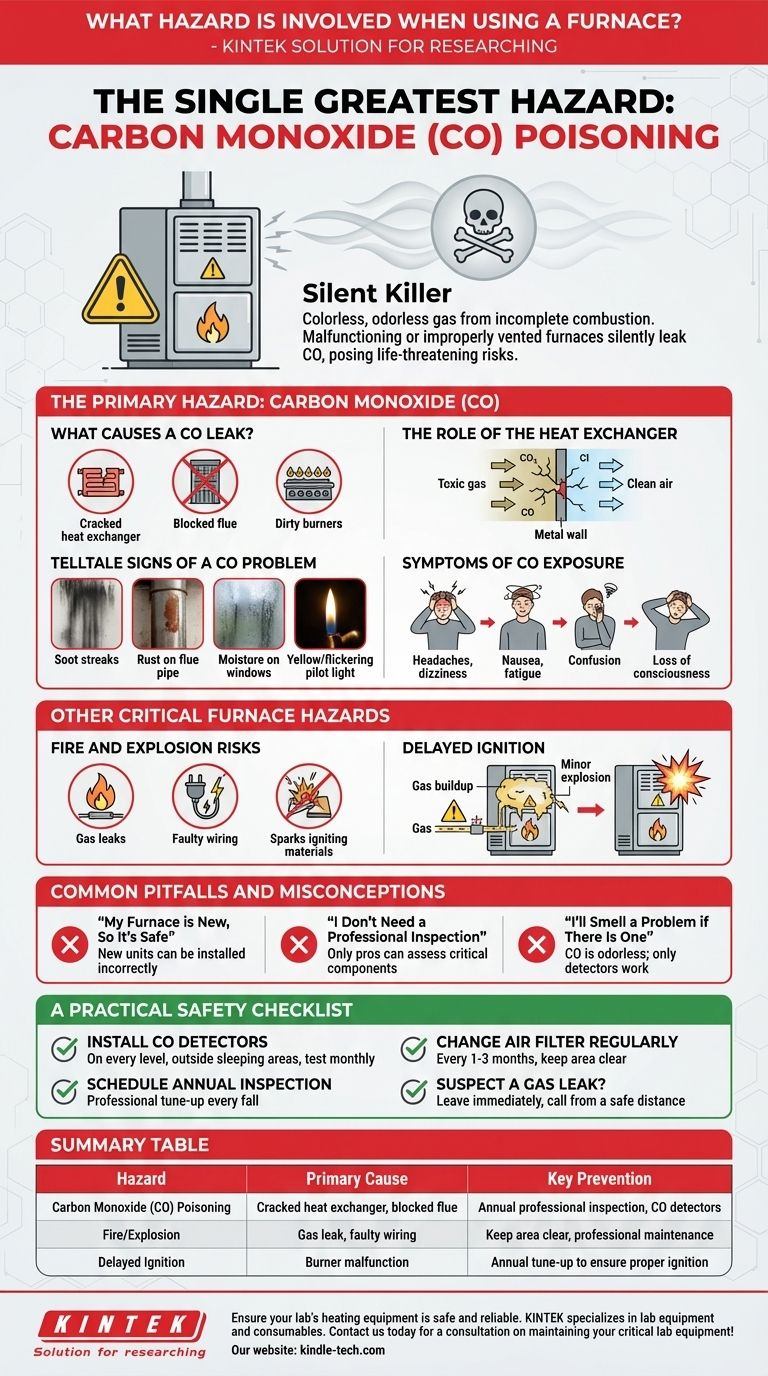
The single greatest hazard when using a furnace is carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning. This colorless, odorless gas is a byproduct of incomplete combustion. If your furnace is malfunctioning or improperly vented, it can silently leak into your home, posing a life-threatening risk.
While modern furnaces are designed with safety in mind, the invisible threat of carbon monoxide necessitates a proactive approach. Understanding the root causes of furnace hazards and implementing simple, consistent safety measures is the only way to ensure your heating system remains a source of comfort, not danger.

The Primary Hazard: Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is often called the "silent killer" for a reason. It's undetectable by human senses and can incapacitate its victims before they are even aware of the danger.
What Causes a CO Leak?
CO is produced when fuel—like natural gas, propane, or oil—doesn't burn completely. This incomplete combustion is most often caused by a cracked heat exchanger, a blocked flue or vent, or burners that need cleaning and adjustment.
The Role of the Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger is the metal wall that separates the toxic combustion gases from the clean air that gets circulated through your home. Over time, this component can develop cracks from the stress of repeated heating and cooling. These cracks create a direct pathway for carbon monoxide to mix with your breathable air.
Telltale Signs of a CO Problem
While you can't smell CO, you can look for warning signs on the furnace itself. Be alert for soot streaks around the unit, excessive rust on the flue pipe, moisture on windows, or a pilot light flame that is yellow or flickering instead of a steady blue.
Symptoms of CO Exposure
Initial symptoms of low-level CO poisoning mimic the flu. They include headaches, dizziness, nausea, and general fatigue. As exposure increases, symptoms worsen to include confusion, blurred vision, and loss of consciousness.
Other Critical Furnace Hazards
While CO is the most insidious threat, it's not the only one. Other mechanical and electrical failures can also create dangerous situations.
Fire and Explosion Risks
A furnace combines fuel, electricity, and ignition. A natural gas leak can lead to an explosion, while faulty wiring or a malfunctioning motor can create sparks that ignite nearby flammable materials.
Delayed Ignition
If the furnace burners don't ignite immediately, gas can build up inside the combustion chamber. When it finally does ignite, the minor explosion can damage the unit—most notably, it can crack the heat exchanger, leading to the CO risk discussed above.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Relying on assumptions is a significant risk factor. A clear understanding of furnace safety requires dispelling common but dangerous myths.
"My Furnace is New, So It's Safe"
A brand-new furnace can be installed incorrectly. Improper venting or incorrect sizing can create hazardous operating conditions from day one. Age is not a guarantee of safety.
"I Don't Need a Professional Inspection"
While a homeowner can and should change the air filter regularly, a professional technician is needed to inspect the critical components. Only a trained eye can properly assess the heat exchanger, check gas pressure, and ensure proper venting.
"I'll Smell a Problem if There Is One"
This is the most dangerous misconception. You cannot smell carbon monoxide. The only reliable way to be alerted to its presence is with a functional, properly placed CO detector. Natural gas has a rotten egg smell added for leak detection, but CO is completely odorless.
A Practical Safety Checklist
Your approach to furnace safety should be built on prevention and preparedness.
- If your primary focus is immediate detection: Install carbon monoxide detectors on every level of your home, especially outside sleeping areas. Test them monthly and replace them according to the manufacturer's instructions (typically every 5-7 years).
- If your primary focus is long-term prevention: Schedule a professional furnace inspection and tune-up every single year, ideally in the fall before the heating season begins.
- If your primary focus is basic upkeep: Change your furnace filter regularly (every 1-3 months) and keep the area around the furnace clear of any flammable materials.
- If you suspect a gas leak (smell rotten eggs): Do not operate any electrical switches or phones. Leave your home immediately, and then call your gas company or 911 from a safe distance.
Proactive maintenance is the key to transforming a potential household hazard into a reliable source of safety and comfort.
Summary Table:
| Hazard | Primary Cause | Key Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) Poisoning | Cracked heat exchanger, blocked flue | Annual professional inspection, CO detectors |
| Fire/Explosion | Gas leak, faulty wiring | Keep area clear, professional maintenance |
| Delayed Ignition | Burner malfunction | Annual tune-up to ensure proper ignition |
Ensure your lab's heating equipment is safe and reliable. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise ensures your furnaces and ovens operate safely and efficiently, protecting your team and your research. Don't compromise on safety—contact us today for a consultation on maintaining your critical lab equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a furnace classified as? Understand the Two Main Types for Your Application
- How do you use the muffle furnace? Master Safe and Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the calcination process? A Guide to Thermal Purification and Material Transformation
- What happens after calcination? A Guide to Material Transformation and Next Steps
- What are the hazards of a muffle furnace? Understanding the Critical Risks for Lab Safety



















