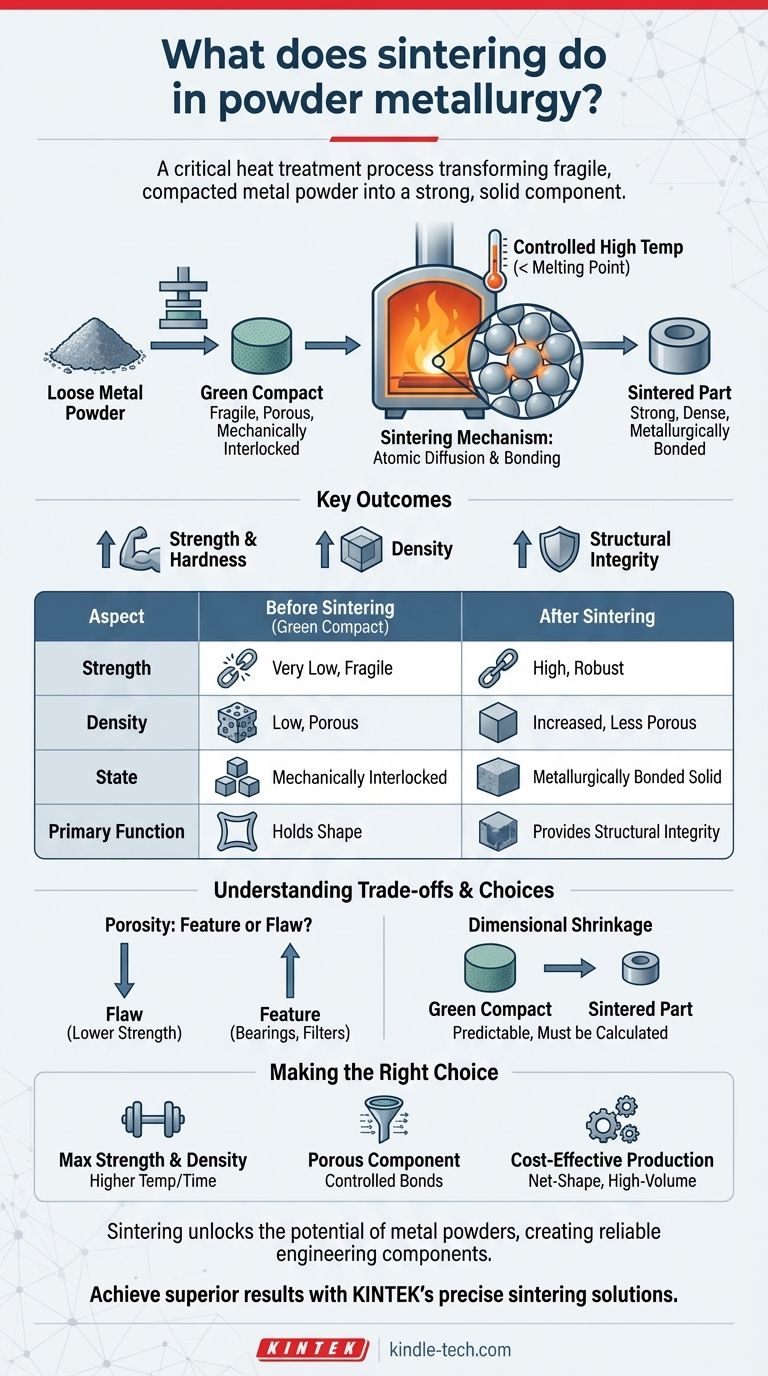
In powder metallurgy, sintering is a critical heat treatment process that transforms a fragile, compacted metal powder shape into a strong, solid component. By heating the material to a temperature just below its melting point, sintering fuses the individual metal particles together, giving the part its final strength and structural integrity.
The core function of sintering is to bond metal particles using heat without melting them. This process is what converts a weakly-pressed powder form, known as a "green compact," into a robust and usable final part.

From Loose Powder to a Solid Part
To understand what sintering does, you must first understand the state of the component before this step. The powder metallurgy process begins with pressing metal powder into a desired shape, which creates a fragile object.
The Starting Point: The "Green" Compact
A part that has been pressed but not yet sintered is called a green compact. While it holds its shape, it has very low strength and is held together primarily by the mechanical interlocking of the powder particles.
This green compact is porous and can often be crumbled by hand. It is not yet a functional engineering component.
The Sintering Mechanism: Fusing Without Melting
Sintering subjects the green compact to a controlled high temperature, which is carefully kept below the material's melting point. This thermal energy allows the atoms at the contact surfaces of the powder particles to diffuse and create strong metallic bonds.
A helpful analogy is how ice cubes in a glass of water will fuse together at their contact points over time, even though the water isn't boiling. Sintering achieves a similar effect at a microscopic level, creating a solid, cohesive mass from individual particles.
Key Outcomes: Strength, Density, and Integrity
The primary result of sintering is a dramatic increase in strength, hardness, and density. As the particles fuse, the pores between them shrink or close, significantly improving the part's mechanical properties.
This step turns the fragile green compact into a finished component with the structural integrity required for its intended application.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While sintering is a powerful process, it is not without complexities. The final properties of a part are directly controlled by the sintering parameters, which involve inherent trade-offs.
Porosity: A Feature or a Flaw?
Even after sintering, most powder metallurgy parts retain some level of porosity. For high-performance applications, this can be a disadvantage, as it may result in lower strength compared to a fully dense, forged component.
However, this porosity can also be a desired feature. For self-lubricating bearings, the pores are intentionally retained to hold oil. For filters, this interconnected network of pores is the primary function of the part.
Dimensional Shrinkage
As the pores within the compact close during sintering, the overall part will shrink. This change in dimension is predictable but must be precisely calculated and accounted for in the initial design of the pressing die.
Failure to properly account for shrinkage will result in a final part that does not meet dimensional specifications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is the defining step that determines the final characteristics of a powder metallurgy component. The process parameters are tuned based on the desired outcome for the part.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: The part will require higher sintering temperatures and longer times to minimize porosity.
- If your primary focus is a porous component like a filter: Sintering is controlled to create strong bonds between particles while intentionally preserving an open network of pores.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of complex shapes: Sintering enables the net-shape manufacturing that makes powder metallurgy an economical choice for high-volume parts.
Ultimately, sintering is the essential process that unlocks the potential of metal powders, transforming them into functional and reliable engineering components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Before Sintering (Green Compact) | After Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Very low, fragile | High, robust |
| Density | Low, porous | Increased, less porous |
| State | Mechanically interlocked particles | Metallurgically bonded solid |
| Primary Function | Holds shape | Provides structural integrity |
Ready to achieve superior results in your powder metallurgy process? The precise control of sintering parameters is key to developing parts with the exact strength, density, and porosity you require. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab furnaces and consumables essential for reliable and consistent sintering. Whether you are producing high-strength components or porous filters, our equipment is designed to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your sintering process and help you manufacture better components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges



















