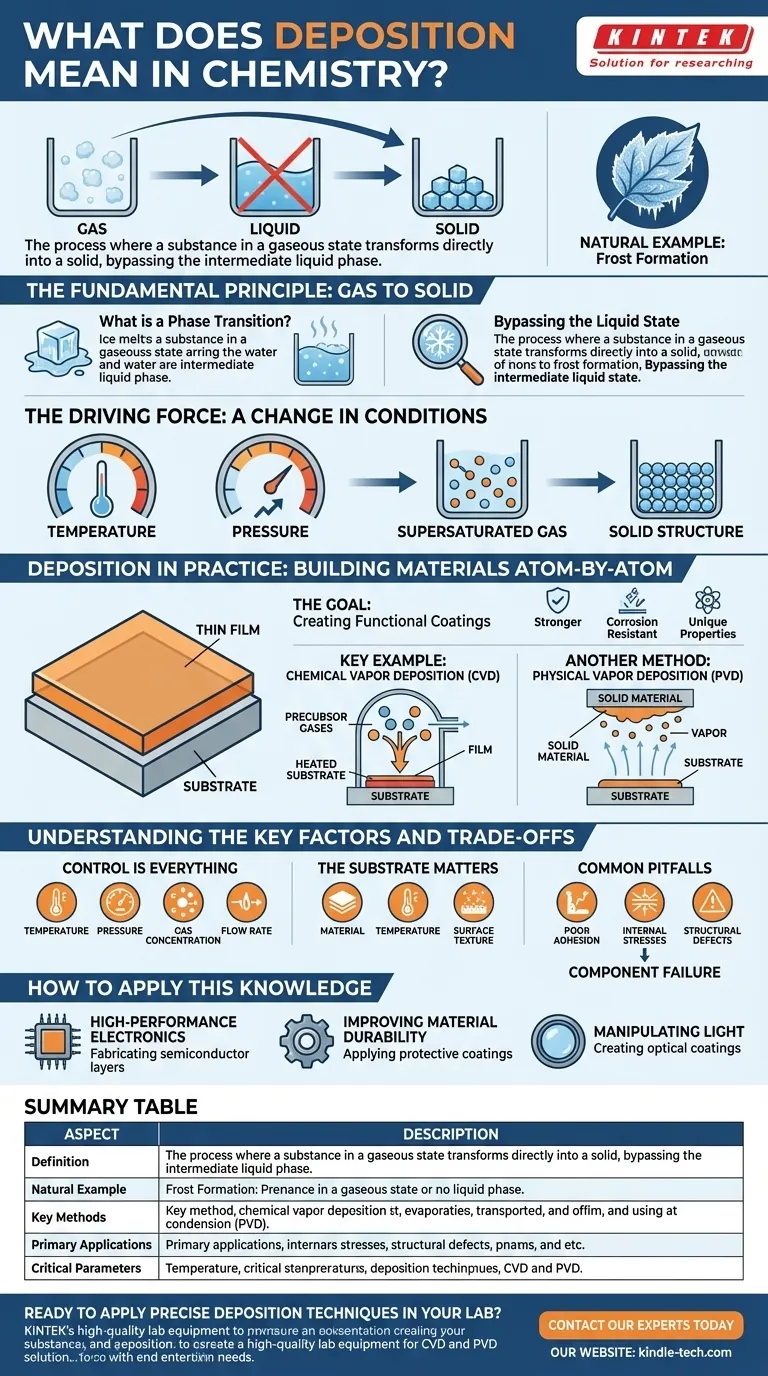
In chemistry, deposition is the process where a substance in a gaseous state transforms directly into a solid, bypassing the intermediate liquid phase. This phase transition is fundamental to many natural phenomena and advanced manufacturing techniques, allowing for the precise construction of materials layer by layer.
Deposition is more than just a change of state; it is a core principle used to build materials from the ground up. By controlling this gas-to-solid transition, we can create ultra-thin, high-performance films and coatings that are essential for modern technology.

The Fundamental Principle: Gas to Solid
Deposition is one of the primary ways matter changes its physical state. Understanding this direct transition is key to grasping its importance.
What is a Phase Transition?
Matter typically exists in one of three states: solid, liquid, or gas. A phase transition, like melting ice or boiling water, is the conversion from one state to another.
Bypassing the Liquid State
Deposition is unique because it skips the liquid phase entirely. A common natural example is the formation of frost, where water vapor in the cold air turns directly into solid ice crystals on a surface without first becoming liquid water.
The Driving Force: A Change in Conditions
This transition is driven by a change in conditions, typically a drop in temperature or an increase in pressure. The gas becomes "supersaturated," meaning it contains more of the substance than it can stably hold, forcing the excess molecules to settle and arrange themselves into a solid structure.
Deposition in Practice: Building Materials Atom-by-Atom
In technology and materials science, deposition isn't just a phenomenon—it's a meticulously controlled engineering process. It's used to apply a thin layer of a substance, known as a thin film, onto a surface or substrate.
The Goal: Creating Functional Coatings
The purpose of creating these thin films is to alter the properties of the substrate. This can make a material stronger, more resistant to corrosion, or give it unique electrical or optical properties.
A Key Example: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
As the name implies, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process where volatile precursor gases are introduced into a chamber. These gases react or decompose on a heated substrate's surface, leaving behind a solid deposit—the desired thin film. This allows for building materials molecule by molecule.
Another Method: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
In contrast to CVD, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) involves physically transforming a solid material into a vapor, transporting it, and then condensing it back into a solid thin film on the substrate. This is often done through methods like sputtering or evaporation.
Understanding the Key Factors and Trade-offs
Successfully applying deposition techniques requires precise control over numerous variables. The quality and properties of the final film depend entirely on getting this process right.
Control is Everything
The outcome is highly sensitive to process parameters. Factors like temperature, pressure, gas concentration, and flow rate must be carefully managed to achieve the desired film thickness, purity, and structure.
The Substrate Matters
The surface receiving the deposit is not a passive observer. The substrate's material, temperature, and surface texture directly influence how the deposited atoms arrange themselves, affecting the film's adhesion and crystalline quality.
Common Pitfalls
If conditions are not optimal, deposition can result in films with poor adhesion, internal stresses, or structural defects. These imperfections can severely compromise the performance of the final product, leading to component failure.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding deposition is crucial for anyone working with advanced materials. Its application depends entirely on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance electronics: Deposition is the essential technique for fabricating the microscopic layers in semiconductors and integrated circuits.
- If your primary focus is improving material durability: Deposition is used to apply extremely hard, protective coatings on cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants.
- If your primary focus is manipulating light: Deposition creates the ultra-thin, anti-reflective optical coatings found on everything from eyeglasses to telescope lenses and solar cells.
Ultimately, deposition is the controlled process of building solids from gases, enabling the creation of materials that define modern technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A phase transition where a gas transforms directly into a solid, bypassing the liquid state. |
| Natural Example | Frost formation from water vapor. |
| Key Methods | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). |
| Primary Applications | Semiconductor fabrication, protective coatings, optical films. |
| Critical Parameters | Temperature, pressure, gas concentration, substrate properties. |
Ready to apply precise deposition techniques in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced material deposition processes like CVD and PVD. Whether you are developing next-generation electronics, durable protective coatings, or specialized optical films, our solutions provide the reliability and control you need for superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and help you build the future, atom by atom.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of the sublimation chamber in TaC CVD? Master Precursor Vaporization and Stability
- What gases are typically used in the High-Density Plasma CVD (HDP-CVD) process? Optimize Your Film Deposition
- What is sputtering method of thin film deposition? A Guide to Precision Coating
- What is chemical vapor deposition for nanoparticles? A Guide to High-Purity Nanomaterial Synthesis
- What is a thermally activated CVD? The Ultimate Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of maintaining a low reaction pressure (2000 Pa) for BDD films? Unlock Precision Nucleation
- What is CVD and application? Unlock High-Performance Materials with Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What kind of dimensional structure graphene has? Discover the Power of the 2D Material



















