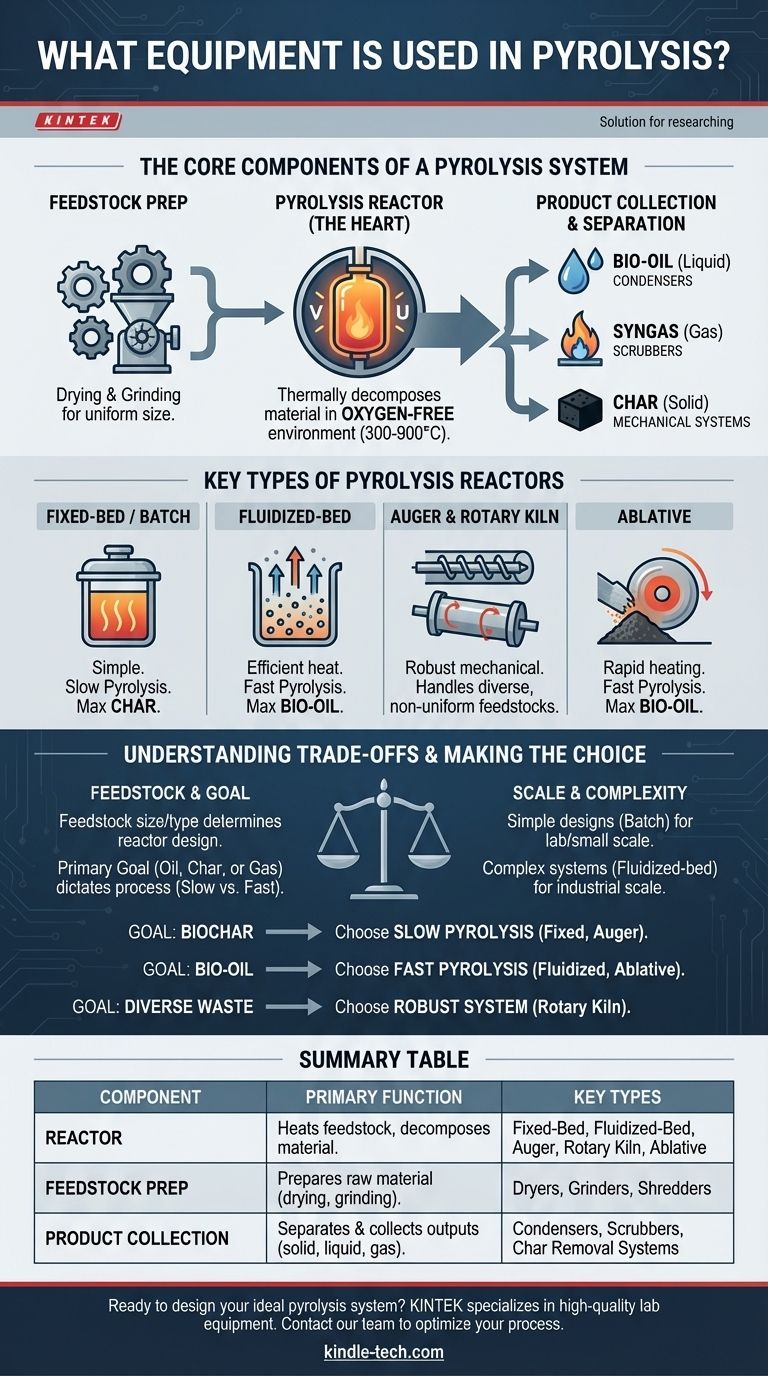
At its core, a pyrolysis system uses a specialized, oxygen-free reactor to thermally decompose material. This central unit is supported by ancillary equipment for feedstock preparation, energy input, and the collection of the resulting solid (char), liquid (bio-oil), and gas (syngas) products. The specific type of reactor and support systems are chosen based on the material being processed and the desired output.
The heart of any pyrolysis setup is the reactor. The vast array of reactor designs exists because there is no single best solution; the right equipment is always a function of the specific feedstock and the primary product you aim to create.

The Core Components of a Pyrolysis System
A complete pyrolysis plant is more than just a reactor. It is an integrated system where each component serves a critical function in a continuous process.
Feedstock Preparation Equipment
Before entering the reactor, the raw material, or feedstock, must be prepared. This often involves equipment for drying to reduce moisture content and grinding or shredding to achieve a uniform particle size suitable for the reactor type.
The Pyrolysis Reactor
This is the central vessel where the chemical transformation occurs. Its fundamental job is to heat the feedstock to high temperatures (typically 300-900°C) in the complete absence of oxygen, preventing combustion and instead causing the material to break down into smaller molecules.
Product Collection and Separation
As the feedstock decomposes, it produces a mix of hot gases and vapors, along with a solid residue.
- Condensers are used to cool the hot vapor stream, causing the bio-oils to liquefy and be collected.
- Scrubbers or filters may be used to clean the remaining non-condensable gases (syngas).
- Mechanical systems like screw conveyors or lock-hoppers are used to safely remove the hot solid char from the reactor.
Key Types of Pyrolysis Reactors
The choice of reactor is the most critical design decision. Different designs offer unique methods for heating the feedstock and managing the flow of materials, each suited for different applications.
Fixed-Bed and Batch Reactors
These are among the simplest designs. The feedstock is loaded into the reactor, sealed, and heated for a set duration. This "slow pyrolysis" process is excellent for maximizing the production of solid biochar.
Fluidized-Bed Reactors
In these reactors, fine feedstock particles are suspended by a hot, upward-flowing gas, creating a "fluidized" bed that behaves like a liquid. This provides extremely efficient heat transfer, making these reactors ideal for fast pyrolysis to maximize liquid bio-oil yield.
Auger and Rotary Kiln Reactors
These are mechanically agitated systems. An auger reactor uses a large screw to transport material through a heated tube, while a rotary kiln is a large, rotating, heated cylinder. Their robust mechanical nature makes them well-suited for handling a wide variety of non-uniform or challenging feedstocks.
Ablative Pyrolysis Reactors
This is a more specialized design for extremely rapid heating. Feedstock is pressed with high pressure against a hot, rapidly moving surface. The resulting friction instantly "melts" and vaporizes the material, making it another method for fast pyrolysis focused on liquid production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right equipment involves balancing competing priorities. The ideal system for one goal may be entirely wrong for another.
Feedstock Determines the Design
The physical characteristics of your feedstock are paramount. A fine, dry sawdust is perfect for a fluidized-bed reactor, but sticky plastic waste or bulky tires would immediately cause it to fail. Those materials require a more robust mechanical system like a rotary kiln or auger.
Desired Product Dictates the Process
Your primary goal—oil, char, or gas—determines the required process conditions.
- Slow pyrolysis (e.g., in a batch reactor) uses longer residence times and lower temperatures to maximize char.
- Fast pyrolysis (e.g., in a fluidized-bed reactor) uses very short residence times and moderate temperatures to maximize liquid oil.
Scale and Complexity
A simple fixed-bed or batch reactor may be suitable for lab-scale research or small community projects due to its low cost and simplicity. However, large-scale industrial production demands the efficiency and continuous operation of more complex and costly systems like fluidized-bed or circulating-bed reactors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the equipment selection process begins with your end goal.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar: A slow pyrolysis process using a simpler design like a fixed-bed, drum, or auger reactor is your most direct path.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil: You must use a fast pyrolysis reactor, such as a fluidized-bed or ablative system, that can achieve very high heating rates.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or difficult waste streams: A mechanically robust system like a rotary kiln offers the greatest feedstock flexibility.
Matching the technology to the feedstock and the desired outcome is the fundamental principle of successful pyrolysis system design.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Types |
|---|---|---|
| Reactor | Heats feedstock in an oxygen-free environment to decompose material. | Fixed-Bed, Fluidized-Bed, Auger, Rotary Kiln, Ablative |
| Feedstock Prep | Prepares raw material for processing (drying, grinding/shredding). | Dryers, Grinders, Shredders |
| Product Collection | Separates and collects the solid, liquid, and gas outputs. | Condensers, Scrubbers, Char Removal Systems |
Ready to design your ideal pyrolysis system? The right equipment is critical to achieving your target output, whether it's biochar, bio-oil, or syngas. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Our experts can help you select the perfect reactor and ancillary components for your specific feedstock and process goals. Contact our team today to discuss your project and optimize your pyrolysis process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















