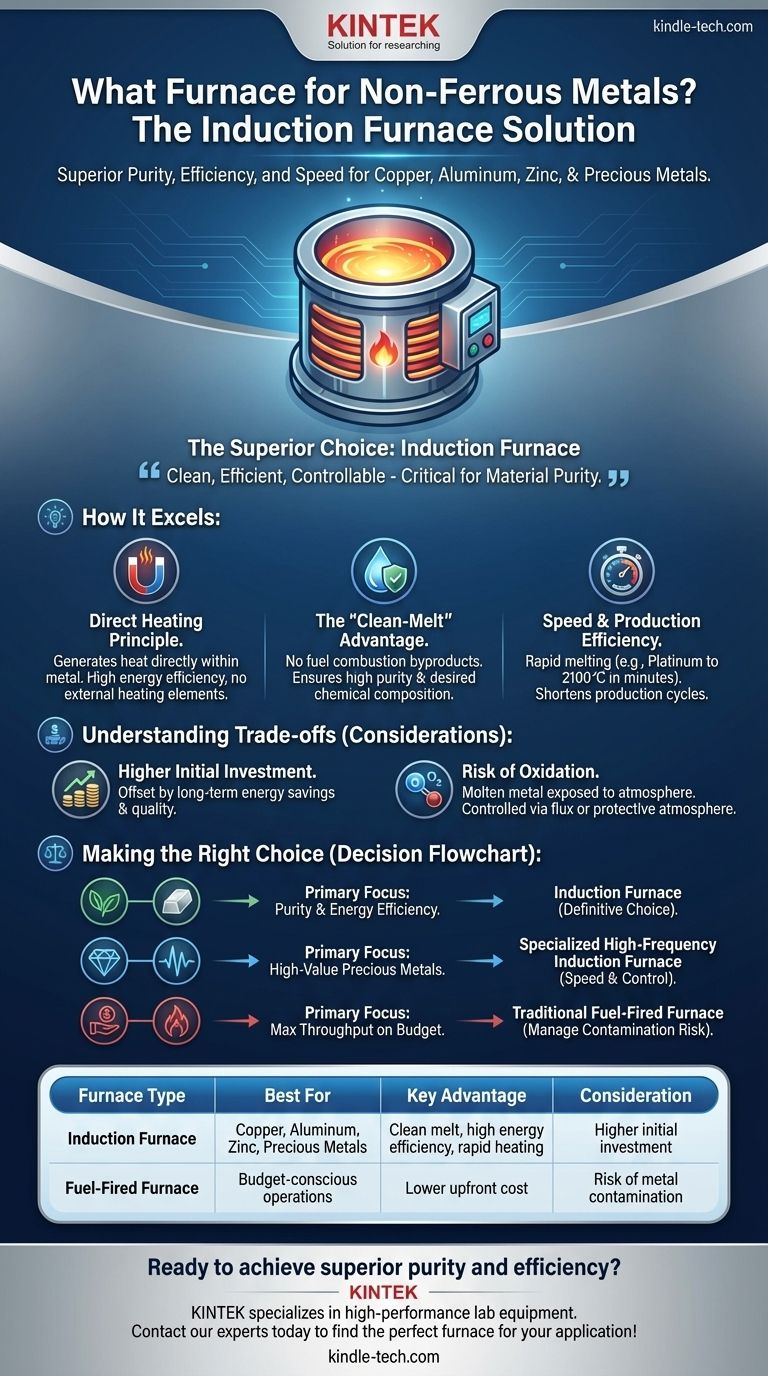
For melting non-ferrous metals like copper, aluminum, and zinc, the most common and advanced solution is the induction furnace. This technology is favored for its energy efficiency, speed, and ability to produce a clean melt, which is critical for maintaining the purity and quality of these materials. Specialized versions are even used for high-temperature precious metals like platinum.
The core decision is not simply which furnace to use, but understanding that the clean, efficient, and controllable nature of an induction furnace makes it the superior choice for most non-ferrous metal applications where material purity is a primary concern.

How Induction Furnaces Excel with Non-Ferrous Metals
The primary reason induction furnaces are so effective is their method of heating. Unlike traditional furnaces that burn fuel to generate external heat, induction furnaces use a fundamentally different and more direct process.
The Principle of Direct Heating
An induction furnace uses powerful magnetic fields to generate heat directly within the metal itself. This internal heating method is incredibly efficient because very little energy is wasted heating the furnace chamber or the surrounding air.
This process eliminates the need for burners, lances, or direct contact with heating elements, which are common sources of contamination in other furnace types.
The Advantage of a Clean Melt
For non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper, purity is paramount. The "clean-melting" characteristic of an induction furnace is its most significant advantage.
Because there is no combustion of fuel, byproducts like gas and soot cannot contaminate the molten metal. This ensures the final cast product has the desired chemical composition and material properties.
Speed and Production Efficiency
Specialized induction furnaces can achieve extremely high temperatures very quickly. For example, a furnace designed for platinum can reach 2100℃ in just a couple of minutes.
This rapid melting capability significantly shortens production cycles and increases overall operational efficiency, a crucial factor in both small-scale and large-scale industrial settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, induction technology is not without its considerations. Acknowledging the trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Investment
Induction furnace systems typically have a higher upfront capital cost compared to simpler, fuel-fired furnace technologies. This investment, however, is often offset by long-term energy savings and higher product quality.
The Risk of Oxidation
Although the process is inherently clean, the molten metal is still exposed to the atmosphere within the chamber. Without proper management, this can lead to the formation of oxides, which can create impurities or material loss.
In many operations, this is controlled by using a layer of protective flux on top of the melt or by introducing a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere into the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application will determine the best path forward. Consider the primary driver of your operation.
- If your primary focus is material purity and energy efficiency: An induction furnace is the definitive choice for melting non-ferrous metals like copper and aluminum.
- If your primary focus is melting high-value precious metals: A specialized, high-frequency induction furnace provides the speed and control necessary for working with materials like platinum.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput on a tight budget: You might investigate traditional fuel-fired furnaces, but you must be prepared to manage the inherent risk of metal contamination.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the technology's strengths to your specific metallurgical goals.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | Copper, Aluminum, Zinc, Precious Metals | Clean melt, high energy efficiency, rapid heating | Higher initial investment |
| Fuel-Fired Furnace | Budget-conscious operations | Lower upfront cost | Risk of metal contamination |
Ready to achieve superior purity and efficiency in your lab or foundry?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for precise melting of non-ferrous metals. Our solutions help you maintain material purity, reduce energy costs, and increase throughput.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific application with copper, aluminum, or precious metals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications



















