At its core, deposition chemistry is the process of building a solid thin film on a surface from gaseous chemical ingredients. Unlike physical methods that simply move a material from a source to a target, chemical deposition uses controlled reactions on a substrate to synthesize an entirely new layer of material, atom by atom.
The crucial distinction to understand is that chemical deposition builds a new material through surface reactions, whereas physical deposition transfers an existing material from a source to a substrate without changing its chemical identity.
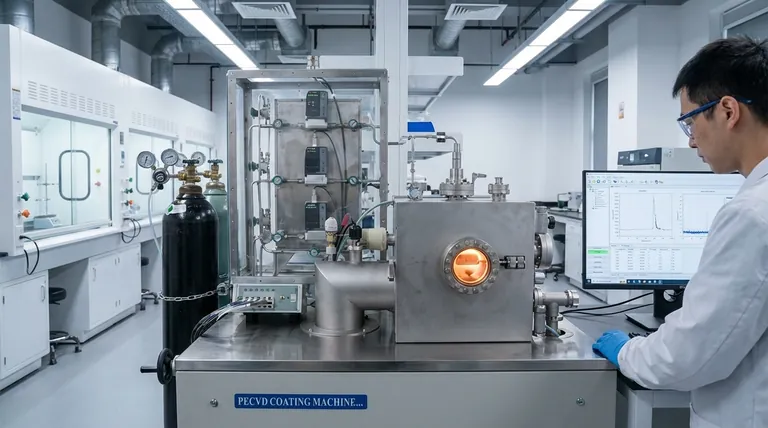

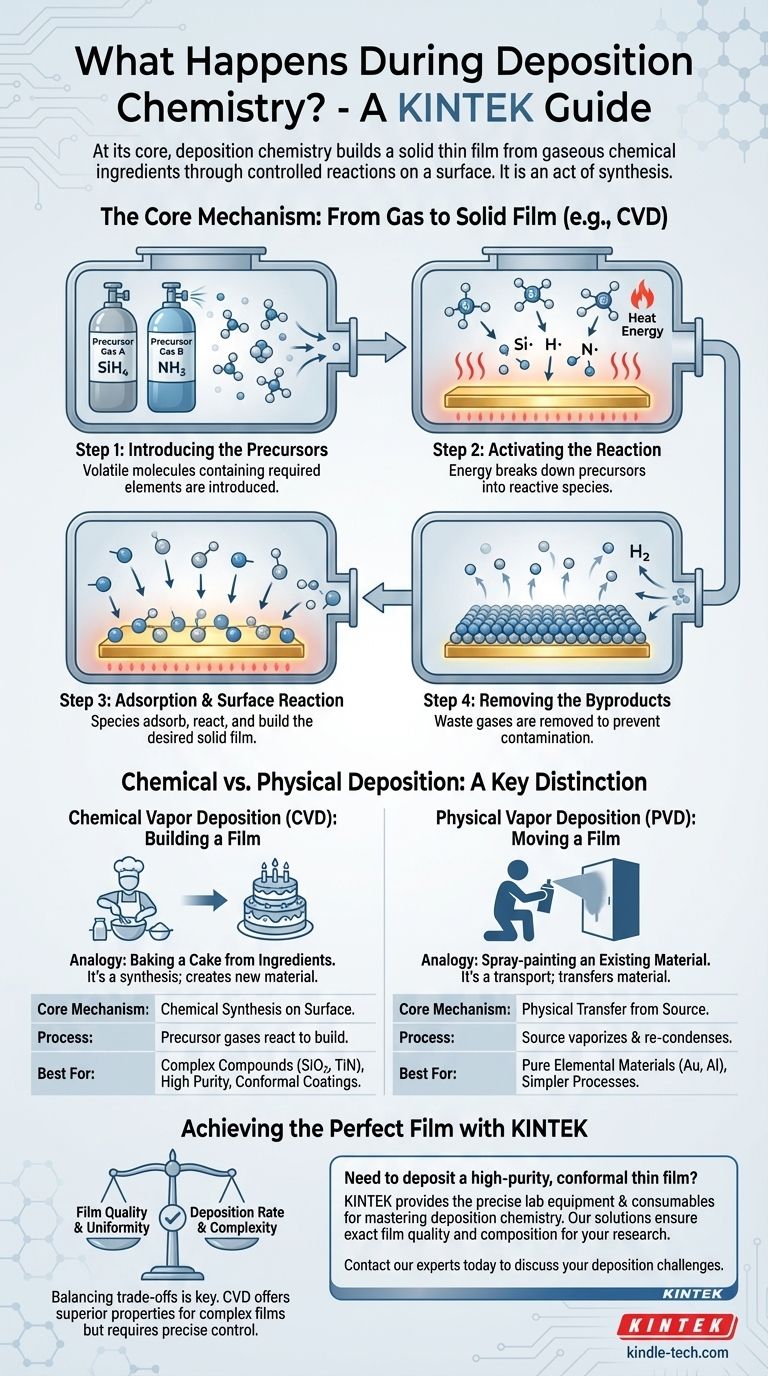
The Core Mechanism: From Gas to Solid Film
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the primary family of processes that relies on deposition chemistry. It involves a series of carefully controlled steps to transform gas-phase molecules into a high-purity solid film.
Step 1: Introducing the Precursors
The process begins with the introduction of one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber. These precursors are molecules specifically chosen to contain the atomic elements required for the final film.
Step 2: Activating the Reaction
Energy, typically in the form of heat, is applied to the substrate. This energy breaks down the precursor molecules into more reactive chemical species.
Step 3: Adsorption and Surface Reaction
These reactive species adsorb (stick) onto the hot substrate surface. Here, they react with each other or with the surface itself to form the desired solid material, creating a stable, thin film.
Step 4: Removing the Byproducts
A critical and defining feature of CVD is the creation of volatile byproducts. These waste gases from the chemical reaction must be efficiently removed from the chamber to prevent them from contaminating the growing film.
Chemical vs. Physical Deposition: A Key Distinction
Understanding what deposition chemistry is becomes clearer when you contrast it with its counterpart, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Building a Film
CVD is an act of synthesis. Think of it like baking a cake: you introduce individual ingredients (precursor gases) into an oven (the heated chamber), and a chemical reaction transforms them into a new, solid product (the film).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Moving a Film
PVD is a process of transport. Using the example of thermal evaporation, a source material is heated until it vaporizes and then simply re-condenses on a cooler substrate. This is more like spray-painting, where you are just moving paint from the can to the wall without a chemical change.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a chemical deposition process involves balancing several critical factors. The conditions that control the reaction chemistry directly impact the final properties of the film.
Film Properties vs. Deposition Rate
Achieving a high-quality, uniform film often requires a slow, carefully controlled reaction. Increasing the temperature or precursor flow to speed up the deposition rate can introduce defects, stress, or non-uniformity into the film's structure.
Process Complexity
CVD requires precise control over temperatures, pressures, gas flows, and the management of often-reactive precursor chemicals and byproducts. This can make it more complex than straightforward PVD techniques.
Material Versatility
The great strength of deposition chemistry is its ability to create highly pure films of complex compounds, alloys, and materials—such as silicon nitride or tungsten carbide—that cannot be simply evaporated and re-condensed like a pure metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a chemical or physical deposition method depends entirely on the material you need to create and the properties you want it to have.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure elemental material (like gold or aluminum) with relative simplicity: A PVD method is often the more direct and efficient approach.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly pure, dense, and conformal compound film (like silicon dioxide or titanium nitride): CVD is the superior method due to its bottom-up, chemical synthesis approach.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental difference between building and transferring a material is the key to controlling the properties of your final thin film.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Chemical Deposition (CVD) | Physical Deposition (PVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Chemical synthesis on the substrate surface | Physical transfer of material from source to substrate |
| Process | Precursor gases react to build a new material | Source material is vaporized and re-condenses |
| Analogy | Baking a cake from ingredients | Spray-painting an existing material |
| Best For | Complex compounds (e.g., SiO₂, TiN), high purity, conformal coatings | Pure elemental materials (e.g., Au, Al), simpler processes |
Need to deposit a high-purity, conformal thin film?
The chemical synthesis process of CVD is ideal for creating complex compound films with superior properties. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to master deposition chemistry.
Our solutions help you achieve the exact film quality, uniformity, and material composition your research or production requires. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific deposition challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition



















