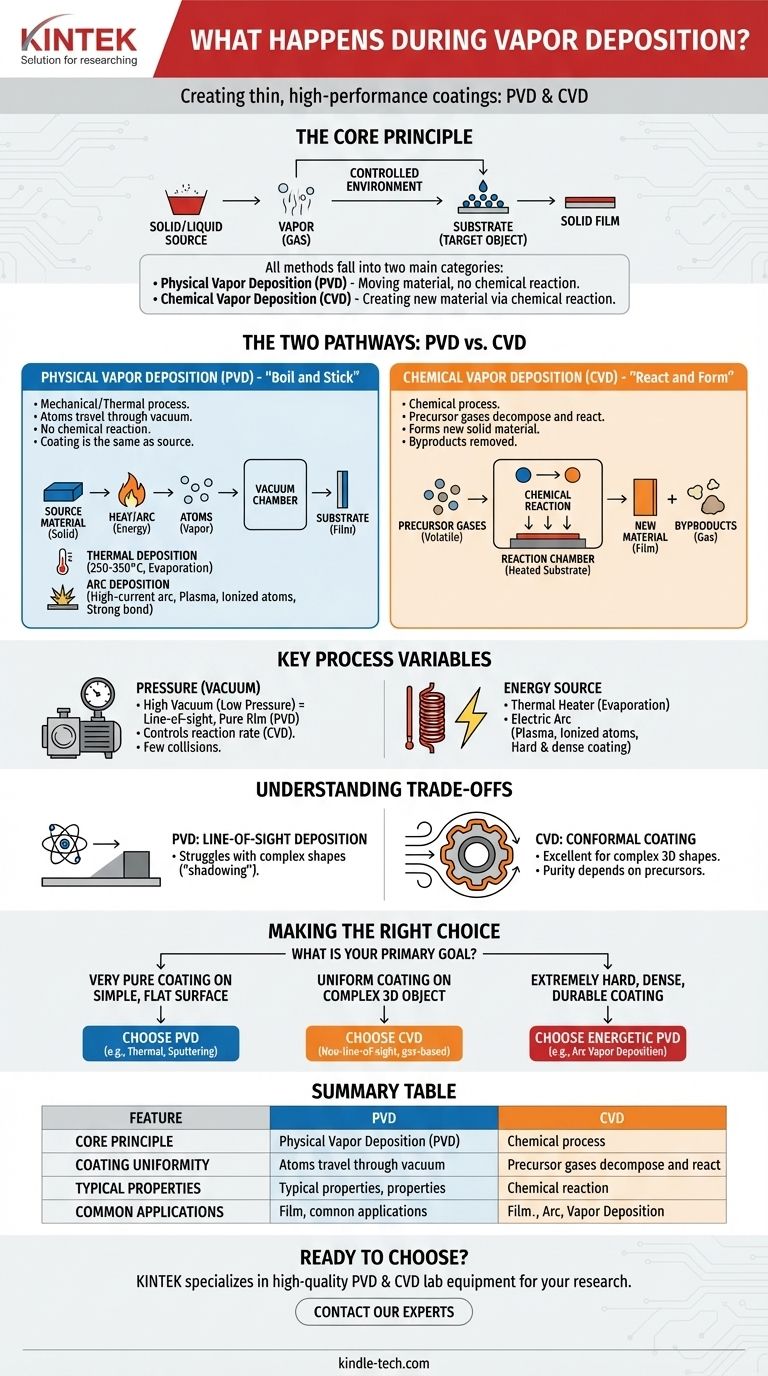
In short, vapor deposition is a family of processes used to create extremely thin, high-performance coatings on a surface. The core principle involves converting a solid or liquid source material into a gas (vapor) within a controlled environment, which then condenses onto a target object—known as a substrate—to form a solid film.
The critical distinction to understand is that all vapor deposition methods fall into two main categories: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The choice between them depends entirely on whether you are simply moving a material (PVD) or creating a new one through a chemical reaction (CVD).
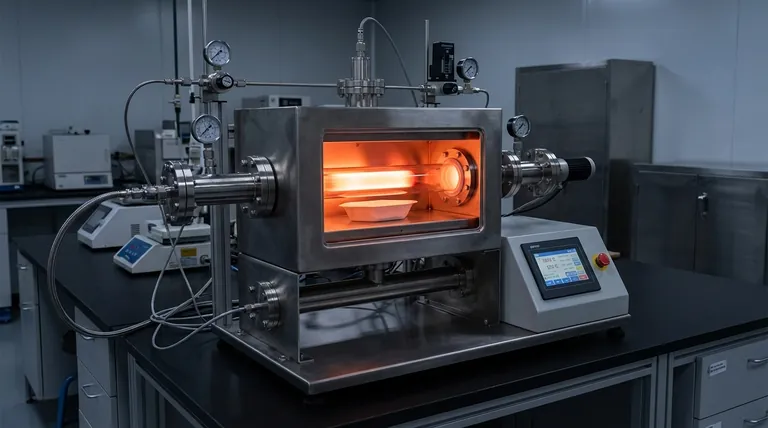

The Two Fundamental Pathways: PVD vs. CVD
While the end goal is the same—a thin film—the journey the atoms take is fundamentally different. Understanding this distinction is the key to navigating the field.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): The "Boil and Stick" Method
PVD is a mechanical or thermal process. Atoms are physically dislodged from a solid source material, travel through a vacuum, and then condense onto the substrate.
There is no chemical reaction. The coating on the substrate is the same material that left the source.
Common PVD methods include:
- Thermal Deposition: A heat source, often ranging from 250-350°C, heats the source material in a high vacuum until it evaporates. This vapor stream travels and coats the substrate.
- Arc Deposition: Instead of simple heat, a high-current electric arc is used to vaporize the source material. This creates a highly ionized vapor (a plasma), where atoms carry an electrical charge, helping them bond more densely to the substrate.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The "React and Form" Method
CVD is a chemical process. It begins with one or more volatile precursor gases being introduced into a reaction chamber.
These gases don't deposit directly. Instead, they decompose and react with each other near the heated substrate, forming an entirely new solid material that then deposits as a film. Unwanted byproducts are removed as gas.
Key Process Variables That Define the Outcome
The specific name of a deposition process (e.g., LPCVD, APCVD) almost always refers to the conditions under which it is performed. These variables control the final film's properties.
Pressure (Vacuum)
The pressure inside the chamber is a critical control parameter. A high vacuum (low pressure) means there are very few other gas molecules for the vapor to collide with.
This allows atoms in a PVD process to travel in a straight "line of sight" from the source to the substrate, resulting in a very pure film. In CVD, different pressure levels (from atmospheric down to ultra-high vacuum) are used to control the chemical reaction rate and resulting film quality.
Energy Source
The method used to turn the source material into a vapor dramatically impacts the process. A simple thermal heater provides enough energy for evaporation.
An electric arc, by contrast, provides much more energy. It creates a plasma of ionized atoms, which can be accelerated toward the substrate with a voltage bias. This results in an exceptionally hard and dense coating, which is why arc deposition is distinct from simple thermal evaporation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is universally superior. The choice involves clear, well-understood compromises.
The PVD Trade-off: Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because PVD atoms travel in straight lines, they can struggle to coat complex, three-dimensional shapes uniformly. Areas that are not in the direct line of sight of the source will receive little to no coating, an issue known as "shadowing."
The CVD Trade-off: Conformal Coating vs. Purity
CVD excels where PVD fails. Because it uses a gas that fills the entire chamber, it can produce a highly uniform, or conformal, coating on even the most complex shapes.
However, the final film's purity depends on the purity of the precursor gases and the successful removal of all unwanted chemical byproducts. The precursor gases themselves can also be highly toxic or corrosive, requiring complex handling procedures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method is a function of your desired outcome. Use your final goal as your guide.
- If your primary focus is a very pure coating on a simple, flat surface: A PVD method like thermal evaporation or sputtering is often the most direct and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is a uniform coating on a complex 3D object: CVD is the superior option due to its non-line-of-sight, gas-based nature.
- If your primary focus is an extremely hard, dense, and durable coating: An energetic PVD process like Arc Vapor Deposition is necessary to create the ionized plasma required for such films.
By understanding the core principles of physical transfer versus chemical reaction, you can effectively evaluate which deposition technique is truly suited for your material and application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Physical transfer of material ("Boil and Stick") | Chemical reaction forms new material ("React and Form") |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight; can struggle with complex shapes | Conformal; excellent for complex 3D objects |
| Typical Coating Properties | Very pure, dense, and hard coatings | Uniform coatings; purity depends on precursor gases |
| Common Applications | Simple, flat surfaces requiring pure/hard coatings | Complex shapes requiring uniform coverage |
Ready to choose the right vapor deposition method for your lab's needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition processes. Whether you require a system for precise PVD or versatile CVD applications, our experts can help you select the ideal solution to enhance your research and development.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















