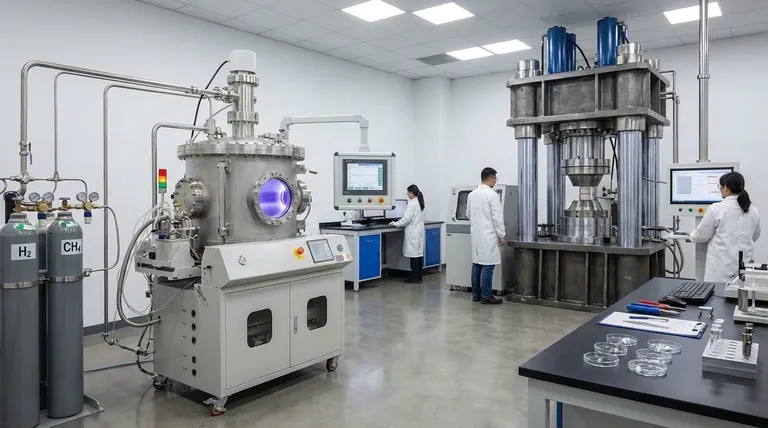
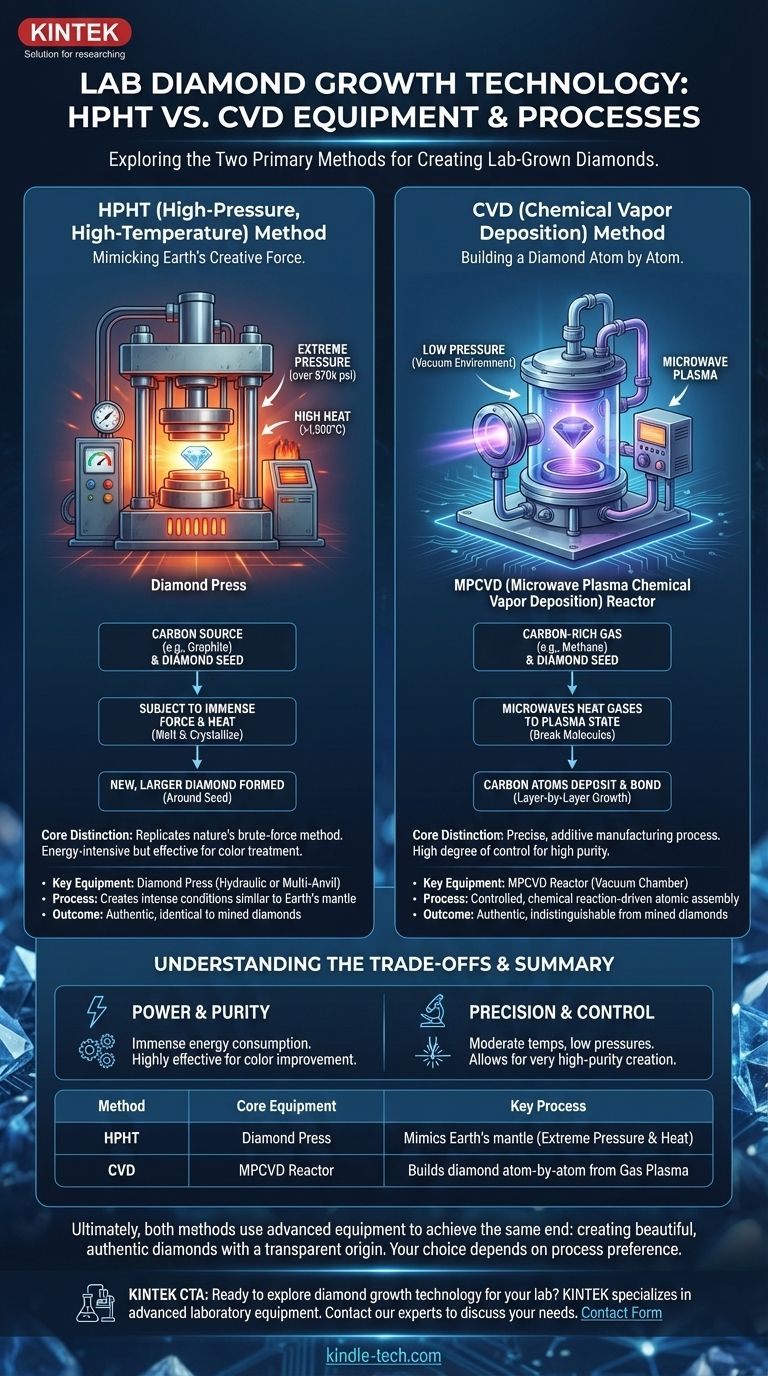
The equipment used to grow lab diamonds centers on two primary methods: High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). HPHT equipment creates immense pressure and heat to mimic the natural diamond-forming conditions deep within the Earth. In contrast, CVD uses a vacuum chamber and superheated gases, like microwave plasma, to build a diamond crystal atom by atom onto a seed.
The core distinction lies in the approach: HPHT replicates nature's brute-force method of creation, while CVD is a precise, additive manufacturing process that builds the diamond in layers. Both methods, however, produce diamonds that are physically and chemically identical to those mined from the Earth.

The High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT) Method
The HPHT process is the original method for creating lab diamonds, designed to directly replicate the intense environment where diamonds form naturally.
Mimicking Earth's Creative Force
This technique's entire purpose is to subject a carbon source to the same conditions found in the Earth's mantle. It uses massive machinery to generate the necessary force and heat.
Key Equipment: The Diamond Press
The central piece of equipment is a diamond press. These are large, powerful machines capable of exerting pressures over 870,000 pounds per square inch (psi) while simultaneously heating the internal chamber to temperatures above 1,500°C (2,732°F).
The Process Explained
A small diamond seed is placed in a chamber along with a source of pure carbon, such as graphite. The press applies extreme pressure and heat, causing the carbon source to melt and crystallize around the seed, forming a new, larger diamond.
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Method
CVD is a more modern approach that "grows" a diamond in a controlled, low-pressure environment. It is less about brute force and more about precise atomic assembly.
Building a Diamond Atom by Atom
This method builds a diamond crystal by depositing carbon atoms from a gas onto a substrate. It doesn't mimic the Earth's pressure but instead relies on specific chemical reactions.
Key Equipment: The MPCVD Reactor
The primary equipment is a Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD) reactor. This is a vacuum chamber where a diamond seed is placed. The chamber is then filled with carbon-rich gases like methane.
The Process Explained
Microwaves are used to heat the gases into a plasma state, breaking the gas molecules apart. These freed carbon atoms then rain down and bond to the diamond seed, slowly building up the crystal structure layer by layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While both methods produce authentic diamonds, the equipment and processes involved have distinct characteristics that influence the final product.
HPHT: Power and Purity
The HPHT method is highly effective and can be used to treat and improve the color of some diamonds (both mined and lab-grown). However, the extreme conditions require immense energy consumption.
CVD: Precision and Control
The CVD process operates at more moderate temperatures and much lower pressures, offering a high degree of control over the growth environment. This allows for the creation of very high-purity diamonds, often with fewer atomic distortions.
Less Common Methods
While HPHT and CVD are the dominant commercial methods, other techniques exist. Methods like detonation of explosives or ultrasound cavitation can also produce nanodiamonds, but they are not used for creating the gem-quality stones found in jewelry.
Applying This to Your Understanding
Choosing between a diamond made with HPHT or CVD equipment is a matter of process preference, as the final gems are indistinguishable without specialized testing.
- If your primary focus is on a process that mirrors nature: The HPHT method, using massive diamond presses, is the direct technological equivalent of the Earth's natural diamond creation.
- If your primary focus is on a modern, additive process: The CVD method, using a sophisticated vacuum reactor, represents a cutting-edge approach to building a diamond atom by atom.
Ultimately, the equipment behind both methods is designed to achieve the same end: creating a beautiful, authentic diamond with a known and transparent origin.
Summary Table:
| Method | Core Equipment | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| HPHT | Diamond Press | Mimics Earth's mantle with extreme pressure & heat |
| CVD | MPCVD Reactor | Builds diamond atom-by-atom from gas plasma |
Ready to explore diamond growth technology for your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables. Whether you're researching synthetic materials or developing new crystal growth processes, our expertise can help you achieve precise and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific equipment needs and how we can support your innovative work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques



















