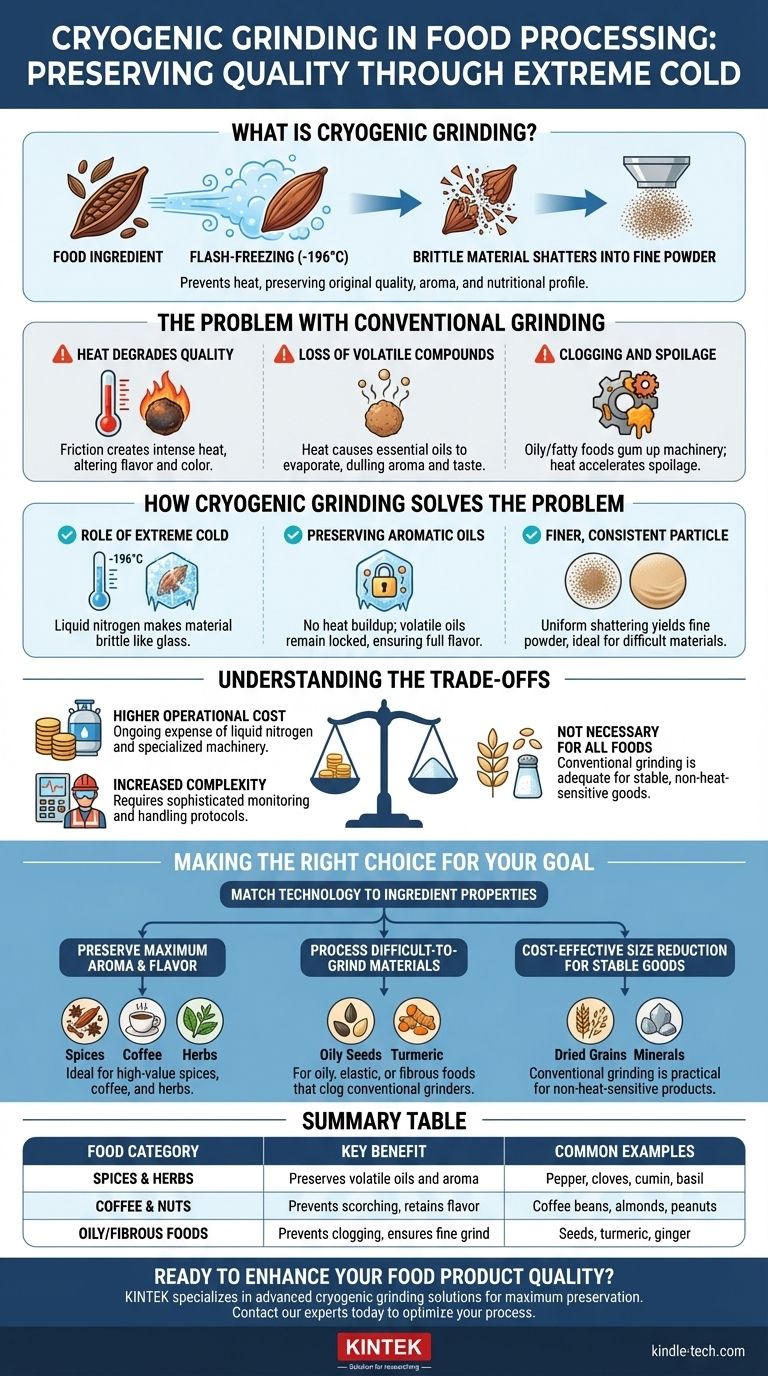
In food processing, cryogenic grinding is a specialized technique where a food material is flash-frozen, typically with liquid nitrogen, to make it brittle before it is crushed into a fine powder. This extreme cold prevents the heat generated by friction during normal grinding, which is critical for preserving the food's original quality, aroma, and nutritional profile.
By eliminating destructive heat, cryogenic grinding is less about pulverizing a material and more about shattering it. This fundamental difference is the key to preserving the delicate volatile compounds that define the flavor and aroma of high-value foods like spices and coffee.

The Problem with Conventional Grinding
Standard grinding methods rely on mechanical force—crushing, shearing, and abrasion—to reduce particle size. While effective for many materials, this process creates significant problems when applied to sensitive foods.
Heat Degrades Quality
The friction generated by industrial grinders can produce intense localized heat. This heat can scorch the material, altering its flavor, color, and nutritional value.
Loss of Volatile Compounds
Many of the most desirable characteristics of foods, especially spices, herbs, and coffee, come from volatile oils and aromatic compounds. Heat causes these compounds to evaporate, leading to a final product with a significantly duller aroma and taste profile.
Clogging and Spoilage
Foods with high oil or fat content can become sticky when heated. This can cause the material to gum up and clog the grinding machinery, reducing efficiency and creating cleaning challenges. The heat can also accelerate oxidation, leading to spoilage and off-flavors.
How Cryogenic Grinding Solves the Problem
Cryogenic grinding addresses these issues by fundamentally changing the physical properties of the food material before it ever enters the grinder.
The Role of Extreme Cold
The food is infused with an inert cryogenic fluid, almost always liquid nitrogen, which has a boiling point of -196°C (-320°F). This flash-freezing process makes the material intensely brittle, almost like glass.
Preserving Aromatic Oils
Because the material is kept at extremely low temperatures throughout the process, there is no heat buildup from friction. The volatile aromatic oils remain locked in their frozen state instead of evaporating, ensuring the ground powder retains the full sensory profile of the original ingredient.
A Finer, More Consistent Particle
Brittle materials shatter cleanly and uniformly when crushed. This results in a finer, more consistent particle size, which can be critical for formulation, mouthfeel, and ensuring even mixing in a final product. This process is ideal for materials that are naturally elastic or gummy at room temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, cryogenic grinding is a specialized solution with specific trade-offs that make it unsuitable for all applications.
Higher Operational Cost
The primary drawback is cost. The ongoing expense of purchasing and safely handling liquid nitrogen, combined with the need for specialized, insulated machinery, makes cryogenic grinding significantly more expensive than conventional methods.
Increased Complexity
Cryogenic systems require sophisticated monitoring, specialized handling protocols, and robust safety measures to manage the extreme cold. This adds a layer of operational complexity not present with standard grinding equipment.
Not Necessary for All Foods
For stable, low-oil, and non-heat-sensitive materials like salt, sugar, or many grains, the benefits of cryogenic grinding do not justify the added cost and complexity. Conventional grinding is perfectly adequate and far more economical for these products.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct grinding method requires a clear understanding of your ingredient's properties and your final product goals.
- If your primary focus is preserving maximum aroma and flavor: Cryogenic grinding is the ideal choice for high-value spices (e.g., pepper, cloves, cumin), coffee beans, and herbs where volatile oils are the key value driver.
- If your primary focus is processing difficult-to-grind materials: Use this method for oily, elastic, or fibrous foods that would otherwise clog or melt in a conventional grinder.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective size reduction for stable goods: Conventional grinding remains the most practical and economical choice for products that are not sensitive to heat, such as dried grains or minerals.
Ultimately, choosing the right grinding method is about matching the technology to the specific chemical and physical properties of your food product.
Summary Table:
| Food Category | Key Benefit of Cryogenic Grinding | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Spices & Herbs | Preserves volatile oils and aroma | Pepper, cloves, cumin, basil |
| Coffee & Nuts | Prevents scorching, retains flavor | Coffee beans, almonds, peanuts |
| Oily/Fibrous Foods | Prevents clogging, ensures fine grind | Seeds, turmeric, ginger |
Ready to enhance your food product quality? KINTEK specializes in advanced cryogenic grinding solutions for laboratories and food processors. Our equipment ensures maximum preservation of flavor, aroma, and nutritional value in heat-sensitive materials like spices, coffee, and herbs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can optimize your grinding process and deliver superior results for your target products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill with Screw Feeder
- lab cryogenic grinding use liquid-nitrogen for pulverizing plastic raw materials and heat sensitive materials
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
People Also Ask
- What is grinding in laboratory? The Key to Accurate Sample Preparation
- How do crushing and grinding systems improve microalgae gas production? Optimize Biomass Pretreatment for Higher Yields
- What is the cryogenic grinding process? Achieve Superior Quality and Efficiency for Sensitive Materials
- What is the purpose of a pulverizer? Unlock Material Potential with Fine Grinding
- What is the purpose of the grinding process for Titanium Dioxide? Maximize Surface Area and Photocatalytic Efficiency



















