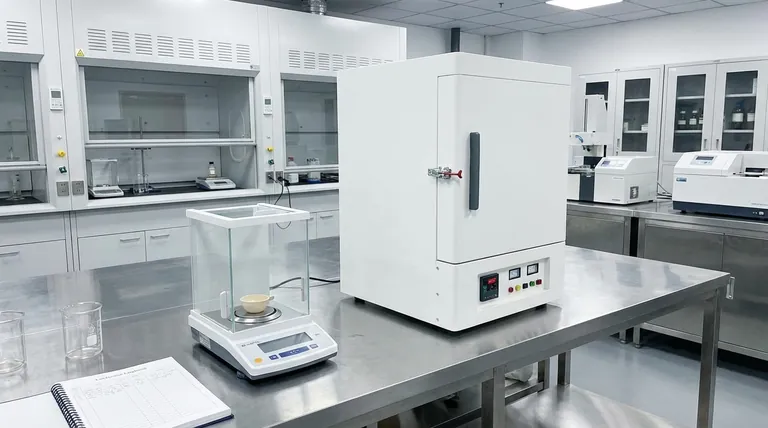
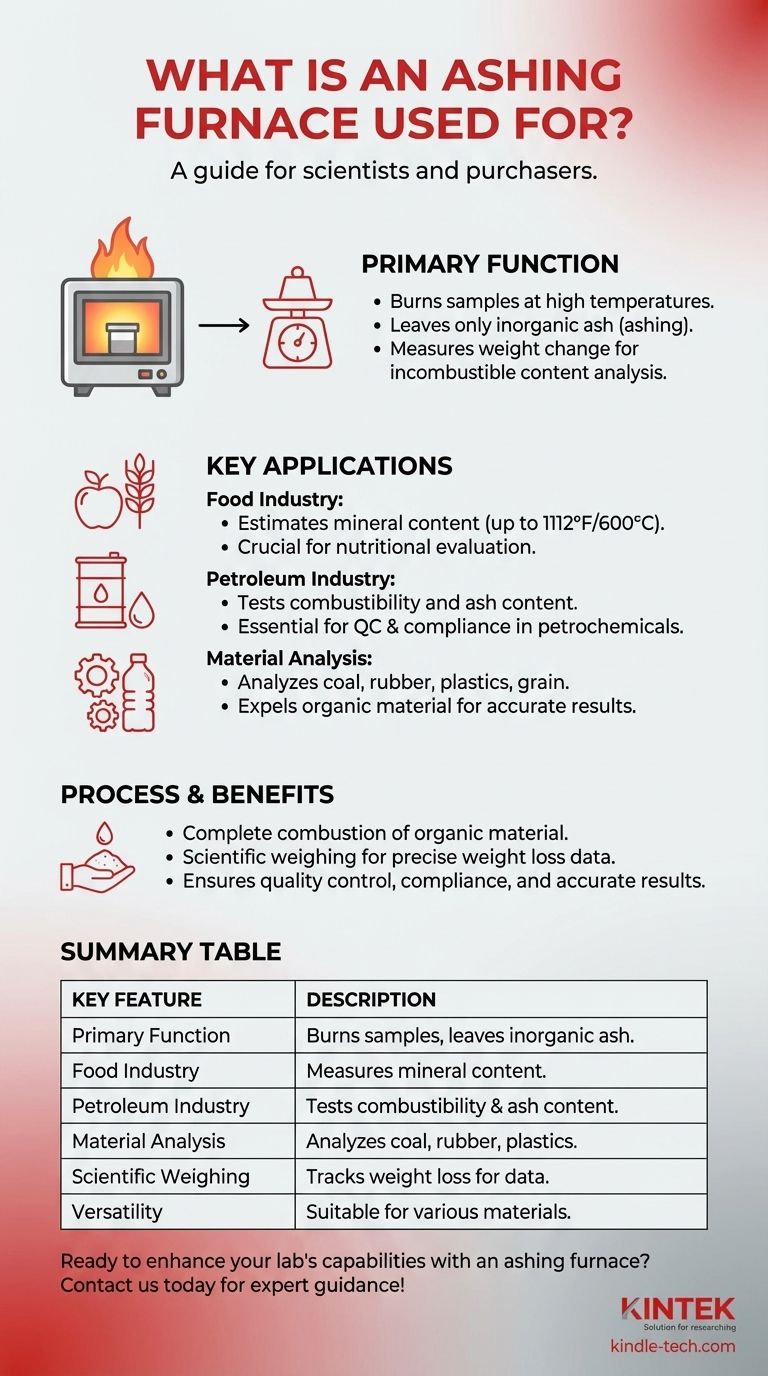
An ashing furnace is a specialized device used to burn samples at high temperatures until only inorganic ash remains. It is widely employed in industries such as food, petroleum, and materials science to determine the incombustible content of samples, which is crucial for nutritional analysis, quality control, and compliance testing. By measuring the weight change of a sample during combustion, ashing furnaces provide valuable data for evaluating the mineral content in food, testing the combustibility of petroleum products, and analyzing materials like coal, rubber, plastics, and grain. This process ensures accurate results by removing organic material before further analysis.

Key Points Explained:
-
Primary Function of an Ashing Furnace:
- An ashing furnace is designed to burn samples at high temperatures until only ash remains. This process is known as "ashing."
- It measures the weight change of the sample during combustion, which helps quantify the incombustible (inorganic) content of the material.
-
Applications in the Food Industry:
- Ashing furnaces are used to estimate the mineral content in food products by heating samples to temperatures as high as 1112 °F (600 °C).
- The ash content serves as a key metric for nutritional evaluation, providing insights into the inorganic components of food.
-
Applications in the Petroleum Industry:
- These furnaces are critical for testing the combustibility of petroleum products, including crude oil, distillate and residual fuels, gas turbine fuels, lubricating oils, and waxes.
- They help determine the ash content, which is a critical parameter for quality control and compliance in petrochemical manufacturing.
-
Material Analysis in Other Industries:
- Ashing furnaces are used to analyze materials such as coal, rubber, plastics, and grain.
- By expelling organic material through combustion, they provide a clean sample for further analysis, ensuring accurate results in material testing.
-
Process of Expelling Organic Material:
- The furnace completely burns away organic components, leaving only inorganic ash.
- This step is essential for preparing samples for accurate analysis, as it removes impurities that could skew results.
-
Importance in Quality Control and Compliance:
- The ash content is a critical parameter in quality control (QC) and regulatory compliance, particularly in industries like food and petrochemicals.
- It ensures that products meet specific standards and provides data for nutritional labeling or performance evaluation.
-
Scientific Weighing During Combustion:
- Ashing furnaces are equipped with weighing mechanisms to measure the sample's weight throughout the combustion process.
- This feature allows scientists to track the exact weight loss, providing precise data for analysis.
-
Versatility Across Industries:
- The furnace's ability to handle a wide range of materials—from food and petroleum products to industrial materials—makes it a versatile tool in scientific and industrial laboratories.
By understanding these key points, purchasers of ashing furnaces can better evaluate their suitability for specific applications, ensuring they meet the needs of their industry and testing requirements.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Burns samples at high temperatures, leaving only inorganic ash for analysis. |
| Food Industry Applications | Measures mineral content in food for nutritional evaluation. |
| Petroleum Industry Uses | Tests combustibility and ash content in petroleum products for quality control. |
| Material Analysis | Analyzes coal, rubber, plastics, and grain by expelling organic material. |
| Scientific Weighing | Tracks weight loss during combustion for precise data collection. |
| Versatility | Suitable for food, petroleum, and industrial material testing. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with an ashing furnace? Contact us today for expert guidance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the stages of melting metal? Mastering the 3-Step Process from Solid to Liquid
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- Does ceramic break with heat? The Real Culprit is Thermal Shock
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What is dry ashing in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Mineral Analysis



















