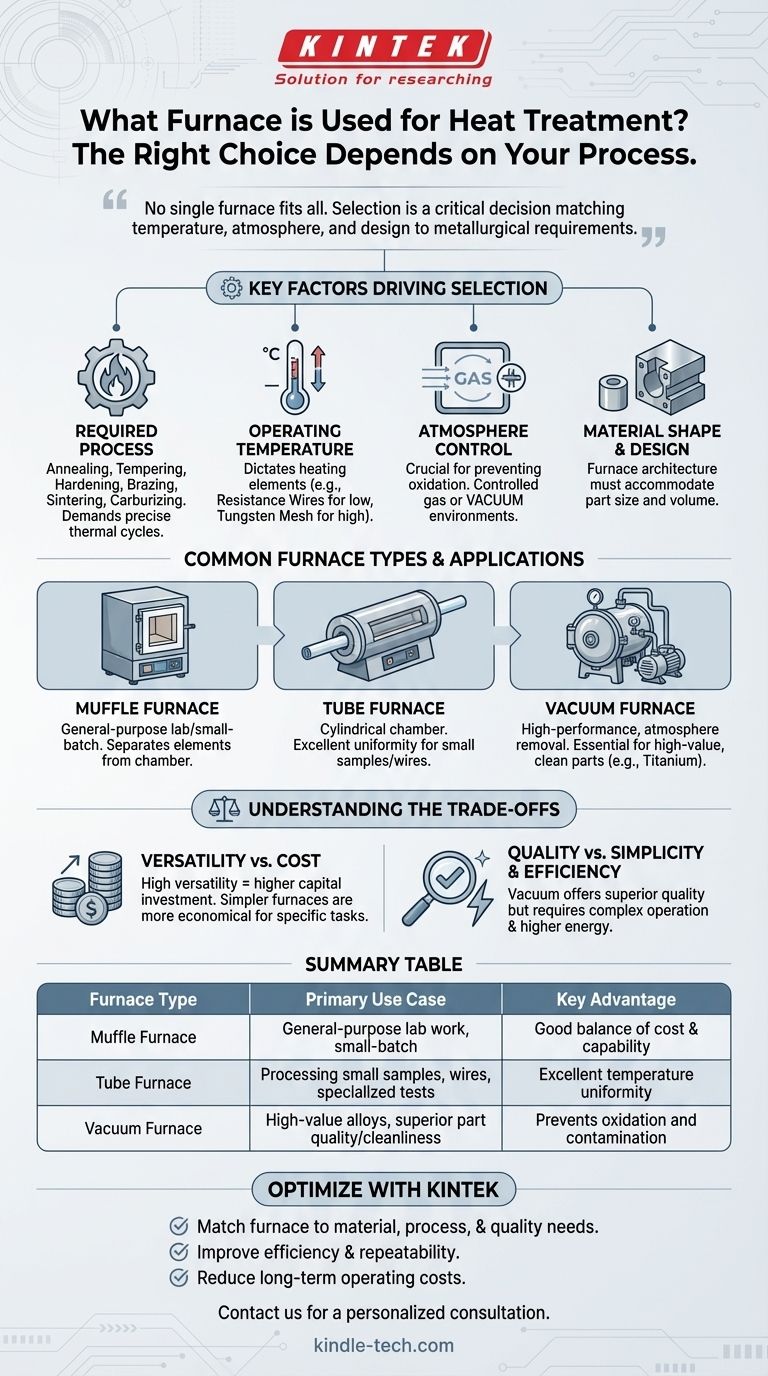
The short answer is that many different types of furnaces are used for heat treatment, including muffle, tube, and vacuum furnaces. There is no single "heat treatment furnace" because the correct choice is entirely dependent on the specific material, the desired outcome, and the process being performed, such as annealing, tempering, or carburizing.
The selection of a heat treatment furnace is not about finding one-size-fits-all equipment. It is a critical engineering decision that involves matching the furnace's specific capabilities—primarily its temperature range, atmosphere control, and physical design—to the precise requirements of the metallurgical process.

Key Factors Driving Furnace Selection
The design of a heat treatment furnace is dictated by its intended function. A furnace optimized for high-temperature sintering at 1300°C will perform poorly for a low-temperature tempering process at 300°C, even if the lower temperature is within its technical range.
The Required Heat Treatment Process
Different metallurgical processes impose unique demands. A furnace must be able to execute the required thermal cycle and create the right environment.
Common processes include annealing, tempering, hardening, brazing, sintering, and carburizing. Each requires precise control over heating rates, holding times, and cooling rates.
Operating Temperature Range
The required process temperature is a primary constraint that dictates the furnace's construction and, most importantly, its heating elements.
Elements like resistance wires are used for lower temperatures, while silicon molybdenum rods, tungsten mesh, or graphite are required for very high-temperature applications. A mismatch can lead to poor temperature uniformity and inefficient operation.
Atmosphere Control
Perhaps the most critical factor is atmosphere control. The environment inside the furnace directly interacts with the metal's surface, affecting its final properties and finish.
An uncontrolled atmosphere can lead to oxidation and scaling. For this reason, many processes require either a specific controlled gas environment or a vacuum. Vacuum furnaces excel at preventing surface reactions, resulting in clean, "bright" parts.
Material Shape and Handling
The physical design of the furnace must accommodate the parts being treated. The shape, size, and volume of the "stock" influence the furnace's architecture.
For example, a vertical tube furnace is well-suited for quenching tests or treating small, cylindrical parts, while large, complex components may require a larger chamber furnace.
Common Furnace Types and Their Applications
While many custom designs exist, a few common types serve as the foundation for most heat treatment operations.
Muffle Furnaces
These are common, general-purpose furnaces, often found in laboratory and small-batch production settings. The heating elements are separated from the main chamber by a "muffle," which helps protect the part from direct radiation and combustion byproducts.
Tube Furnaces
As the name implies, these furnaces use a cylindrical tube as their heating chamber. They provide excellent temperature uniformity along their length and are ideal for processing small samples, wires, or for conducting specialized tests in a highly controlled environment.
Vacuum Furnaces
Vacuum furnaces represent a high-performance standard in modern heat treatment. By removing the atmosphere, they prevent oxidation and contamination, making them essential for high-value materials like titanium or for processes like high-purity brazing and sintering.
Modern vacuum furnaces, such as the "Vector" type mentioned in industry literature, are extremely versatile and can perform a wide range of processes, including hardening, tempering, annealing, vacuum-carburizing, and brazing, all within a single unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing capability, cost, and complexity. An informed decision requires acknowledging the inherent compromises.
Versatility vs. Cost
A highly versatile vacuum furnace that can perform ten different processes is a significant capital investment. For a facility that only performs low-temperature tempering, a simpler, less expensive furnace is a more economical and efficient choice.
Process Quality vs. Simplicity
A simple air atmosphere furnace is easy to operate but offers no protection against oxidation. A vacuum furnace produces superior, bright parts but requires more complex support equipment, such as vacuum pumps, and more sophisticated operator knowledge.
Energy Efficiency
High-temperature heating elements and vacuum systems consume significant energy. The furnace's insulation, element type, and overall design directly impact its long-term operating costs, which can sometimes outweigh the initial purchase price.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection must align directly with the primary objective of your heat treatment operation.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work or small-batch treatments: A robust muffle furnace often provides the best balance of cost and general capability.
- If your primary focus is processing high-value alloys or achieving the highest part quality and cleanliness: A vacuum furnace is the undisputed industry standard.
- If your primary focus is a repeatable, single-purpose process like annealing wire: A specialized continuous or tube furnace will deliver the highest efficiency and consistency.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is a strategic decision that directly determines the quality, consistency, and cost-effectiveness of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | General-purpose lab work, small-batch treatments | Good balance of cost and capability |
| Tube Furnace | Processing small samples, wires, specialized tests | Excellent temperature uniformity |
| Vacuum Furnace | High-value alloys, superior part quality/cleanliness | Prevents oxidation and contamination |
Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process with KINTEK
Selecting the right furnace is critical to achieving consistent, high-quality results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions tailored to your specific heat treatment needs—whether you require a versatile muffle furnace for R&D or a high-performance vacuum furnace for precision manufacturing.
Let our experts help you:
- Match the perfect furnace to your material, process, and quality requirements
- Improve efficiency and repeatability with equipment designed for your application
- Reduce long-term operating costs with energy-efficient, durable designs
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance



















