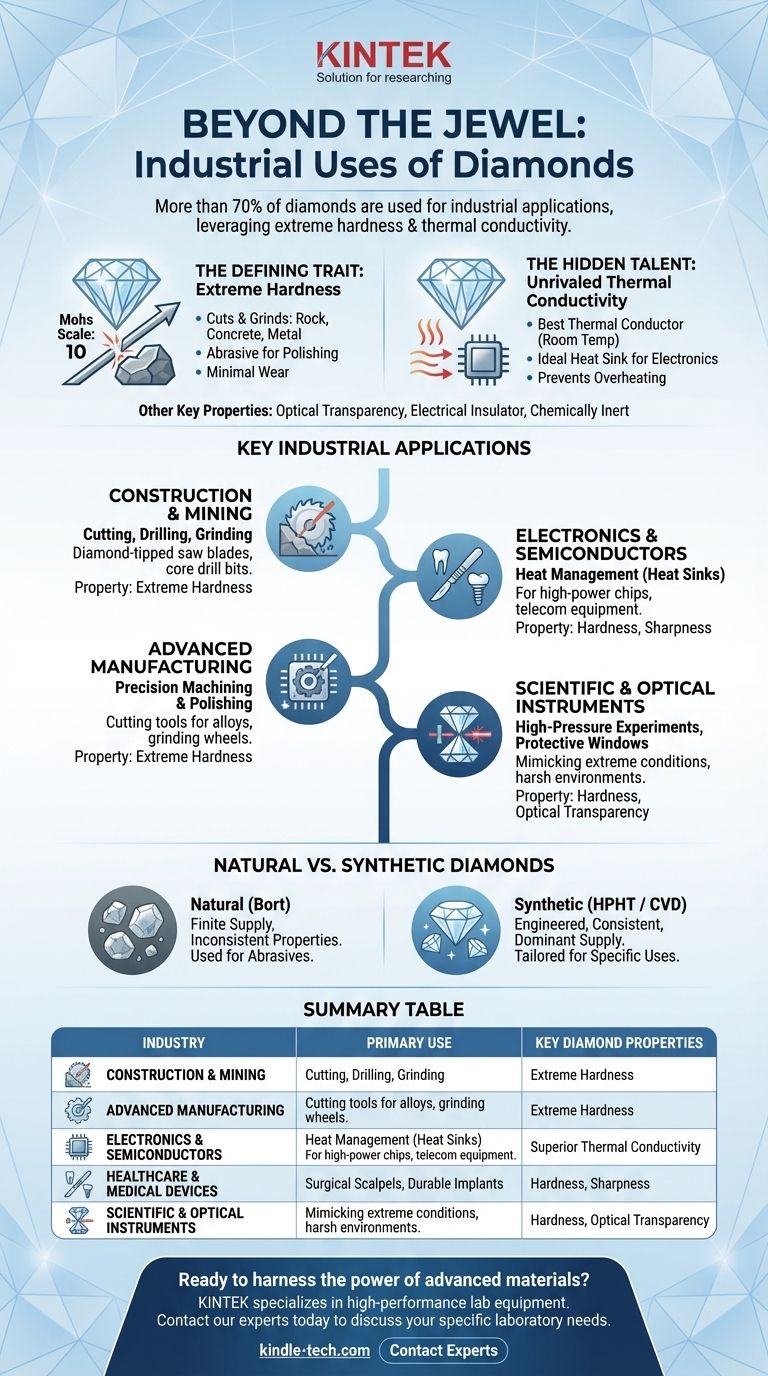
In short, while the jewelry industry is the most visible user of diamonds, it accounts for only a fraction of their total use. The vast majority of diamonds—over 70% by weight—are used for industrial applications in fields like construction, manufacturing, electronics, and scientific research, where their unparalleled hardness and thermal conductivity are essential.
The true story of the diamond is not one of luxury, but of utility. Its value in the modern world is derived less from its sparkle and more from its physical properties, which make it a critical, high-performance material for our most demanding technological challenges.
Beyond the Jeweler's Case: The Diamond's Core Properties
To understand where diamonds are used, you must first understand why they are used. Their applications are a direct result of a few extreme physical characteristics that are unmatched by nearly any other material.
The Defining Trait: Extreme Hardness
A diamond is the hardest known natural material, scoring a 10 on the Mohs hardness scale. This is its single most important feature for industrial use.
This hardness means a diamond can cut, grind, scratch, and wear away any other material, including rock, concrete, metal, and other gemstones, with minimal damage to itself.
The Hidden Talent: Unrivaled Thermal Conductivity
Less known but equally important, diamond is the best thermal conductor at room temperature. It can transfer heat more effectively than copper or silver.
This property makes it an ideal heat sink, a material that draws damaging waste heat away from sensitive electronic components, allowing them to operate at higher power without overheating.
Other Key Characteristics
Diamonds are also optically transparent across a wide spectrum of light, from ultraviolet to far infrared. They are electrical insulators (in their pure form) and are chemically inert, meaning they don't react with most corrosive substances.
A Breakdown of Key Industrial Applications
These properties make diamonds indispensable in a range of industries that have little to do with luxury. The diamonds used here are typically synthetic or natural "bort"—diamonds that are not of gem quality.
Construction and Mining
This is one of the largest consumers of industrial diamonds. Diamond's hardness is essential for cutting through rock and concrete.
Applications include diamond-tipped saw blades for cutting concrete and asphalt, core drill bits for extracting geological samples, and grinding wheels for smoothing concrete surfaces.
Advanced Manufacturing and Machining
In manufacturing, precision is key. Diamond tools enable the shaping of extremely hard or abrasive materials that would quickly destroy conventional tools.
This includes cutting tools for shaping non-ferrous alloys in the automotive and aerospace industries, grinding wheels for finishing hard materials like tungsten carbide, and diamond powders used as a super-fine abrasive for polishing.
Electronics and Semiconductors
As electronics become smaller and more powerful, managing heat is a primary challenge. Diamond's thermal conductivity is the solution.
Thin, synthetic diamond layers are used as heat sinks for high-power microchips, telecom equipment, and powerful lasers, preventing them from melting or failing. There is also extensive research into using doped diamonds as a next-generation semiconductor material for high-power, high-frequency devices.
Healthcare and Medical Devices
The ability to create an incredibly sharp and durable edge is valuable in medicine.
Diamond-bladed scalpels create cleaner incisions with less tissue damage, promoting faster healing. Diamond coatings are also used to improve the durability and performance of medical implants.
Scientific and Optical Instruments
Researchers use diamonds to replicate and study extreme conditions. A diamond anvil cell uses two opposing diamonds to subject samples to immense pressures, mimicking the conditions deep within the earth.
Because of their transparency and durability, diamonds are also used as protective windows for high-power lasers and sensors operating in harsh chemical or high-pressure environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Natural vs. Synthetic
It is a common misconception that industrial applications rely on low-quality natural diamonds. While this was once true, the modern industrial diamond market is dominated by synthetic diamonds.
The Role of Natural Industrial Diamonds
Naturally occurring, non-gem-quality diamonds (bort) are still used for some abrasive applications. However, their supply is finite, and their properties can be inconsistent.
The Dominance of Synthetic Diamonds
Today, scientists can grow high-quality diamonds in a lab using methods like High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
These synthetic diamonds are not just cheaper; they are better for industrial use. Their properties, such as size, purity, and conductivity, can be precisely engineered for a specific application, from a heat sink to a cutting tool.
Limitations to Consider
Diamond is not the ideal material for every task. For example, when machining steel at high temperatures, diamond can chemically react with the iron and degrade. In these specific cases, other superhard materials like cubic boron nitride (cBN) are often preferred.
How to Understand a Diamond's Role in Any Context
To determine why a diamond is being used, analyze the core problem it is solving.
- If the primary focus is aesthetics or status: It's using a gem-quality diamond for its brilliance, rarity, and cultural value.
- If the primary focus is cutting, grinding, or drilling: It's using an industrial diamond (likely synthetic) for its extreme hardness.
- If the primary focus is managing heat in electronics: It's using a synthetic diamond for its superior thermal conductivity.
- If the primary focus is research under extreme conditions: It's using a diamond for its unmatched strength and transparency.
Ultimately, a diamond's true value is defined by its function, whether as a symbol of beauty or as an irreplaceable tool of modern industry.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use of Diamonds | Key Diamond Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Construction & Mining | Cutting, Drilling, Grinding | Extreme Hardness |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Precision Machining & Polishing | Extreme Hardness |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Heat Management (Heat Sinks) | Superior Thermal Conductivity |
| Healthcare | Surgical Scalpels, Durable Implants | Hardness, Sharpness |
| Scientific Research | High-Pressure Experiments (Diamond Anvil Cells) | Hardness, Optical Transparency |
Ready to harness the power of advanced materials in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Whether your research requires materials with extreme hardness, superior thermal management, or optical clarity, we have the solutions to enhance your precision and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- Are CVD diamonds better than HPHT? The Real Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Quality
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose













