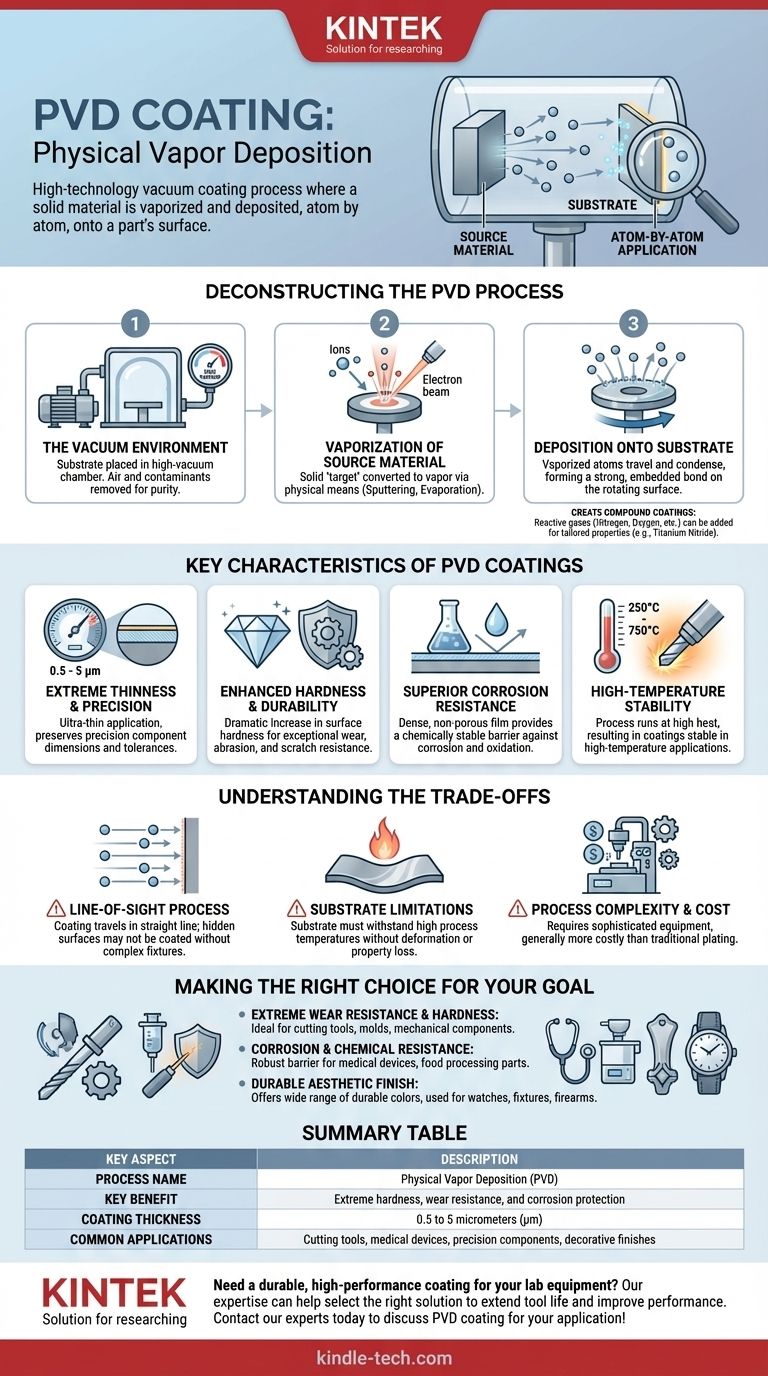
In short, PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. It is a high-technology vacuum coating process where a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum chamber and deposited, atom by atom, onto the surface of a part. This process forms an extremely thin, hard, and durable coating that dramatically enhances the part's physical properties.
The core concept of PVD is simple: take a solid material, turn it into a gas, and then have it condense back into a solid film on a target object. This atom-by-atom application creates a layer that is fundamentally bonded to the surface, providing superior hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection.
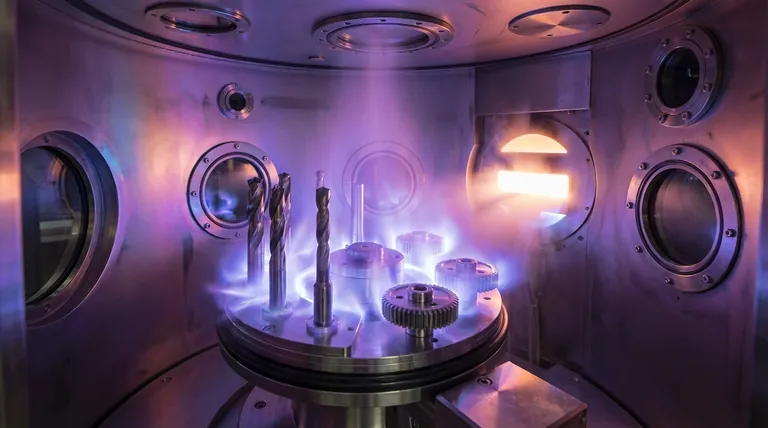

Deconstructing the PVD Process
To truly understand Physical Vapor Deposition, it's best to break it down into its essential stages. The entire process takes place inside a sealed, high-vacuum chamber to ensure the purity and quality of the final coating.
The Vacuum Environment
First, the parts to be coated (known as the substrate) are placed inside the chamber. All the air is pumped out to create a high-vacuum environment. This step is critical because it removes any particles or contaminants that could interfere with the coating process.
Vaporization of the Source Material
Next, the coating material (the target) is converted from a solid into a vapor. This is the "Physical" part of the name, as it uses physical means rather than a chemical reaction.
Common methods include sputtering, where the target is bombarded with high-energy ions, or evaporation, where the target is heated until its atoms evaporate into the chamber.
Deposition onto the Substrate
The vaporized atoms travel through the vacuum chamber and condense onto the cooler substrate. Because this happens at a high energy level, the atoms embed themselves into the surface of the part, forming an incredibly strong bond.
The parts are often carefully rotated during this stage to ensure the coating is applied evenly across all necessary surfaces.
Creating Compound Coatings
To create specific coating properties, reactive gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or acetylene can be introduced into the chamber. These gases react with the metal vapor to form compound films (like Titanium Nitride), tailoring the coating's final characteristics.
Key Characteristics of PVD Coatings
PVD is chosen for its ability to impart significant performance improvements to a surface. These improvements are a direct result of the process's unique characteristics.
Extreme Thinness and Precision
PVD coatings are remarkably thin, typically between 0.5 and 5 micrometers (μm). This means they can be applied to precision components without affecting their dimensions or tolerances.
Enhanced Hardness and Durability
The primary benefit of PVD is a dramatic increase in surface hardness. This creates exceptional resistance to wear, abrasion, and scratching, significantly extending the life of tools and components.
Superior Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
The deposited film is dense and non-porous, creating a chemically stable barrier. This protects the underlying substrate from corrosion, oxidation, and chemical attack.
High-Temperature Stability
The process itself runs at high temperatures (from 250°C to 750°C), resulting in a coating that remains stable and performs well in high-temperature applications, such as cutting tools.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
A "Line-of-Sight" Process
The vaporized coating material travels in a straight line. This means that if a surface is hidden or blocked, it will not be coated. This limitation requires complex fixtures and rotation to cover intricate shapes and makes it difficult to coat internal channels.
Substrate Material Limitations
The high temperatures required during the PVD process can be detrimental to certain materials. Substrates must be able to withstand these temperatures without warping, melting, or losing their core properties.
Process Complexity and Cost
PVD requires sophisticated and expensive equipment, including vacuum chambers and high-energy sources. This makes it a more costly process compared to traditional plating methods, typically reserved for high-performance applications where its benefits justify the investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PVD depends entirely on the performance you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and hardness: PVD is an industry-leading choice for cutting tools, molds, and mechanical components that see heavy use.
- If your primary focus is corrosion and chemical resistance: PVD provides a robust, inert barrier ideal for medical devices, food processing equipment, and parts exposed to harsh environments.
- If your primary focus is a durable aesthetic finish: PVD offers a wide range of colors with a finish that is far more durable than paint or traditional plating, often used for watches, fixtures, and firearms.
Ultimately, Physical Vapor Deposition is a precise engineering tool used to build a better surface, atom by atom.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Name | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Key Benefit | Extreme hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection |
| Coating Thickness | 0.5 to 5 micrometers (µm) |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, medical devices, precision components, decorative finishes |
Need a durable, high-performance coating for your lab equipment or components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables. Our expertise in surface enhancement technologies can help you select the right coating solution to extend the life and improve the performance of your critical tools and parts.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD coating can benefit your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating



















