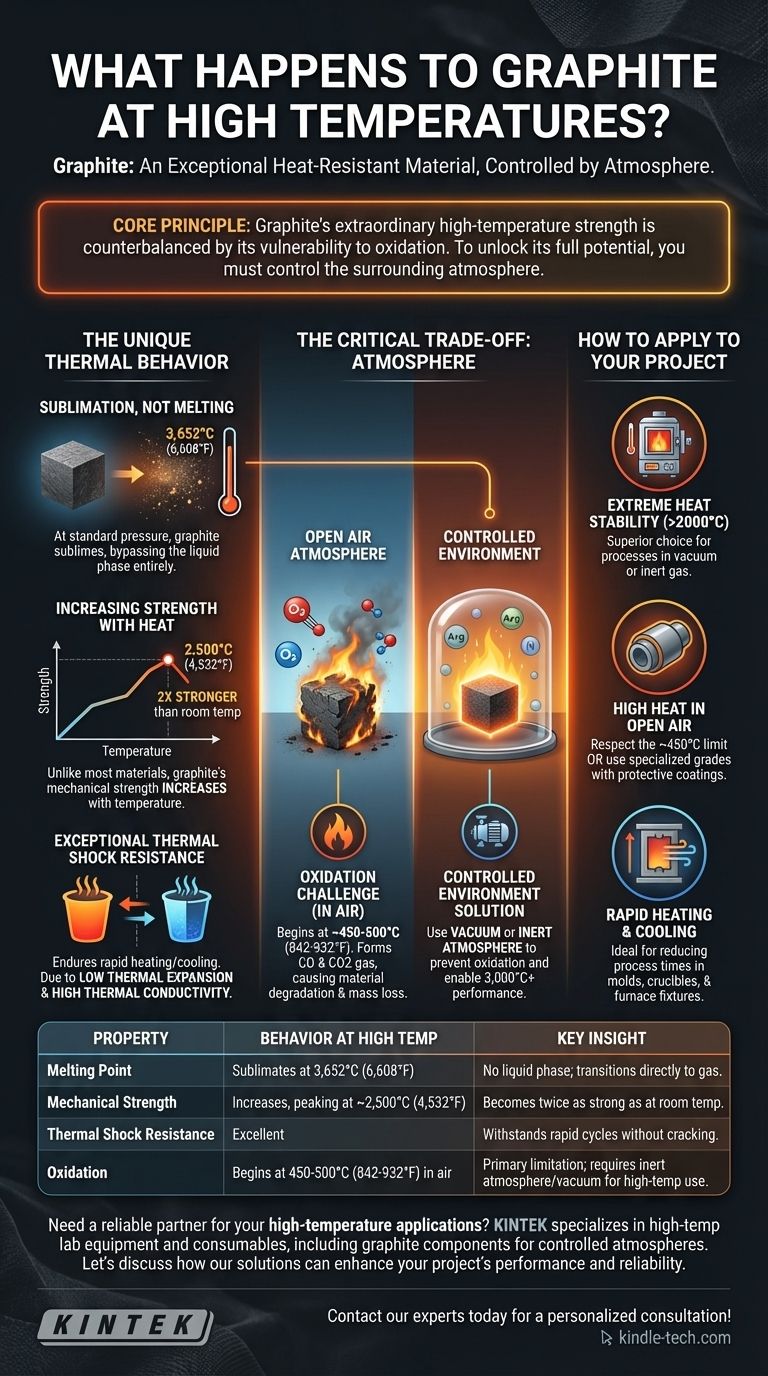
In short, graphite is one of the most heat-resistant materials known. Unlike metals that melt, graphite remains solid at extreme temperatures and only turns directly into a gas (sublimates) at a staggering 3,652°C (6,608°F) under standard pressure. Critically, its performance depends entirely on the atmosphere it is in.
The core principle to understand is that graphite's extraordinary high-temperature strength is counterbalanced by its vulnerability to oxidation. To unlock its full potential, you must control the surrounding atmosphere.

The Unique Thermal Behavior of Graphite
Graphite does not behave like other materials when heated. Its atomic structure gives it a unique set of properties that make it ideal for extreme thermal applications, provided its primary limitation is managed.
Sublimation, Not Melting
At atmospheric pressure, graphite has no melting point. Instead of turning into a liquid, its carbon atoms gain enough energy to break free directly into a gaseous state, a process called sublimation.
This transition temperature is incredibly high, making graphite stable and solid long after most metals have become liquid.
Increasing Strength with Heat
Most materials weaken as they get hotter. Graphite does the opposite.
Its mechanical strength increases with temperature, peaking at around 2,500°C (4,532°F). At this point, it is roughly twice as strong as it is at room temperature.
Exceptional Thermal Shock Resistance
Graphite can endure rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or failing. This resilience is known as thermal shock resistance.
It stems from two key factors: a very low coefficient of thermal expansion (it doesn't expand or contract much when its temperature changes) and high thermal conductivity (it dissipates heat quickly and evenly).
Understanding the Trade-off: The Critical Role of Atmosphere
While graphite's thermal stability is immense, it comes with one significant vulnerability that dictates how it can be used in practice.
The Challenge of Oxidation
In the presence of oxygen (i.e., in normal air), graphite will begin to oxidize, or burn, at a much lower temperature.
This process typically starts around 450-500°C (842-932°F), where the carbon reacts with oxygen to form CO and CO2 gas. This reaction causes the material to degrade and lose mass.
Operating in a Controlled Environment
To prevent oxidation and take advantage of graphite's 3,000°C+ stability, it must be used in a controlled environment.
This typically means placing it within a vacuum or an inert atmosphere, such as one filled with argon or nitrogen gas. These environments remove the oxygen, allowing the graphite to perform without degradation.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your decision to use graphite should be based on a clear understanding of your application's environment and temperature requirements.
- If your primary focus is stability in extreme heat (above 2000°C): Graphite is a superior choice, but only if your process occurs in a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
- If your application involves high heat in open air: You must respect graphite's oxidation limit of ~450°C, or you must invest in specialized grades with protective coatings.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: Graphite's excellent thermal shock resistance makes it an ideal material for reducing process times in things like molds, crucibles, and furnace fixtures.
By managing its one key vulnerability—oxidation—you can leverage graphite's exceptional properties to solve the most demanding high-temperature challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Behavior at High Temperature | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | Sublimates at 3,652°C (6,608°F) | No liquid phase; transitions directly to gas. |
| Mechanical Strength | Increases, peaking around 2,500°C (4,532°F) | Becomes twice as strong as at room temperature. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Can withstand rapid heating/cooling without cracking. |
| Oxidation | Begins at 450-500°C (842-932°F) in air | The primary limitation; requires an inert atmosphere or vacuum for high-temperature use. |
Need a reliable partner for your high-temperature applications?
Graphite's unique properties make it ideal for demanding processes, but success depends on using the right materials in the right environment. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment and consumables, including graphite components designed for performance in controlled atmospheres.
We help laboratories and researchers like you leverage materials like graphite to achieve precise, efficient, and repeatable results. Let's discuss how our solutions can enhance your project's performance and reliability.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of temperature in metal working process? Master Strength, Ductility, and Microstructure
- What is the effect of sintering temperature on density? Mastering the Balance for Optimal Material Properties
- Why is a vacuum drying oven necessary for Pt/Nb-TiO2 catalyst preparation? Optimize Your Material Activity
- What is the temperature of the annealing process? Achieve Perfect Material Properties
- What can be sintered? Discover the Vast Range of Materials from Metals to Ceramics
- How do constant temperature shakers enhance lignin removal? Optimize Alkaline Pretreatment with Mechanical Force
- What is the difference between VAR and ESR? A Guide to Understanding Tail Risk in Financial Modeling
- What materials are direct energy deposition? Key Metals & Alloys for High-Performance 3D Printing



















